The world is increasingly dependent on technology for communication, commerce, and collaboration. Businesses and organizations of all sizes require a reliable and secure network connection to keep pace with the demands of the digital age.
WAN bonding is a technology that helps organizations achieve this goal by combining multiple wide area network (WAN) connections into a single, high-performance link.
In this blog post, we will discuss what WAN bonding is, its benefits, types of bonding, how it works, implementation, use cases, and future outlook. And we’ll share how Digi partnered with Bondix Intelligence to develop the integrated Digi WAN Bonding solution.
What Is WAN Bonding?

WAN bonding refers to the process of combining two or more separate Internet connections into a single, virtual connection. The goal of WAN bonding is to improve network performance, reliability, and redundancy. It enables organizations to take advantage of multiple Internet service providers (ISPs) to achieve higher bandwidth and lower latency.
Benefits of WAN Bonding
WAN bonding provides several benefits, including:
- Improved network performance: By combining multiple WAN connections, WAN bonding increases the overall bandwidth and speed of the network. This is especially beneficial for businesses that require a high level of network performance for activities such as video conferencing, online gaming, and data transfers.
- Increased reliability: WAN bonding provides failover protection, which ensures that if one WAN connection fails, the other connections immediately take over. This results in a more reliable network and minimizes downtime.
- Cost savings: WAN bonding allows businesses to take advantage of multiple ISPs, which can result in cost savings. By using multiple providers, organizations can negotiate better pricing and find a provider that offers the best value for their specific needs.
Types of WAN Bonding
There are several types of WAN bonding, including:
- Link Aggregation (LAG): LAG involves combining multiple physical network connections into a single, logical link. This type of bonding is commonly used in local area networks (LANs) and is a simple way to increase bandwidth.
- Link Load Balancing (LLB): LLB involves distributing network traffic across multiple connections. This type of bonding helps to reduce congestion and increase overall network performance.
- Bonding using VPN: VPN bonding involves combining multiple VPN connections into a single link. This type of bonding is useful for businesses that require a secure connection between remote offices or branch locations.
- Cellular WAN bonding: Cellular WAN bonding involves combining multiple cellular connections into a single, virtual connection. This type of bonding is useful for businesses that require a secure and reliable mobile connection, such as field service organizations or remote workers.
How WAN Bonding Works

WAN bonding works by combining multiple WAN connections into a single, virtual connection. This virtual connection is then used to route network traffic. WAN bonding software manages the process of bonding and ensures that traffic is properly distributed across the different connections.
The bonding process involves three key elements:
- Bonding multiple WAN connections: The first step in WAN bonding is to combine multiple WAN connections into a single, virtual connection. This requires WAN bonding software, which manages the process of bonding and ensures that traffic is properly distributed across the different connections.
- Traffic routing and load balancing: Once the WAN connections have been bonded, the software routes network traffic across the different connections. This helps to ensure that the network is utilized effectively, and that performance is optimized.
- Failover and redundancy: WAN bonding also provides failover protection, which means that if one of the WAN connections fails, the other connections immediately take over. This helps to ensure that the network remains operational and minimizes downtime.
Implementing WAN Bonding
Implementing WAN bonding requires careful planning and the right equipment and software. The following are the key elements to consider when implementing WAN bonding.
Equipment and Software
To implement WAN bonding, you will need a WAN bonding device or software. There are several solutions available, ranging from hardware-based solutions to cloud-based software solutions. We will discuss Digi’s integrated hardware and software solution powered by Bondix S.A.NE in a later section.
Network Design and Topology
It is important to design the network topology carefully to ensure that WAN bonding can be effectively implemented. This includes considering the number of WAN connections required, the location of the WAN bonding device, and the routing of traffic between the different connections.
Configuration and Setup
Once the equipment and network topology have been determined, the next step is to configure and set up the WAN bonding device or software. This typically involves specifying the different WAN connections, configuring the routing and load balancing settings, and setting up failover protection.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
An administrator will need to regularly monitor the performance of the WAN bonding solution and perform routine maintenance to ensure that it continues to function optimally. Troubleshooting may be required in the event of any issues, and it is important to have a plan in place to quickly resolve any problems.
Use Cases for WAN Bonding

WAN bonding can be used in a variety of different scenarios, including:
- Remote offices and branch locations: WAN bonding is particularly useful for businesses with remote offices or branches. By combining multiple WAN connections, these businesses can achieve a high-performance, reliable network connection that supports the needs of their remote employees.
- Cloud connectivity: WAN bonding can also be used to improve cloud connectivity. By combining multiple WAN connections, businesses can ensure that their cloud-based applications and services are available and responsive, even in the event of a connection failure.
- Backup and disaster recovery: WAN bonding is an excellent solution to support a backup or disaster recovery plan. By combining multiple WAN connections, businesses can ensure that their network remains operational in the event of a failure or disaster.
- High-bandwidth applications: WAN bonding is particularly useful for businesses that require high-bandwidth applications, such as video conferencing, online gaming, and data transfers. By combining multiple WAN connections, these businesses can achieve the bandwidth and performance they need to support these applications.
- Connectivity on trains and buses: WAN bonding enables transportation authorities to obtain Internet speeds faster than any single connection for the myriad of connected devices on today’s modern trains and buses, including data-intensive applications, live video streaming to multiple media displays, security cameras, and onboard passenger Wi-Fi.
- Mission-critical data in remote locations: This is where WAN bonding’s packet duplication feature excels. The use case here is not focused on increasing throughput, but on providing 100% surety that the data going to/from mission-critical applications at a site will be delivered, even on high-latency or spotty Internet connections.
Introducing Digi WAN Bonding
Digi WAN Bonding provides all of the functionality and benefits we have described, in an easy-to-implement solution available as an add-on service to a Digi Remote Manager® premium license. Fully integrated with Digi cellular solutions and the DAL operating system, Digi Remote Manager (Digi RM) is a powerful cloud-based platform that orchestrates connectivity and management of your Digi device network.
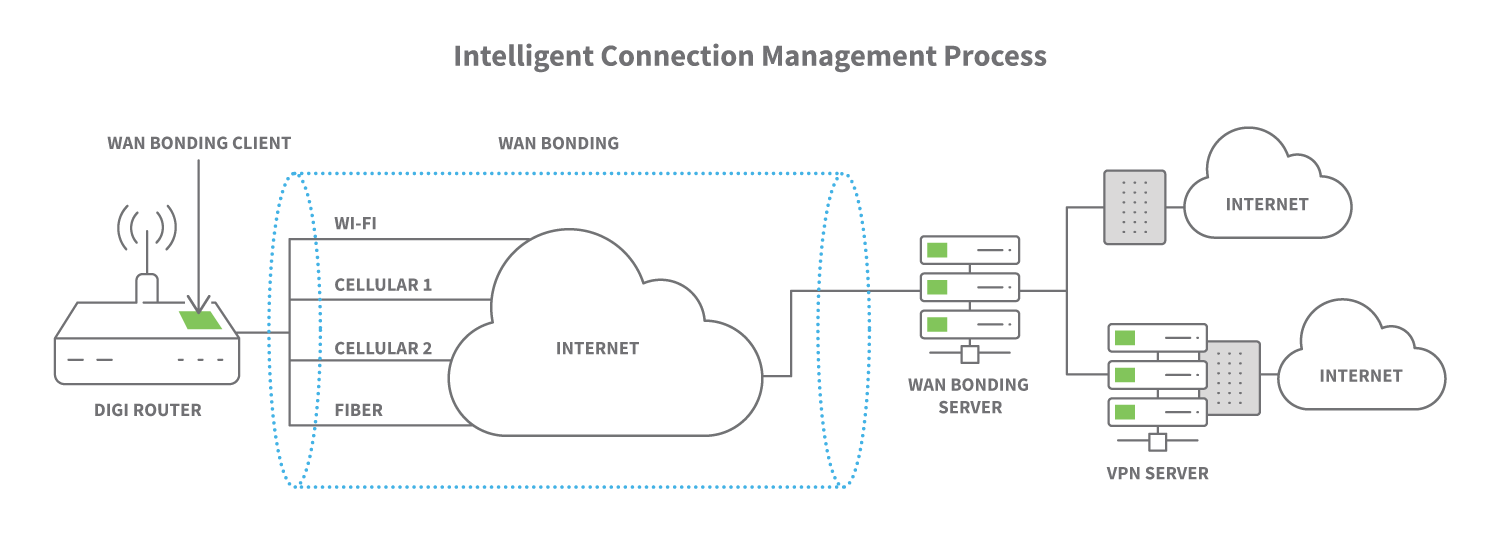
Developed by Bondix Intelligence, S.A.NE is short for Simple Aggregation of Networks, the software-driven technology from Bondix designed to ensure reliable voice, video and data transmission connectivity for both mobile and stationary deployments. Digi WAN Bonding enables customers running DAL OS on their Digi devices to centrally set up, deploy and manage the bonding together of multiple WAN connections. This WAN aggregation supports dramatically increased throughput speeds, WAN smoothing, packet redundancy and seamless failover for always-on Internet connectivity.
Conclusion
WAN bonding enables organizations to combine multiple WAN connections into a single, virtual connection. Digi WAN Bonding harnesses these capabilities to improve network performance, reliability, and redundancy, and can be particularly useful for businesses with remote offices or high-bandwidth applications.
The future of WAN bonding looks promising, with advances in technology and the increasing demand for reliable and secure network connections. Organizations that are looking to improve their network performance and reliability should consider implementing WAN bonding as part of their overall network strategy.
In summary, WAN bonding is a powerful tool for businesses looking to improve their network performance, reliability, and resilience. With the right equipment, configuration, and maintenance, organizations can reap the benefits of WAN bonding and stay connected, even in the face of network failures or other challenges.
Next Steps