For most organizations, the swift collection and analysis of data is crucial for streamlining operations, ensuring safety, and gaining timely IT and OT insights. Rapid computation and data management are also critically important for Industry 4.0, manufacturing automation, autonomous vehicles and other data-intensive applications. Edge computing solutions available today allow organizations to capitalize on the Internet of Things (IoT) by deploying smart devices at the network edge to reduce latency and bandwidth usage by managing data where it’s generated.
What Is Edge Computing?
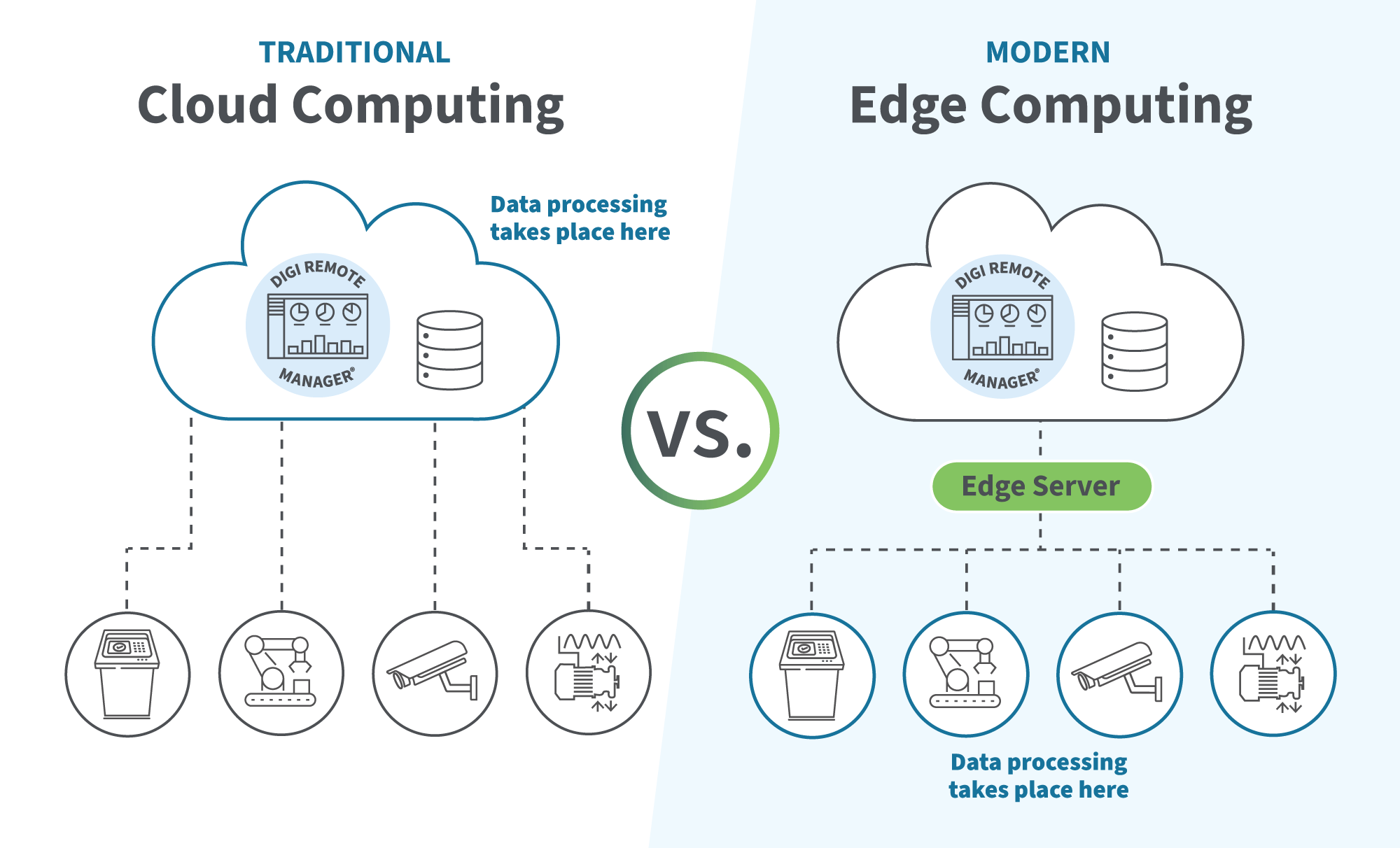
Edge computing is an architecture that uses a distributed computing model to eliminate data management inefficiencies and reduce latency. IoT and mobile devices within the distributed framework use IoT devices like embedded systems, cellular routers and serial servers to collect and process data at its source instead of transferring it to a central server, data center, or cloud solution for processing, as would be required with a traditional approach to cloud computing and IoT data management.
The edge computing model enables organizations to save bandwidth, time, and money. This model harnesses the power of smart edge devices, edge intelligence and cellular connectivity as a means of reducing cross-network traffic and enhancing efficiency. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can accelerate the processing speed of the IoT architecture by performing edge analytics, identifying patterns, taking actions and routing data.
IoT and Edge Computing
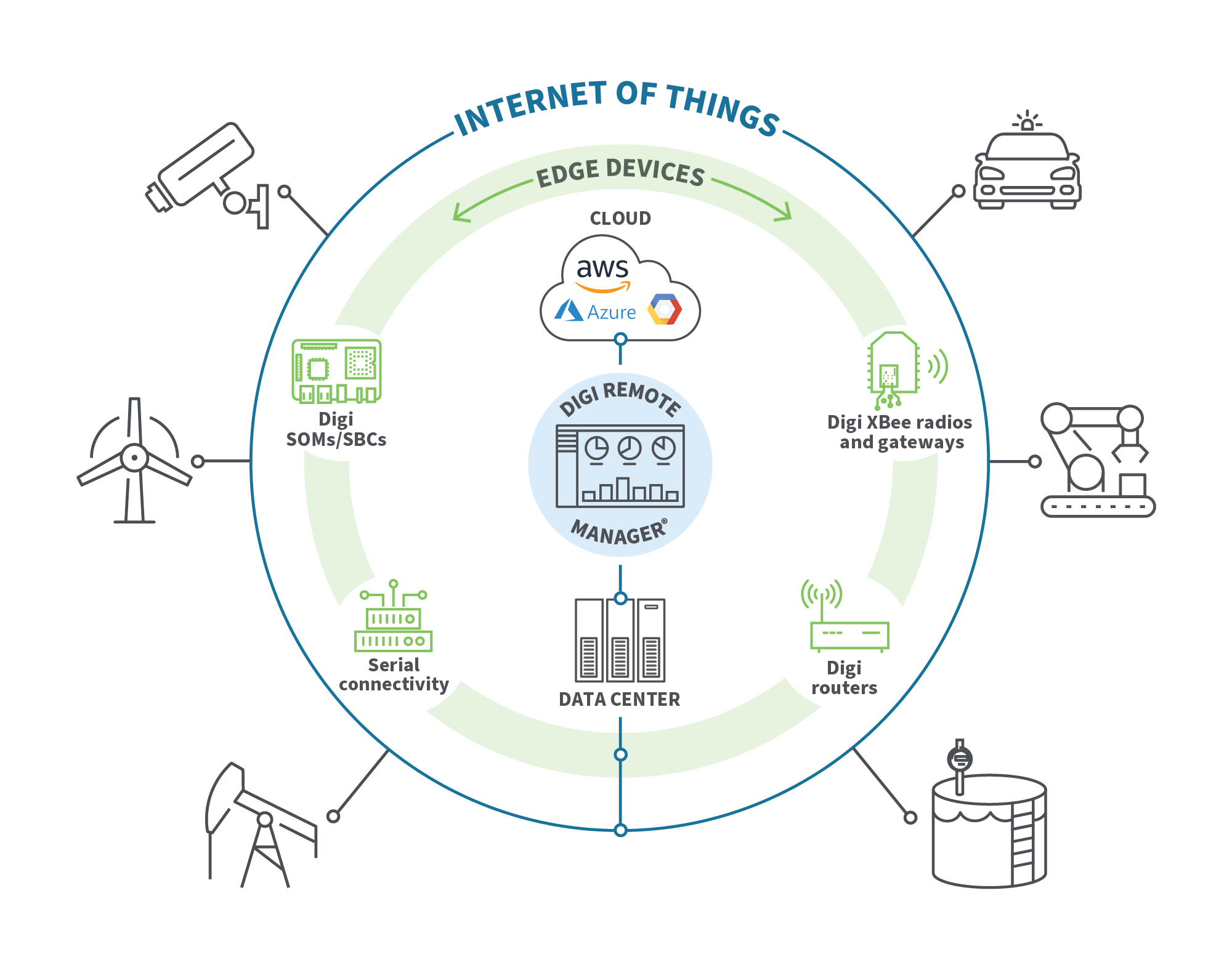
IoT refers to a variety of data collection devices, which may or may not process data at the edge. Some examples of IoT devices include:
- Manufacturing production monitors
- Health wearables
- Security motion sensors
- Smart lighting systems
- Self-driving vehicles
- Smart traffic light controls
- Environmental monitoring sensors
- Smart utility meters
- Fleet tracking devices
Edge computing in IoT allows devices to increase data usage efficiency and streamline operations. When coupled with edge computing technology, IoT devices can support real-time data processing to improve data routing speeds in critical applications, provide improved bandwidth management, and lower data costs.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing solutions support a range of operational goals. The edge infrastructure can include cameras, sensors, and a range of IoT devices that perform processing immediately and locally, and route only specific data to centralized servers for further analysis, operational insights or storage. Intelligent edge devices can also take a number of actions, from performing analytics, to initiating reports or service tickets, to immediately causing machinery or operations to cease due to safety issues.
After initial processing, edge computing devices determine what data needs to transfer to other systems. As a result, the amount of data sent over the network is limited, ensuring only critical information is relayed to data centers or cloud solutions for business intelligence. A combination of purpose-built edge computing chips, device processing capabilities and remote monitoring and management tools are required to enable this sophisticated edge computing paradigm.
Edge Processing
Traditional approaches to data analysis typically rely on centralized processing solutions, such as data centers, cloud solutions, or servers. While those methods provide sufficient computing power, they require sending data from IoT devices or other collection points across the network for processing. Ultimately, that leads to latency and requires significant bandwidth, resulting in less efficiency.
With an edge deployment, mobile, IoT, and other edge computing devices have processing capabilities to analyze collected information and support automation, real-time decision-making or operational adjustments. This is accomplished using embedded edge chips and smart edge devices, allowing immediate edge processing where data is generated.
Edge computing benefits, compared with fog computing, are also considerable. With fog computing, there’s a processing layer between the edge layer and the central data center or cloud solution. While those servers assist with processing, they still require data transmission away from the collection point, and that can use substantial bandwidth and lead to latency. Distributed edge computing allows each edge device across the network to collect, store, and process data on its own. A consistent connection to the network is often not required, allowing operations to continue regardless of connection stability.
Edge Infrastructure
Edge infrastructure encompasses all network components, connected mobile devices and IoT access points within the broader system. The exact edge computing hardware and software solutions vary, and may include a range of edge computing nodes and devices:
There is also a software component to consider. For example, platforms like Digi Remote Manager® allow organizations to monitor and control hardware at the edge, making them a necessary part of the equation.
For example, Digi Remote Manager provides network-wide visibility, remote access, device configuration and security monitoring from a “single pane of glass.” Additionally, this solution provides instant alerts and notifications from the network edge, based on specified conditions, and enables out-of-band access to edge devices for remote management.
Benefits of Edge Computing
There are many benefits of edge computing that make this approach valuable for a wide range of use cases. Here are a few examples:
- With IoT edge computing, industrial companies can actively monitor production, allowing them to make operational decisions based on real-time data.
- And in Industry 4.0 applications, edge computing is crucial for real-time processing in robotics and manufacturing automation.
- Real-time data processing creates opportunities for immediate intervention in healthcare when a patient’s condition changes, and ensures finance companies can capitalize on quickly shifting market conditions.
- Edge computing tools and smart devices enable companies in any sector to reduce network strain and bandwidth usage. Along with a cost savings, this reduces exposure to potential threats. Plus, it allows critical operations to continue even if cloud connections are lost, allowing edge computing applications and systems to support business continuity.
Here is a closer look at some of the benefits of edge computing platforms, software, services, and infrastructure:
- Real-time data analysis: Edge computing software and solutions eliminate processing delays. In turn, organizations can receive immediate insights, supporting real-time decision-making to enhance efficiency, address issues quickly, or capitalize on brief windows of opportunity.
- Security and privacy: Because edge processing requires less information to be transmitted across networks, exposure to threats is minimized, as sensitive data may never need to cross the Internet. Plus, a significant amount of data isn’t stored with a third-party cloud provider.
- Bandwidth and efficiency: Because edge computing services perform computing, analytics and automation at the edge, that reduces the use of network resources and bandwidth and increases efficiency. Additionally, lower bandwidth usage often results in a cost-savings, allowing organizations to either reduce service calls or avoid unexpected overages that may trigger additional fees.
- Speed and reduced latency: Edge computing allows a faster response to local events. With edge computing, latency can commonly be reduced to near zero. Along with benefiting organizations directly, the speed provides a better experience for user-centric applications like gaming, streaming, and real-time communications.
- Remote management: Remote management platforms allow organizations to oversee the deployed edge devices remotely, making device and network management simpler. These centralized platforms are a crucial part of the equation, ensuring accessibility, insights and notifications from anywhere via a desktop or mobile device.
- Scalability: Deploying edge infrastructure supports expansion of deployed devices and overall scalability, enabling organizations to ramp up or add functionality when needed, and allowing edge computing systems to handle increasing data loads from a growing number of connected devices.
- Cost containment: Edge computing can help organizations lower costs by reducing the need for extensive cloud infrastructure. Additionally, localized processing and storage can be more cost-effective, especially for organizations operating in resource-constrained environments.
- Sustainability: With edge computing, companies can reduce their carbon footprint and improve sustainability. Edge devices are often low energy battery-powered devices. The real-time decision making they support can also eliminate waste by identifying inefficiencies or adjusting processes, and the ability to scale up or down rapidly can keep operations right-sized continuously, ensuring efficient use of energy and resources.
- AI at the edge: Integrating AI with edge computing products and solutions enhances the capabilities of IoT devices. Advanced data processing and analysis capabilities are available at the device level, leading to more powerful insights, often in real time.
Edge Computing Solutions
For an effective solution, organizations must tailor their edge infrastructure to the organization’s industry and use case. This ensures the solution will serve the unique needs, priorities, and pain points with a targeted approach.
Comprehensive edge computing solutions also allow organizations to harness cutting-edge technologies to improve results. Incorporating 5G cellular connectivity reduces latency and enhances connectivity for edge devices across the network. Implementing AI and machine learning can enable advanced real-time data processing at the device level, supporting speed and agility when it matters most.
Enterprise Edge Computing
Traditional enterprise computing relies heavily on data transmission, with data created at endpoints like user computers before being transferred to centralized servers. Enterprise edge computing utilizes the compute power of devices across the network, reducing strain on network resources, cutting data costs, enhancing reliability, and boosting speed.
With tailored enterprise edge computing solutions, organizations can create a customized ecosystem to support scalability and maintain affordability while improving efficiency.
Industrial Edge Computing
Industrial edge computing provides edge devices, automation systems, machinery and robotics with the high-speed processing power they require and gives organizations access to real-time analytics that support rapid decision-making in fast-paced, ever-changing environments. IIoT Edge devices (Industrial Internet of Things) designed for this sector are typically ruggedized — ensuring they can withstand environmental challenges like extreme temperatures and continue operating optimally — and have high reliability with built-in failover and redundancy.

Edge Computing Applications and Use Cases
Today, edge computing applications are already in use all around us, from fingerprint readers on smartphones to real-time traffic monitoring at intersections. Let’s look at some edge computing examples across verticals.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, edge computing solutions enable manufacturing automation, robotics and predictive maintenance. IoT edge devices in the Industry 4.0 paradigm can perform factory assemblies, rapidly scale production up or down based on demand, and improve production speed and accuracy — freeing up personnel to handle engineering, technician, and management tasks.
Additionally, video cameras and IoT edge devices can detect anomalies in production and remove parts that are not up to specification. They can monitor production efficiency and compare data to historical timelines to support proactive repairs. And they can use adaptive diagnostics to alert technicians to the potential source of problems to speed up troubleshooting. IoT and edge computing today are driving a complete digital transformation in the manufacturing industry, enabling manufacturers to build smart factories, using edge devices to support industrial automation and predictive maintenance.
Retail
In the retail sector, edge data processing supports real-time in-store analytics, allowing retailers to adapt quickly to shifting conditions. IoT devices can automate inventory management, alerting retailers when quantities of specific products fall below set thresholds. Edge computing can also personalize shopping experiences for customers, using data-driven insights to personalize customer recommendations and make dynamic price adjustments to increase sales of products and services.
Healthcare
Edge computing enables real-time processing of data generated by medical devices, wearables, and sensors. This is crucial in healthcare scenarios requiring immediate decisions and responses, such as sudden changes in patient vitals or emergency medical situations.
Medical wearable devices can store information on heart rate, temperature, blood sugar and other metrics that can then deliver important notifications to the patient or physician and provide intelligent reminders for medication. In addition, edge computing enables healthcare organizations to enhance security and privacy, by limiting the transmission of sensitive and protected patient information. Edge computing can also boost the capabilities of telemedicine solutions, and IoT devices can perform rapid data analytics during critical medical procedures, improving patient experiences and outcomes.
Transportation
Edge computing plays a crucial role in transforming transportation systems, offering various uses and benefits to enhance efficiency, safety, and overall performance. Here are some key applications and advantages of edge computing in transportation:
- Autonomous vehicles: Edge computing enables self-driving vehicles to analyze data in real time and take rapid action to respond to shifting conditions, read and respond to road signs and traffic signals and maintain safety.
- Real-time traffic management and public transit routing: IoT and edge computing enable smart cities to proactively manage traffic by adapting traffic lights to shifting conditions on roadways. Today, transit signal processing allows buses to navigate more fluidly through congested city streets to ensure public transit passengers get to their destinations on time.
- Emergency vehicles: With sophisticated on-board cellular routers, police vehicles are increasingly taking advantage of edge processing to manage data locally from on-board devices and peripherals, as well as body-worn cameras and communication devices, to improve response times.
- Logistics: Shipping and receiving organizations benefit from IoT and edge computing in asset tracking and monitoring of vehicles and cargo.
Smart Cities
With edge computing, today’s smart cities can increase sustainability by proactively managing energy usage in infrastructure, including utilities, city lighting, water/wastewater management and urban mobility systems. Similarly, edge solutions can keep public safety organizations connected, ensuring real-time data is available during emergencies, including natural disasters. IoT and edge computing also support waste management, trash compaction and smart routing of sanitation vehicles. Additionally, IoT devices allow cities to monitor government-owned buildings and vehicles, improving safety and ensuring proper usage.
Edge Computing Technology
Edge computing technology brings together the power of faster networks, smart edge devices and enhancements in programming, enabling computations and data management to occur at the network edge. Let’s look at the components of an edge computing model.
Edge Systems
Edge systems are comprehensive solutions that provide organizations with all of the necessary components to process data at the edge. Typically, there are four primary components: mobile and IoT devices, network connectivity, storage solutions, and system management platforms. Devices collect and process data at the edge, while networks allow designated data to be transmitted to storage solutions, such as servers or cloud storage. System management platforms provide oversight into the edge system, providing monitoring for devices, connection speeds, and more.
Here are some examples of Digi edge systems:
Edge Devices
Edge devices are specialized computing hardware solutions that support data processing at the edge. Additionally, they may support various connectivity needs, ensuring any data transmission that needs to occur can do so with limited latency and suitable reliability. Some common edge devices include:
Edge Platforms
Edge computing requires software platforms to support and manage the overall system. Digi Remote Manager is an example of a comprehensive solution. With Digi Remote Manager, device configuration and deployment are centralized. Additionally, organizations can set up automatic device updates, monitor security, and receive instant alerts. Advanced security options are also available, such as VPN.
- Digi Remote Manager
- Microsoft Azure IoT Edge
- Google Distributed Cloud Edge
Edge Computing Products and Services
Digi is a leading provider of edge computing products and services, offering high-performance solutions that are tailored to specific industries. These comprehensive solutions provide the critical devices, software, and supporting services organizations need to transition to edge infrastructure seamlessly.
Here is an overview of various Digi edge computing products and services and how they can benefit your organization.
Edge Computing Hardware
Digi’s edge computing hardware solutions are designed to meet the needs of organizations seeking to gain the most from their IoT investment, ensuring they have the computing capacity, security, and reliable connectivity to streamline operations, improve safety, automate processes, and support advanced capabilities like AI. From embedded systems to cellular routers, Digi solutions enable advanced edge computing across every industry. These include:

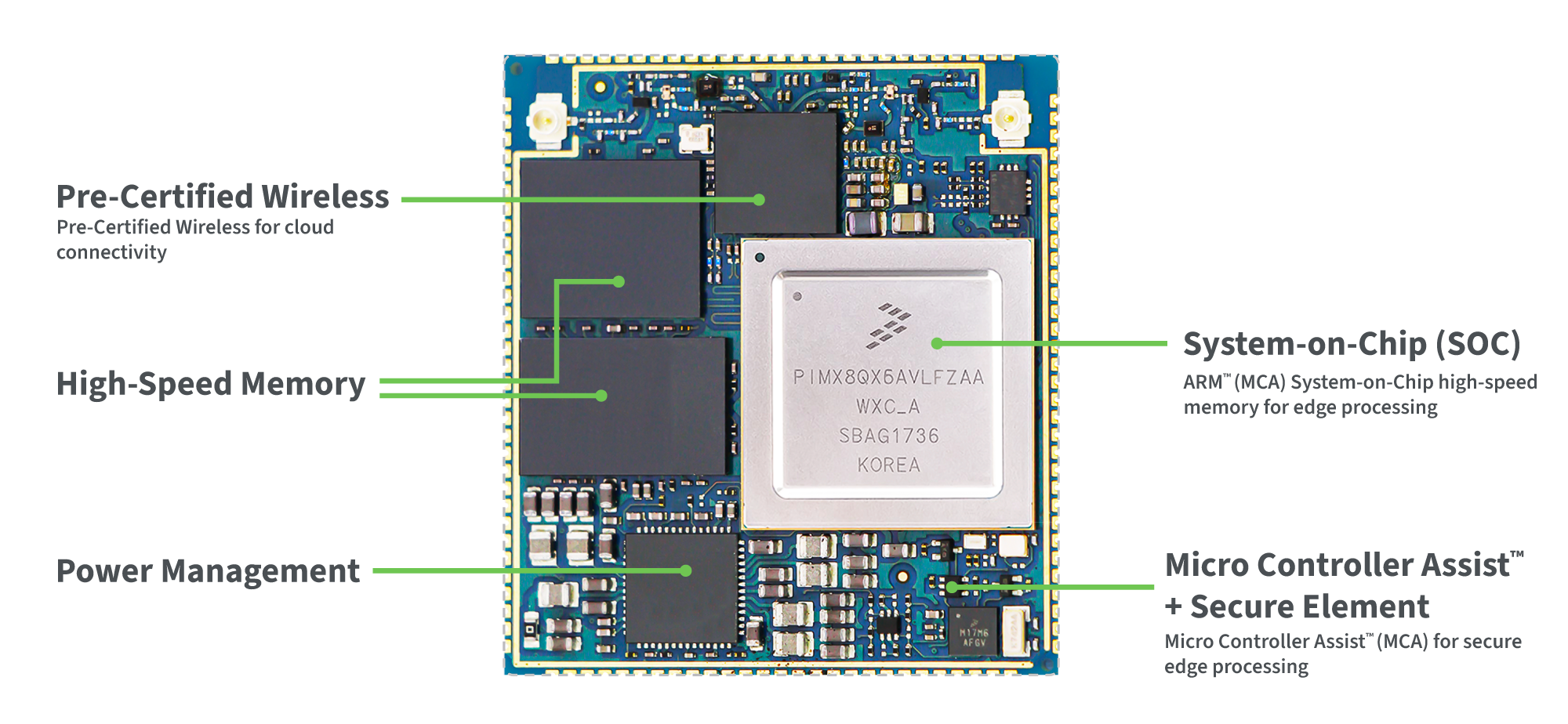
Edge Chips
Edge chips are components embedded into system-on-modules, that are designed to support the most advanced requirements of IoT applications across medical, industrial and transportation use cases. These SOMs support AI at the edge, enhancing the capabilities of edge devices and supporting real-time data analytics for rapid decision-making and operational adjustments. Digi integrates the industry’s most powerful application processors from manufacturers such as NXP and STMicroelectronics, with design-ready solutions that enable organizations in any industry to benefit from these cutting-edge technologies with rapid time-to-market.
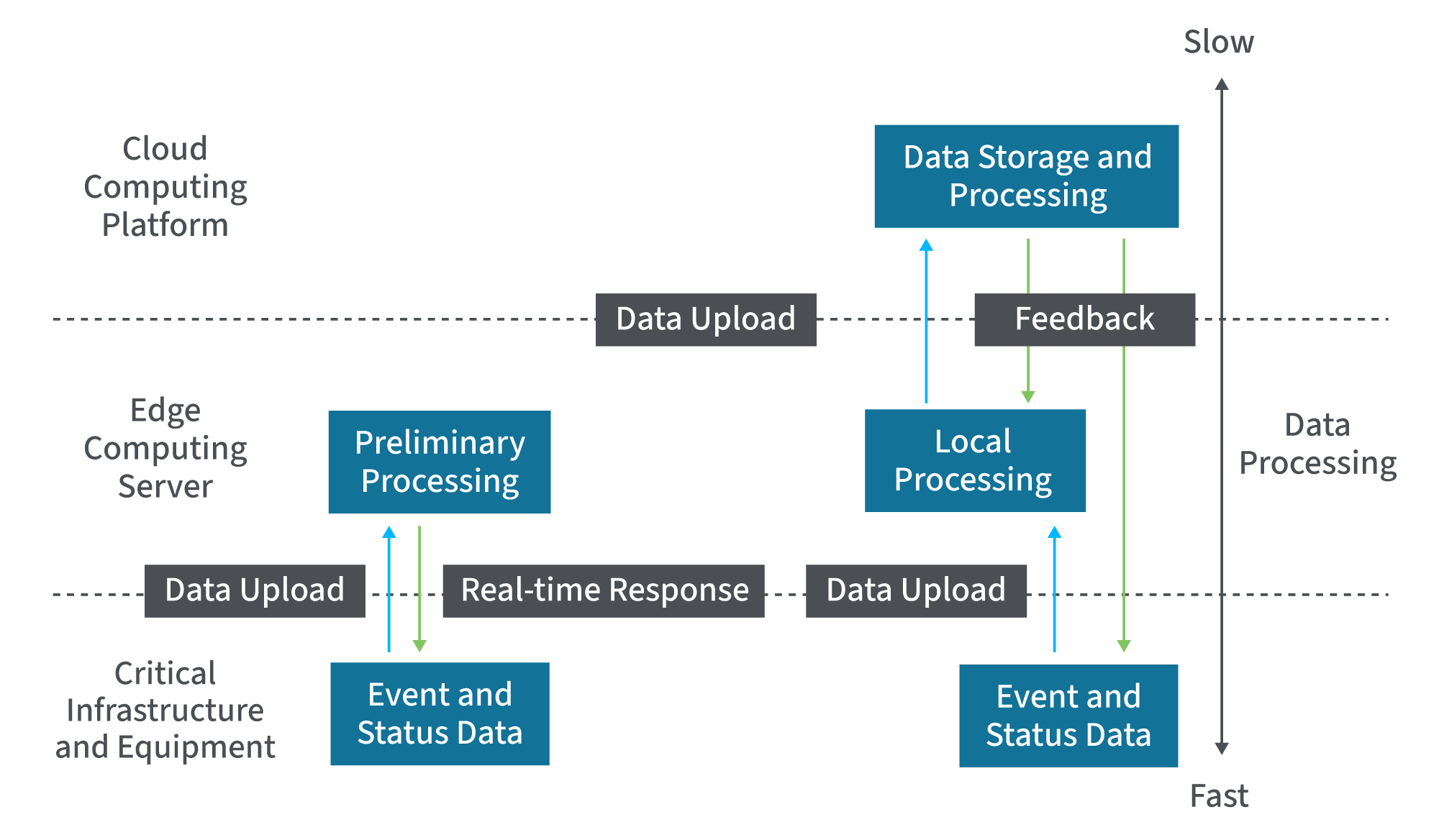
Edge Servers
Edge servers exist outside of the core data center or cloud solution, positioning them closer to end users and data-generating devices. Incorporating edge servers enhances computing capacity while dramatically reducing latency. Plus, edge servers are connected to internal networks, eliminating the need to transfer data over the Internet, making them more secure.
Digi offers an array of server options designed to meet a variety of needs and use cases, including:
Edge Computing Nodes
Edge computing nodes are physical or virtual machines positioned at the edge of a network and include the range of edge devices and edge servers we’ve discussed. Typically, they function as routers, gateways, application processors or edge servers, allowing IoT devices to communicate between networks, perform edge computing tasks (in the case of smart devices) and transfer data to and from other edge devices or an intermediary edge server connected to the cloud. Additionally, they can potentially assist with data collection and analysis, as well as run containerized applications that IoT devices need to interact with as part of their operations.
Digi’s edge computing nodes — which include all of the edge hardware devices listed earlier — are flexible, programmable, easy-to-deploy and manage solutions that can be configured to meet the needs of a vast range of edge computing applications. Additionally, our solutions prioritize security, ensuring your environment is protected.
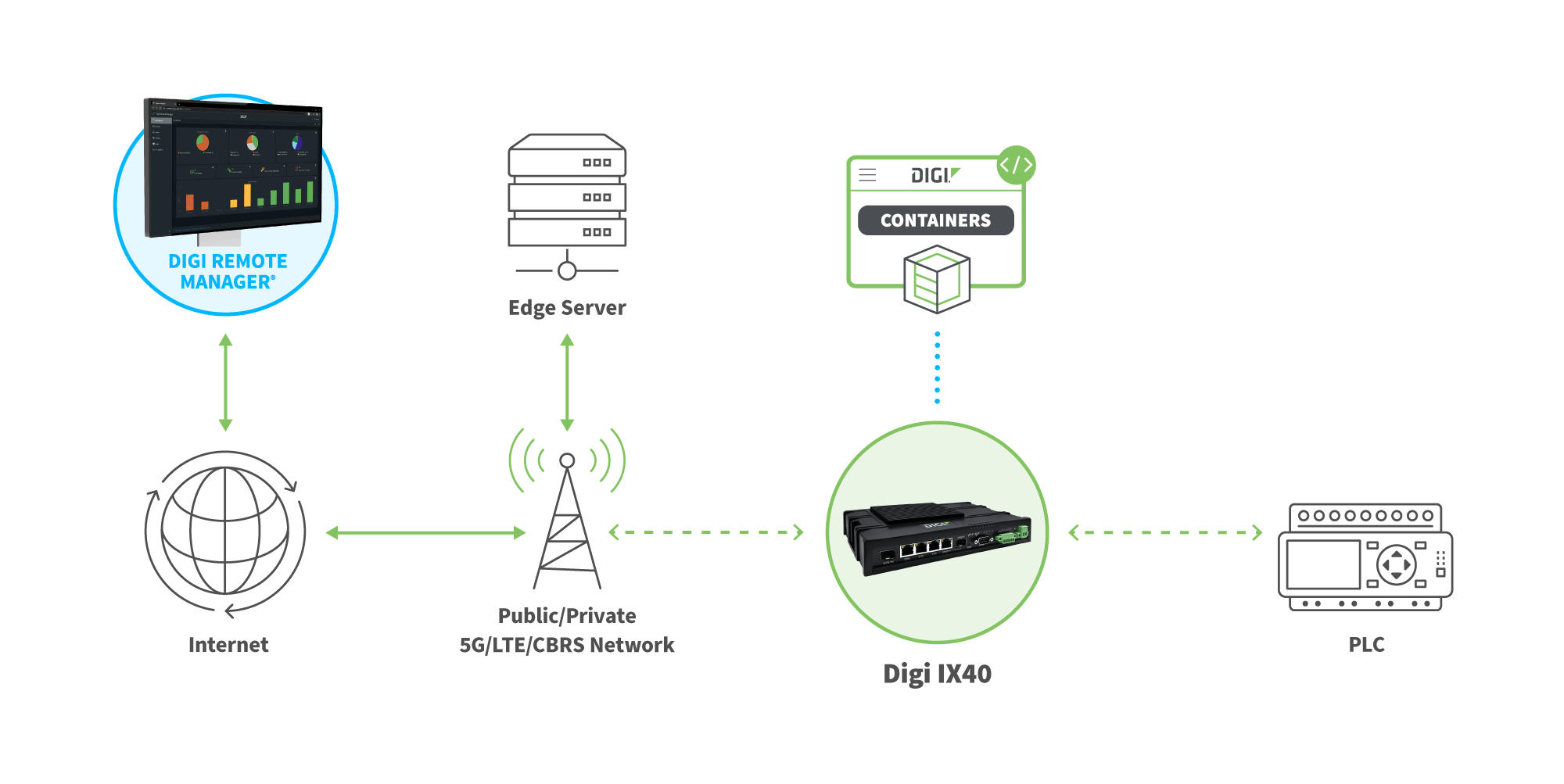
Edge Computing Software
Edge computing software makes managing an intelligent network simpler. Along with providing oversight, Digi Remote Manager streamlines device configuration and deployment. Plus, it supports mass firmware and software updates over your product lifecycle to simplify security and compliance, as well as providing real-time alerts on device conditions and network health.
Edge Computing Services
IoT and edge computing offer enormous benefits as organizations today seek to best utilize their workforces, resources and budgets to optimize their operations, their IT and technical services and their security. But undertaking these initiatives can add complexity to the organization’s objectives during the planning, development and deployment, as well as ongoing management of that deployment.
Digi has a comprehensive suite of services to support the initiatives of organizations across every industry, whether they are designing and building products with embedded systems, deploying IoT and edge computing devices at the network edge, or upgrading their existing infrastructure to improve operations:
- Digi Wireless Design Services: This team of highly talented engineers can support OEMs in prototyping, developing, certifying, managing and taking products to market.
- Digi Professional Services: This team of experts can provide a wide range of support as you plan your deployment, from site surveys as well as procurement and deployment, to scripting and programming, to supporting the ongoing management of your deployed network.
- Digi Connectivity Services: The Digi Connectivity Services team helps OEMs developing products with Digi XBee Cellular modules to quickly set up data plans, making it a simple and convenient process to add cellular connectivity and build wireless networks.
- Digi Technical Support: This team of professionals can help with technical troubleshooting and problem solving with a range of support options, including priority support contracts for mission-critical deployments.
Digi International: Leaders in Edge Computing Solutions
In today’s digital age, edge computing solutions offer critical functionality while streamlining operations. Processing data at the source enables automation, real-time analytics, and rapid decision-making in ever-changing environments. Ultimately, edge systems ensure ongoing agility and scalability, along with enhancing computing power and making cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning easier to integrate and deploy.
Digi provides edge solutions designed to meet the needs of a range of industries, from manufacturing automation to healthcare, retail, transportation, the public sector and more. Our solutions are designed with robustness and compliance in mind, ensuring they function optimally in challenging conditions and provide critical security mechanisms to safeguard data.