The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming a wide range of industries and sectors by bringing unprecedented levels of automation, intelligence, and connectivity at price/performance points that were previously unthinkable. Let's talk about some IoT device examples to demonstrate the ways in which our world is becoming more connected. First – what products and applications are connected by IoT devices and why?
In the consumer space, we see many different home automation applications, like intelligent thermostats, connected doorbells, smart coffee makers, and networked refrigerators, which are changing the way consumers think about and interact with their personal infrastructures.
However, it's in the commercial and industrial spaces where the
IoT has the largest impact, improving efficiency, accuracy, safety, security and providing data, reports, alerts and insights.
In energy and industry, we're seeing smart meters, remote tank monitoring, and electric vehicle-charging stations. Smart cities are deploying the IoT to create connected lighting, traffic management systems and smart transit systems. Precision agriculture is leading to greater crop yields and lower costs, and creating efficiencies that have a
positive impact on the environment. And in retail settings, the IoT is dramatically improving everything from smart ATMs to digital signs and kiosks.
When it comes to IoT hardware and connectivity – the underlying infrastructure that brings the Internet of Things to life – Digi offers the vital IoT devices for your application development, or closely partners with key suppliers. The IoT device examples we will discuss in this blog post include the following:
- Sensors
- Radio devices
- Systems on Modules (SOMs) and Single Board Computers (SBCs)
- Gateways
- Cellular Routers
Additionally, we will talk about another important aspect of building out a wireless application with IoT devices: enterprise device management software that provides the central monitoring, management and decision-making insights needed to effectively keep tabs on the deployed device network. Digi supplies enterprise-class software to manage the broad portfolio of devices and components, improve uptime, and enhance security.
 What Do Sensors Do in IoT Applications?
What Do Sensors Do in IoT Applications?
In IoT devices and applications, sensors act as the "eyes and ears" of installations in a vast range of use cases from oil and gas to agriculture, C&I metering, industrial tanks, municipal wastewater systems, security systems and more. There are a wide range of components from a variety of Digi partners that can monitor and capture data about their environment – motion, temperature, humidity, volume, pressure, flow, acceleration, sound, light – essentially anything that moves or fluctuates in some way.
The sensor converts its findings into a human-readable format displayed at the sensor location or transmits that data to a central server for reading or further processing. In many cases a sensor report will kick off a process. This can be anything from water flow management to turning on a fan or irrigation system or sending an alert.
Common Uses for Sensors
- Agricultural (e.g. soil conditions and moisture levels)
- Tank monitoring
- Flow metering
- Gas level monitoring
Considerations for Selecting Sensors
When you're choosing a sensor for an IoT application, some of the key factors to consider are accuracy, environmental conditions, temperature/humidity operating conditions, range (upper and lower limits), calibration, and cost. The sensor you deploy must be designed to withstand the environment in which it will be installed. Since many sensors work in rugged outdoor environments, and often must work optimally 24x7, this is a key consideration.
What Do Radio Devices Do in IoT Applications?
A radio frequency module wirelessly sends signals between two devices equipped with a transmitter and receiver. For many applications, RF modules are ideal for several reasons:
- They do not require you to design radio circuitry from scratch
- In the case of Digi XBee® radios, they come with FCC and other needed certifications.
- They use unlicensed spectrum.
- What's more, their transmissions do not require line-of-sight connectivity and can extend for many miles.
Related blog post: How Do IoT Devices Communicate?
Common Uses for Radio Devices
- Industrial automation
- Smart city lighting
- Smart agriculture
- Digital signage
- Solar fields
- Rideshare applications
Considerations for Selecting Radio Devices
Electronic radio design is notoriously complex because of the sensitivity of radio circuits and the accuracy of components and layouts required for a specific frequency.
In addition, you must carefully monitor the manufacturing process to ensure RF performance is not adversely affected. Radio circuits are usually subject to limits on radiated emissions, which necessitates compliance testing and certification by a standards organization such as ETSI or the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
For these reasons, many design engineers find that it's easier to "drop in" a pre-made, pre-certified radio module rather than attempt a discrete design, saving time and money on development.
RF modules are often used in consumer applications (such as garage-door openers), and wireless alarm/monitoring systems, as well as in industrial remote controls and smart sensor applications. They are increasingly replacing older infrared communication applications because they do not require line-of-sight for operation.
The most commonly used frequencies in commercially available RF modules are the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) radio bands (such as 433.92 MHz, 915 MHz, and 2.4 MHz). These frequencies are used because of national and international regulations governing the use of radio for communication. Short range devices may also use frequencies available for unlicensed spectrum such as 315 MHz and 868 MHz.
RF modules may comply with a defined protocol for RF communications such as Zigbee, Bluetooth low energy, or Wi-Fi, or they may implement a proprietary protocol. While a cellular radio operates in a similar fashion, unlike an RF module, a cellular radio module connects directly to a cell tower for communications, whereas an RF module requires a gateway in order to interact with the outside world – the Internet.
 What Do System-on-Modules and Single-Board Computers Do in IoT Applications?
What Do System-on-Modules and Single-Board Computers Do in IoT Applications?
A system on module (SOM) integrates a system function in a single module, bringing simplicity and intelligence to an embedded IoT system.
For IoT applications, integrated wireless connectivity (including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connections) enable broad deployment in numerous scenarios. Low power consumption is also a high priority. One notable benefit of SOMs is that they reduce the time and cost to develop a PCB-based design. SOMs provide excellent design reusability and can be integrated into many embedded computer applications.
A single-board computer (SBC) provides an entire computer built on a single circuit board, including microprocessors, memory, input/output and connectivity. Unlike a desktop personal computer, SBCs usually have no expansion slots. Digi SBCs rely on NXP microprocessors and offer pre-certified Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, superior power management, and enterprise-level security.
Common Uses for SOMs and SBCs
- Medical imaging
- Medical devices such as precision care
- Precision agriculture
- Electric vehicles and electric vehicle charging stations
- Interactive kiosks and vending machines
Considerations for Selecting SOMs and SBCs
Choosing the right product for your application is an important evaluation process. Development teams often start with single board computers in the evaluation and prototyping phase, then settle on a SOM for the final design that provides the form factor, connectivity features and performance requirements of the final application.
Some of the important factors are the development environment and whether there are supporting libraries and documentation. For example, Digi system-on-modules and SBCs are built on open source operating systems and are supported with libraries and documentation to help drive fast prototyping and development and ensure fast time-to-market. You can read more about Digi SOMs and SBCs on Digi.com.
 What Do Gateways Do in IoT Applications?
What Do Gateways Do in IoT Applications?
A gateway is an IoT device that serves as the connection point between the Internet (cloud) and controllers, sensors and other IoT hardware. All data moving to the cloud, or vice versa, goes through the gateway, which can be either a dedicated hardware appliance or a software program.
With IoT applications, sensors can generate thousands of data points per second. The gateway processes that data locally before sending it to the cloud, which minimizes the volume of data that needs to be forwarded. As a result, response times and network costs improve significantly.
The IoT gateway can also provide additional security for the IoT network and the data it transports. Since an IoT gateway manages information in both directions, it protects that data from leaks and prevents IoT devices from being compromised, thanks to tamper detection, encryption, hardware random number generators, and crypto engines.
Common Uses for Gateways
- Connecting radio devices
- Connection to the Internet
- Railside communications
- Data encryption and management in edge computing
- Sensor communications
Considerations for Selecting Gateways
Gateways can operate in a wide range of scenarios to temperature-managed indoor installations to remote outdoor installations. When the application requires the gateway to operate in a rugged environment, it is important to choose a gateway with a hardened encasement that is designed to withstand environmental factors such as temperature extremes, moisture and vibration.
 What Do Cellular Routers Do In IoT Applications
What Do Cellular Routers Do In IoT Applications
A cellular router provides shared Internet access through a cellular gateway. A standard wireless interface makes it easy for network-enabled devices to share the connection. The cellular router obtains its Internet access through a cell tower.
There are no wired connections, enabling the cellular router to create an Internet gateway on the move, such as on a moving train, or in an area lacking landlines or as a failover means of alternate connectivity.
Common Uses for Cellular Routers
- Retail and enterprise business connectivity
- Transportation systems (e.g. communication between dispatch and operators, security systems and on-board Wi-Fi)
- Digital signage, ATMs and kiosks
- GPS routing
- Smart elevators
Today, with cellular routers such as the First-Net Ready™ Digi® TX54, cellular routers with integrated Band 14 capabilities can be installed to provide pre-emptive cellular communications for first responders and extended primary users in the event of an emergency or catastrophic event.
Considerations for Cellular Routers
The breadth of choices in routers is vast, as routers serve an enormous range of purposes, from simple data routing on a small network to pre-emptive emergency response communications for first responders. Routers can be built for internal environments or for rugged outdoor installations that face dramatic ranges in temperatures as well as moisture, vibration and other environmental factors.
Additionally, routers have a wide range of features depending upon the connectivity needs, whether the communications are from stationary or mobile points, the application requirements for security, communications partitioning, cellular connectivity with multiple carriers, and the failover requirements of the business use case.
To support customers in evaluating the right router for their application, Digi has three different categories for cellular routers:
Contact Digi with inquiries or advice in choosing the right cellular router for your application needs.
The Difference Between Routers, Gateways and Extenders
When it comes to cellular communications hardware, the first piece of equipment to address is the modem, which is basically a "dumb" device – not intelligent and not programmable. The modem simply sends traffic from point A to point B, without any manipulation or data protection. Conversely, a router or extender is a highly intelligent device. In fact, every Digi router actually contains a cellular modem, and most Digi routers even support multiple cellular carriers with dual SIMs.
A quality router should also provide a robust firewall to handle packet-level traffic inspection, reconcile incoming traffic with outgoing requests, and support numerous types of tunnel options for data security, such as IPSec, GRE, L2TP, PPTP, or even open VPN. Many industrial-grade cellular routers contain an input/output or I/O option to handle simple operations for field devices, such as shutting down an overheating pump.
A cellular gateway doesn't possess the degree of networking traffic control that a router does, but it usually offers simplified configuration. Gateways often have an onboard programming model or simple control options. By definition, gateways provide protocol translation. So it might be Zigbee, wired hard, or Modbus to cellular, or even other technologies. There are numerous options where cellular gateways are concerned.
Related blog post: Cellular Routers, Extenders and Gateways: What Is the Difference?
Enterprise Device Management Software
 For an IoT solution to serve your needs, it is vital to have enterprise device management software to successfully deploy and manage your devices. Once deployed, your devices may not be physically accessible, or the size of your deployment may make it highly impractical to manually tend to the devices. Enterprise management software such as Digi Remote Manager® (Digi RM) allows your team to successfully move a project from proof of concept all the way through deployment and long-term management of devices once they are at the final location.
For an IoT solution to serve your needs, it is vital to have enterprise device management software to successfully deploy and manage your devices. Once deployed, your devices may not be physically accessible, or the size of your deployment may make it highly impractical to manually tend to the devices. Enterprise management software such as Digi Remote Manager® (Digi RM) allows your team to successfully move a project from proof of concept all the way through deployment and long-term management of devices once they are at the final location.
IoT devices often must be updated in terms of configuration, capabilities, and security necessary to address current business needs. A proper management solution allows an administrator to quickly and securely change configuration, update firmware or push out security patches to IoT devices. This software allows you to access data from IoT devices from anywhere, whether in the home office or in the field, as well as to integrate this data into your own cloud platform.
Enterprise device management software such as DRM also allows you to easily get detailed reports and real-time alerts via text, email, or internal management software on network health and device conditions that would previously have gone unnoticed.
The IoT in Action: Use Cases for IoT Devices
When it comes to designing an IoT device deployment, there is no one size fits all. The following illustration shows IoT device examples in an industrial IoT (IIoT) use case in which data is gathered from multiple points, then routed via cellular IoT devices to the cloud where various devices and end-user applications can access and manage that information. 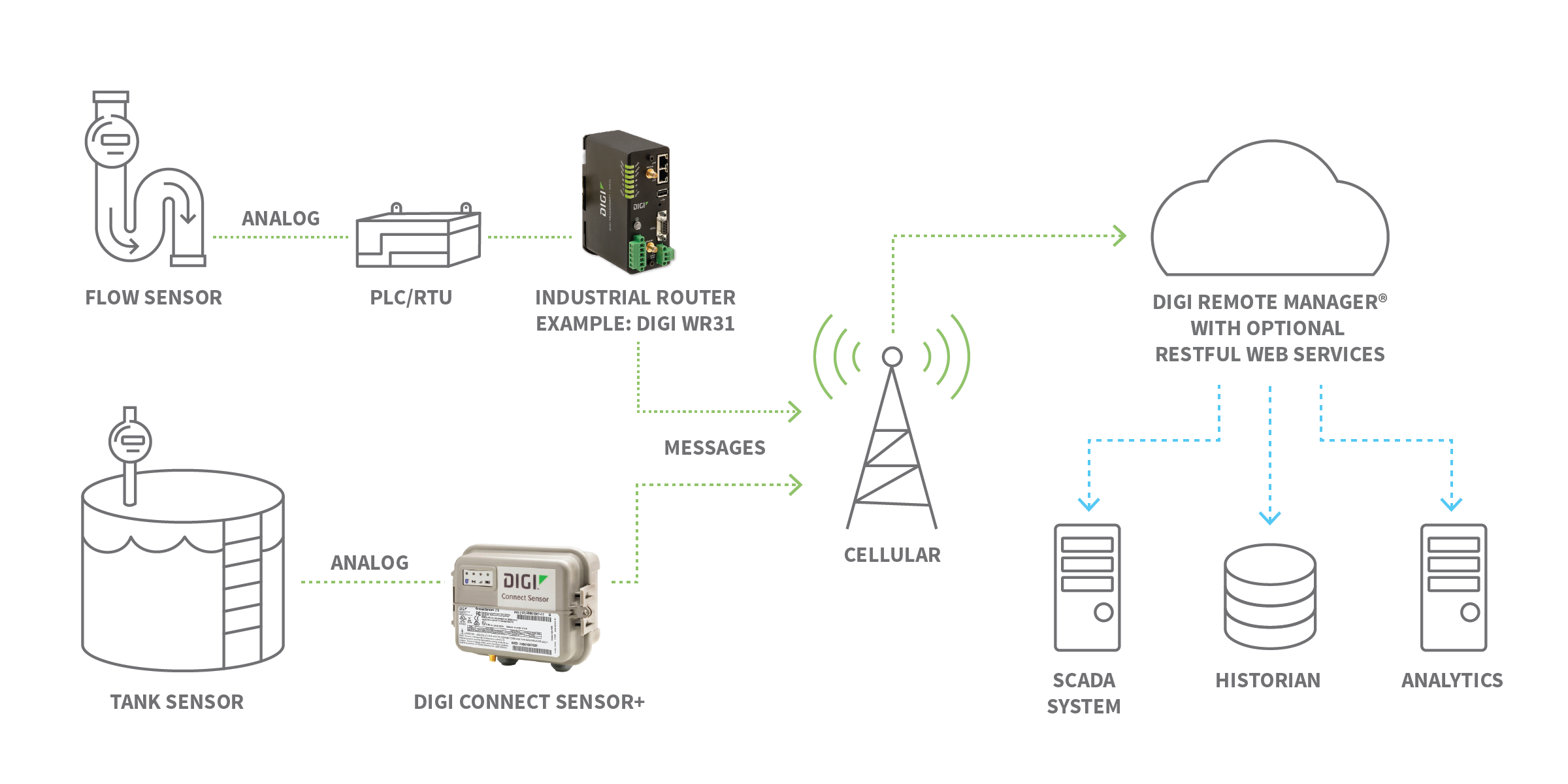 Perhaps the best way to understand the power and scope of the IoT is to see how leading organizations have applied Digi IoT hardware to bring greater intelligence, speed, and connectivity to tight spaces and faraway places. Here are some use cases to illustrate how the IoT can help your organization create efficiencies and improve processes.
Perhaps the best way to understand the power and scope of the IoT is to see how leading organizations have applied Digi IoT hardware to bring greater intelligence, speed, and connectivity to tight spaces and faraway places. Here are some use cases to illustrate how the IoT can help your organization create efficiencies and improve processes.
- Intelligent Streetlights: Lighting the streets and public spaces is a major expense for local governments. IoT devices embedded in streetlights enable municipalities to wirelessly and remotely monitor and manage pertinent parameters and control streetlights – from dimming lights at certain hours to setting schedules to conserve energy. Smart streetlights allow cities to monitor the status of lamps on roadways, parks, transit stations and other public areas to improve safety and security, cut operational costs, reduce CO2 emissions, and optimize maintenance schedules.
- Public Transportation: Transit agencies deploy IoT solutions to facilitate communication between vehicles and control centers. IoT devices are also enabling passenger Wi-Fi, collecting real-time diagnostics from onboard computers and sensors, real-time fare collection, mobile ticketing and enhancing safety and security through vehicle tracking and remote video access.
- Smart Metering: The IoT can deliver connected solutions for smart metering that streamline IT support and related expenses while delivering meter data to SCADA software and/or other database and turning it into valuable knowledge. IoT solutions deliver the highest levels of security and reliability, eliminate unnecessary wiring costs and reduce installation times. As a result, you can easily monitor remote devices and gain real-time consumption metrics. What's more, long-life IoT applications can increase worker safety and efficiency by deploying wireless sensor networks instead of requiring people to travel to dangerous work environments.
- Waste Management: The IoT is an ideal solution for water, waste, and wastewater management through its ability to improve efficiencies, cut costs and increase operational control. Deploy IoT devices for wireless monitoring in wells, lift stations, sewers, and other water-treatment systems that provide remote communications in the harshest of environments. The IoT connects local and remote assets to make it easy for treatment facilities to upgrade, automate and manage critical control systems. Make sure water levels, flowage, and other key monitoring and performance data are delivered in a timely, consistent and accurate manner. Digi's connectivity solutions are specifically designed to handle the demands of water and wastewater treatment plant monitoring, SCADA communications, chemical usage, pump house and flow control – even remote video surveillance. Your plant managers can set thresholds and alerts, reduce or eliminate manual processes, and optimize safety and security – especially in dangerous work areas – to avoid overflows and regulatory penalties.
- Kiosks and Digital Signage: The IoT enables kiosk operators to deploy integrated solutions with reliable, affordable Internet connectivity. That enables you to accept credit cards in an unattended environment (with PCI-DSS 3.0 compliance) and perform M2M transmissions to and from data centers that maintain inventory and other critical operating information. If you're operating digital signage, you can update your content in real-time across dispersed locations. The IoT eliminates unnecessary wiring and trenching costs and cuts installation times dramatically. And you can easily monitor, manage and limit on-site support with comprehensive device management and services.
Read about these and other projects in the Customer Stories section of the Digi site.
The IoT is revolutionizing a vast array of markets in the United States and around the world. In order to keep up and surpass competitors in your market, whether that be energy, smart cities, medical, industrial, retail or transportation, IoT devices are key in gaining advantages such as allowing for automation, increasing efficiency, gaining intelligence, garnering data metrics, and allowing for connectivity and communication.
In today's market, disruption is much easier and can spread across vast swaths of market segments very quickly due to the development of technology leading to lower prices on devices with greater capabilities. Commercial and industrial spaces are realizing many of these gains and profits that have been made possible by the IoT. For example, companies like Progressive and Redbox have used new technologies in the IoT to surpass players that were once thought of as untouchable like Allstate and Blockbuster.
In terms of IoT hardware Digi is here to be your partner and facilitator in all things IoT. We have a full portfolio of offerings designed to help address new challenges in your business as they present themselves, as well as the longstanding expertise to help you navigate this journey using any and all of the IoT products discussed above.
Digi can support your IoT evaluation or development initiatives, at any phase. Our Wireless Design Services team can support application prototyping, development, testing and go-to-market planning, and our Professional Services team can help with site surveys, planning and IoT deployment with Digi cellular devices. Contact us to get started.
Note: This blog post was originally published in 2019, and was updated in April, 2021.