Modern companies are more aware than ever of the value of data collected in the field and how it can ensure their equipment, systems and processes stay environmentally safe, efficient and productive. So — what is
environmental monitoring? While the use cases are broad, we can define it as a system of distributed sensors, wireless connectivity, edge computing and visibility tools that monitor conditions, processes and equipment to track environmental health and/or prevent events and failures that can harm the environment.
Even more broadly, "environmental conditions" in many cases indicate heat, cold, moisture, vibration and other environmental variables that can be adverse to consistent and reliable equipment operations. In other words, while we may first think of the ecological definition of environmental monitoring, the term is inclusive of these variables and their impact on operations as well.
Although environmental monitoring technology has been around for some time, organizations that need to quickly respond to changing environmental conditions can find it challenging to act on this data, which is generated well outside traditional on-prem or cloud environments. Industries like manufacturing, agriculture and energy are using networks of Internet of Things (IoT) devices to integrate environmental monitoring into their operations, dramatically transforming the way these businesses interact with and respond to their surroundings.
What Does Environmental Monitoring Mean?

Environmental monitoring means using observational techniques and tools (such as sensors, wireless communications and remote management software) to detect, observe and measure environmental conditions at a specific site or location. However, the actual reality of these processes — the tools used, what parameters are selected, and how the processes are implemented — can vary greatly depending on the use case.
In the past, environmental monitoring has been primarily used for ecological purposes. For example, researchers that want to observe air pollution, or the effect of industrial pollution on protected areas and habitats, might employ disconnected methods for the measurement of environmental conditions long-term.
Periodically, they would need to go collect the monitoring devices they’ve distributed in the field in order to retrieve the desired data. Now, with IoT devices, wireless connectivity, and platforms supporting near-instant access to information from anywhere, the principles of environmental monitoring have become applicable to new use cases, from monitoring water treatment plants and groundwater supply to monitoring oil and gas pipelines for leaks.
Objectives of Environmental Monitoring
When adopting environmental monitoring, each organization needs to consider what its primary and secondary objectives are. Doing so will allow them to plan the strategic deployment of appropriately designed IoT devices.
In industrial applications, reasons for environmental monitoring include:
- Optimizing operations for safety and efficiency. Environmental monitoring allows companies to observe and react to changing conditions on-site, reducing the risk of equipment failure, accidents and resulting damage.
- Minimizing an organization’s impact on the environment. Industrial sites can track and find ways to decrease pollution or carbon output using ecological monitoring techniques.
- Validating ongoing safety protocols. In industries that require specific site conditions to operate effectively, companies can assess their existing procedures using environmental monitoring reports.
Techniques of Environmental Scanning and Monitoring
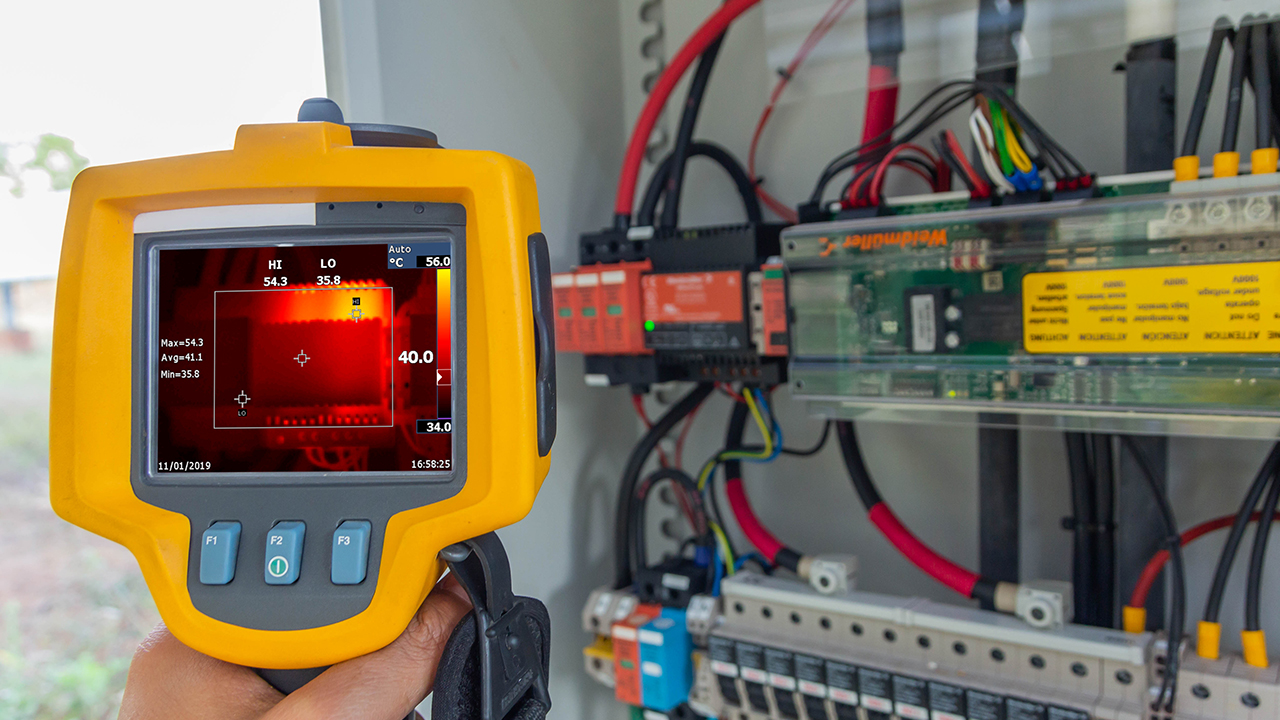

When monitoring environmental systems, organizations have a variety of scanning and monitoring techniques to choose from. Data streams generated at edge sites can produce thousands of data points, often much more than can be processed or stored in the cloud for real-time use, so it’s important to consider which techniques are best suited for each organization's industry, priorities and operational needs.
These techniques can be broken down based on three major categories of environmental problems:
- Monitoring air quality
- Using sensors to measure temperature, humidity, or emissions
- Air dispersal modeling using networks of sensors and Geographic Information System (GIS) models
- Monitoring water quality
- Using sensors to monitor temperature, chemical composition and radioactivity
- Environmental sampling to measure biological and chemical parameters
- Monitoring soil quality
- Grab or composite sampling to measure organic material, contamination, pH levels, or biodiversity
- Using remote sensors, electromagnets and GIS to measure salinity
- Erosion and instability monitoring
- Soil compaction testing
Examples of Environmental Monitoring Systems
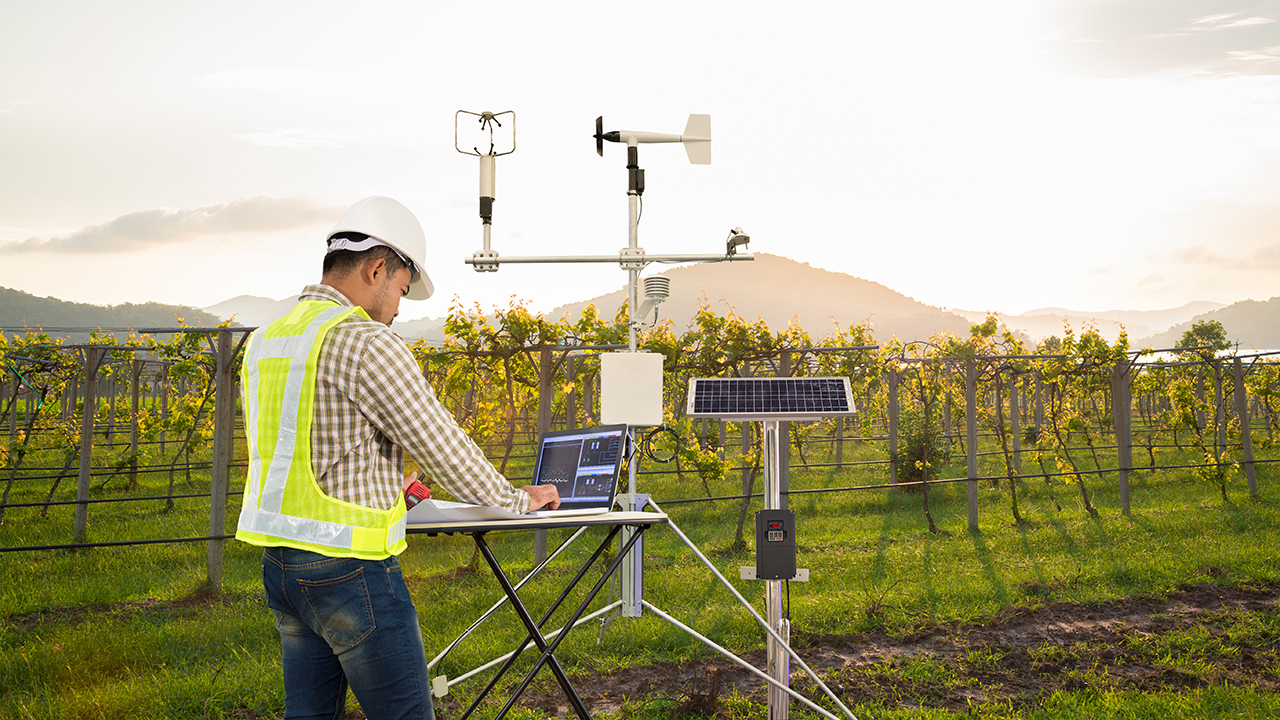

The availability of remote monitoring solutions and new wireless technology has made it possible for companies in oil and gas, manufacturing, agriculture and even healthcare to gain value from environmental monitoring. Using IoT-based environmental monitoring systems [link to IoT Based Environmental Monitoring once published], businesses can implement proactive environmental monitoring and assessment into their on-site management and operational processes.
And as the following examples of environmental monitoring systems will show, adopting these IoT-based monitoring systems can help businesses accelerate and improve their response to situations that need immediate attention (such as leaks or equipment failures) and long-term issues (like pollution and changes in water supply conditions).
Pollution Monitoring Systems
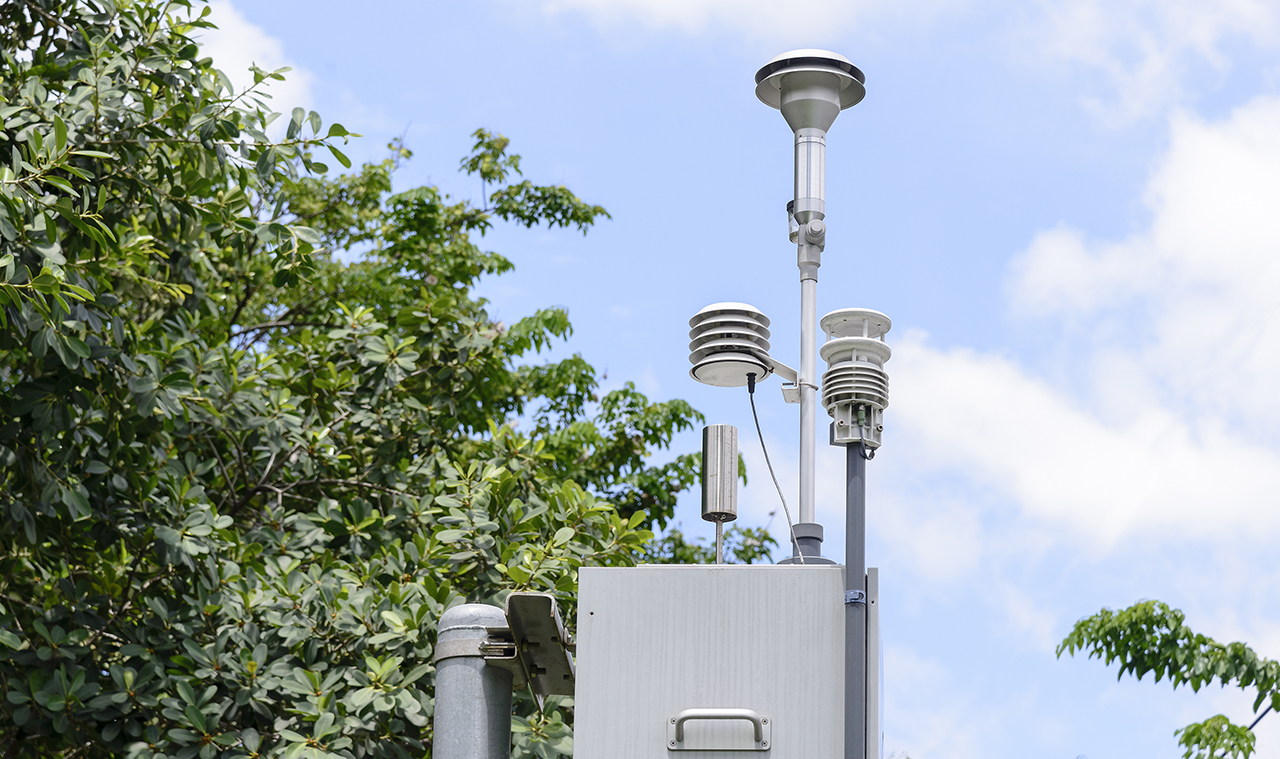

Pollution monitoring has become an incredibly valuable tool in manufacturing, civil planning and agriculture. These systems can allow organizations to observe, measure and even mitigate pollution and contamination that affect both natural and manmade water stores, air quality and soil quality. Monitoring the acidity and overall chemical composition of these environmental elements can provide both private and public organizations with valuable information – but they also need the ability to process and react to that information quickly.
When these environmental monitoring capabilities are integrated and managed via IoT platforms, companies and local governments can react faster to pollution’s effect on project timelines, equipment uptime, public health, worker safety and sustainability efforts. For example, construction companies and agricultural operations that require environmental monitoring impact assessments to begin and complete regulated projects can implement continuous environmental monitoring to always remain aware of and responsive to site conditions.
Download our IX40 5G Industrial Cellular Router Datasheet
5G edge computing industrial IoT cellular router solution, purpose-built for Industry 4.0
Download PDF
Leak Detection Systems
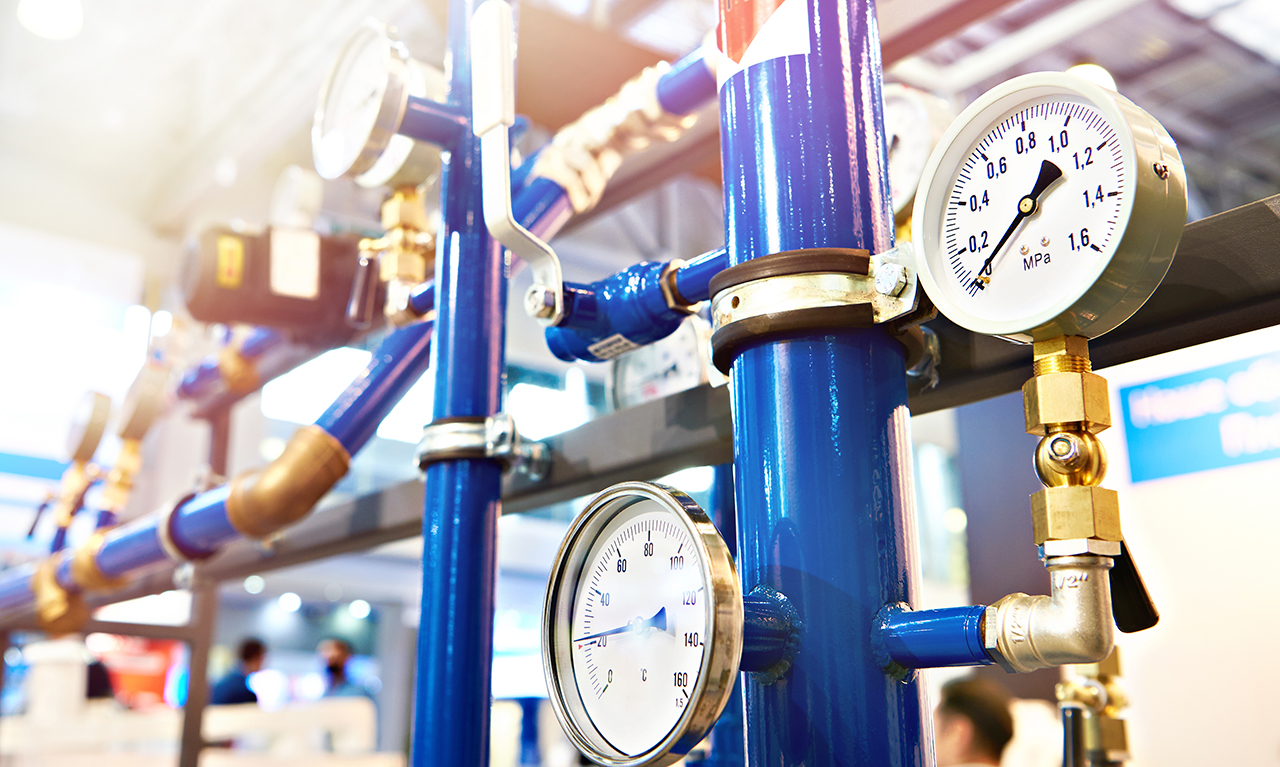

While many environmental monitoring types are important to consider in the oil and gas industry, leak detection systems are especially critical to ensuring worker safety, preventing ecological harm and minimizing potential financial losses. The environmental monitoring systems that oil and gas companies rely on need to be optimized for early, reliable leak detection for buried and above-ground pipelines.
Both liquid and gas fuels are highly combustible, which makes the equipment-packed environment of a natural gas field, oil field, or oil rig a very dangerous place to be. Additionally, if left unchecked, an ongoing leak poses a significant threat to surrounding plant and animal life, not to mention the public health considerations if the leaked oil or gas contaminates groundwater. With the right IoT devices to serve as environmental condition monitors, oil and gas companies can create leak detection systems that alert them of the problem quickly so they can address it early and minimize any resulting damage.
Wastewater Lift Station and Tank Monitoring Systems
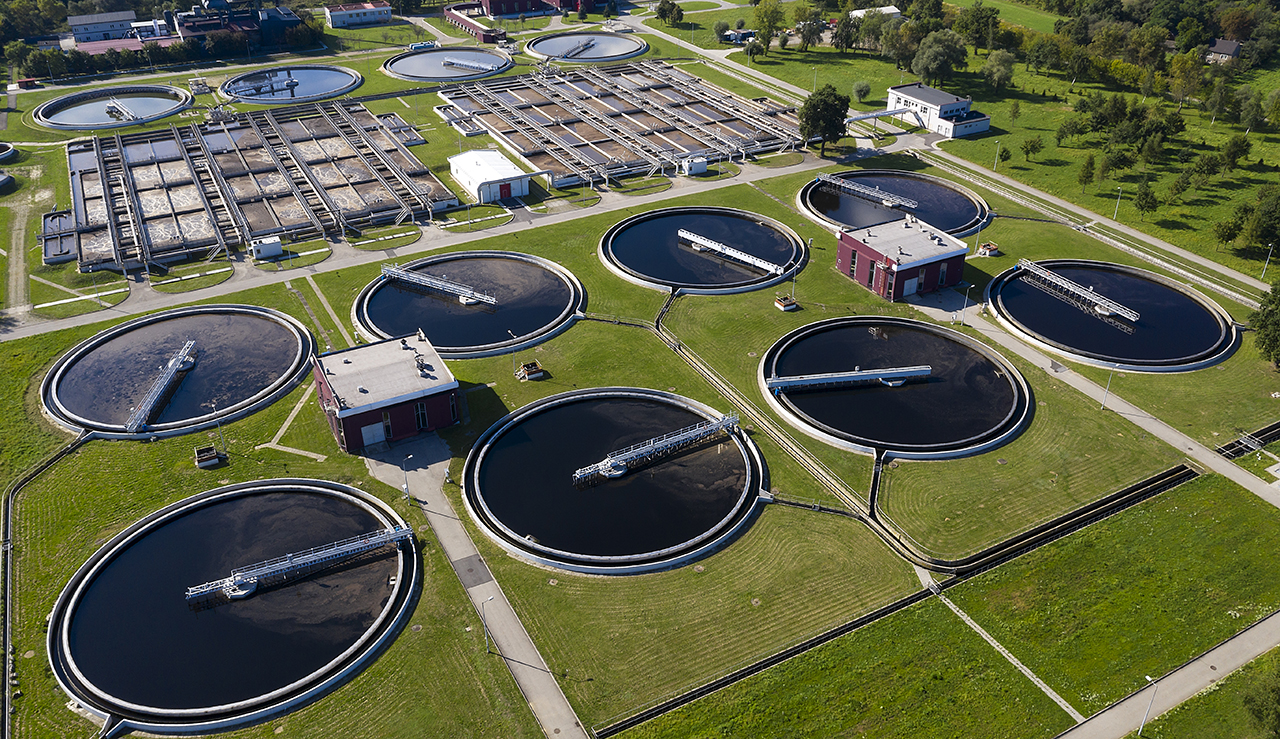

Although people may not commonly correlate sewage management and the importance of environment quality, wastewater processing and storage systems represent some of the most critical use cases for environmental monitoring. Wastewater management impacts public health, water availability, agricultural yields and more. When mishandled or malfunctioning, wastewater equipment and storage facilities can cause lasting damage to surrounding communities.
By deploying and connecting networks of IoT devices, the municipalities responsible for operating and overseeing wastewater lift stations and tanks can build effective environmental monitoring systems that record and measure the chemical properties of treated water in real time. Additionally, these systems can be combined with leak detection sensors that help prevent the contamination of groundwater and limit municipal workers’ exposure to harmful pollutants, including pathogenic bacteria or viruses.
Groundwater and Aquifer Monitoring Systems

Another way that IoT-based environmental monitoring can be used to improve public health and agricultural productivity is to improve groundwater protection. In the United States, groundwater comprises 37% of the public water supply – the water that local municipalities supply to residential and commercial properties – and more than 90% of drinking water for rural populations.
The consequences and characteristics of environmental pollution of groundwater and aquifers may only become obvious after significant time has passed, but once that contamination happens it can be very difficult to reverse or resolve. Industrial and commercial operations can be the most common culprits, potentially resulting in ecological harm and public health concerns as well as fines from regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
Why Is Environmental Monitoring Important?

With IoT devices designed to observe and measure specific environmental conditions, businesses and government entities can implement environmental monitoring at a variety of locations. Whether measuring water, soil or air quality, these IoT sensors can provide visibility into site conditions and deliver data-driven insights, allowing site managers to address problems more proactively and effectively.
Instead of waiting for a negative environmental survey report to come back or for long-term consequences to arise, industrial and commercial businesses can responsively clean up contaminants, repair malfunctioning equipment or adjust operations to reduce risk and prevent financial losses.
As more companies and government bodies focus on developing and deploying intelligent operations to support sustainability efforts, environmental monitoring technology becomes increasingly relevant to their goals. With IoT-based environmental monitoring, organizations in agriculture, manufacturing, waste management, public utilities and other critical industries can:
- Reduce the risk of equipment failure by halting operations in poor conditions.
- Prevent the build-up of harmful pollution in groundwater, soil and indoor and outdoor air.
- Make workplace accidents less likely by implementing leak detection and pollution monitoring systems in risk-prone environments like oil and natural gas fields.
- Protect the local plant and animal life, as well as agricultural production and public health, by improving groundwater and aquifer protection.
Learn More About Environmental Monitoring and Green Tech Solutions

IoT device deployments support environmental monitoring of air, soil and water quality across a variety of use cases and vertical industries. Wireless connected IoT devices can also make it easy and less impactful to the environment (versus trenching and running cable.) Not only does responsive, IoT-based environmental monitoring support the goals of many ongoing sustainability initiatives, but it also allows commercial and industrial operations to lessen the risk of operational accidents or equipment failures, as well as ecological or human exposure to dangerous contaminants.
Having insight into the environmental conditions at distributed operational sites and distributed properties means companies can use remote monitoring solutions to identify sources of contamination or environmental change earlier. In the long run, that means less system downtime, reduced risk of accidents and greater ecological health and productivity. Learn more about environmental monitoring, green tech, IoT solutions and how we all benefit from them. Or contact us to start a conversation.