We are at a turning point for telemedicine (also known as telehealth). For hundreds of years, interactions between doctors and patients have been mostly face-to-face in medical offices, hospitals, homes and care facilities. But today, medical technology and faster networks like 4G LTE and 5G are changing the face of healthcare.
Telemedicine technologies have been progressing gradually. Most noticeable has been the rise of wearable health devices to monitor vital signs. The idea of doctors seeing patients over the Internet has been appealing yet not widely put into practice.
However, the COVID-19 pandemic has changed that. To keep patients and medical staff safe, health organizations are increasingly using telehealth technology to serve patients. As a result, growth in the telemedicine market is accelerating worldwide. Medical device companies are racing to meet demand. Furthermore, todays 4G LTE and evolving 5G wireless technologies is fueling the growth of telehealth and other healthcare functions as never before. Some of the contributing technology factors include widespread
cellular network availability,
ease and speed of deployment and vastly
improved bandwidth.
5G new radio (NR) technology is a major improvement over the current 4G LTE technology. Using millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, 5G can deliver a theoretical download speed of 20 gigabits per second compared with less than two gigabits per second for LTE. This 10x performance improvement means more and better information in near real-time.
5G mmWave uses very high frequencies between 24 GHz and 100 GHz, capable of delivering high data rates, but at a much shorter distance than LTE. Therefore, more 5G antenna towers are needed. Currently, mobile infrastructure suppliers like Nokia or Ericsson are already able to demonstrate 5G download speeds of up to 10 gigabits per second.
Because of its super speed and robustness, 5G will accelerate telehealth’s development. But there is more. 5G can also support massive Internet of Things (IoT) and smart city infrastructure. As a result, it will propel the growth of home healthcare, remote patient monitoring, remote and robotic surgery assistance, and smart city infrastructure. Patients and healthy individuals alike will see direct impact to their well-being and available resources for health management.
Improved Home Healthcare
.jpg?lang=en-US&width=594&height=367)
The aging population is creating a demand for home healthcare. While it is more comfortable to stay or recover at home, there are safety concerns when an outpatient or elderly individual lives alone. Adult children may live many miles away and not have easy access to their parents. This creates a dilemma. On one hand, the elderly individual(s) would prefer the freedom to live on their own. On the other hand, the children may find it difficult to provide the care needed to support a parent or parents living alone and worry that their health and safety needs will not be met. Fortunately, home healthcare technology will be able to solve the problem.
People Power, a Palo Alto based technology company, has partnered with the University of California at Berkeley to come up with the idea of AI-based telehomecare (THC). Based on artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing, “People Power Family Care” can monitor individuals’ activities 24 hours a day with a remote support team to monitor their well-being.
Compared with other solutions available on the market, this approach using AI is much more advanced. For example, in addition to sending an emergency alert if the motion sensors detect a fall, the system can also send warning alerts if the system predicts that a fall may occur. People Power Family Care consists of a personal assist button and an AI-based home activity monitoring network. It optionally supports the Apple Watch for outdoor tracking and Amazon Alexa for voice communications.
The AI algorithms automatically learn the behavior of the individual(s) being monitored. If there is activity which causes concern, the system can automatically alert a Trusted Circle of family and friends as well as a 24/7 emergency call center. To prevent disconnects, the system includes battery backup and today relies on dual-SIM cards from multiple carriers like AT&T, T-Mobile or Verizon as well as Wi-Fi.
As technology progresses from 4G LTE to 5G, it is expected that a single 5G connection will be sufficient for communication. Therefore, more and more home healthcare solutions like this would be able to connect using 5G alone rather than using two carriers, reducing cost and complexity.
Remote Patient Monitoring

Medical electronics have made major strides in the past few years. Maxim Integrated, a semiconductor manufacturer, offers a silicon platform for device makers who are designing products to monitor common vital signs. These include pulse/heart rate, blood oxygen (SpO2), stress, electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG), body temperature, and UV light (skin exposure). A new smart watch from Apple, Series 6, can monitor blood oxygen and ECG with built-in GPS and cellular. Fitbit has introduced its Sense smartwatch, which can monitor blood oxygen, ECG, skin temperature, and stress with a Wi-Fi connection.
To reduce healthcare costs, hospitals are trying to discharge patients such as those recovering from heart attacks as quickly as possible once the condition is stabilized. Following discharge, hospitals will use wireless technology to remotely monitor patients’ health conditions. Smart watches are useful for frequently monitoring the wearer’s health conditions but are not yet up to the standard required for clinical use.

Based in Charlottesville, Virginia, Caretaker Medical, a medical device company with investments from Philips and others, offers the Caretaker 4 device. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued a 510(k) clearance for the unit. Caretaker 4 provides wireless continuous non-invasive “Beat-by-Beat” blood pressure (“CNIBP”) and a heart rate monitor, using a patented finger cuff technology. With this device, the patient can be monitored 24 hours a day remotely by caretakers and/or family members. In the future, 5G will provide robust, real-time connection in the near future. More patients will be able to receive remote monitoring over a reliable connection.
5G-Enabled Remote Surgery Support
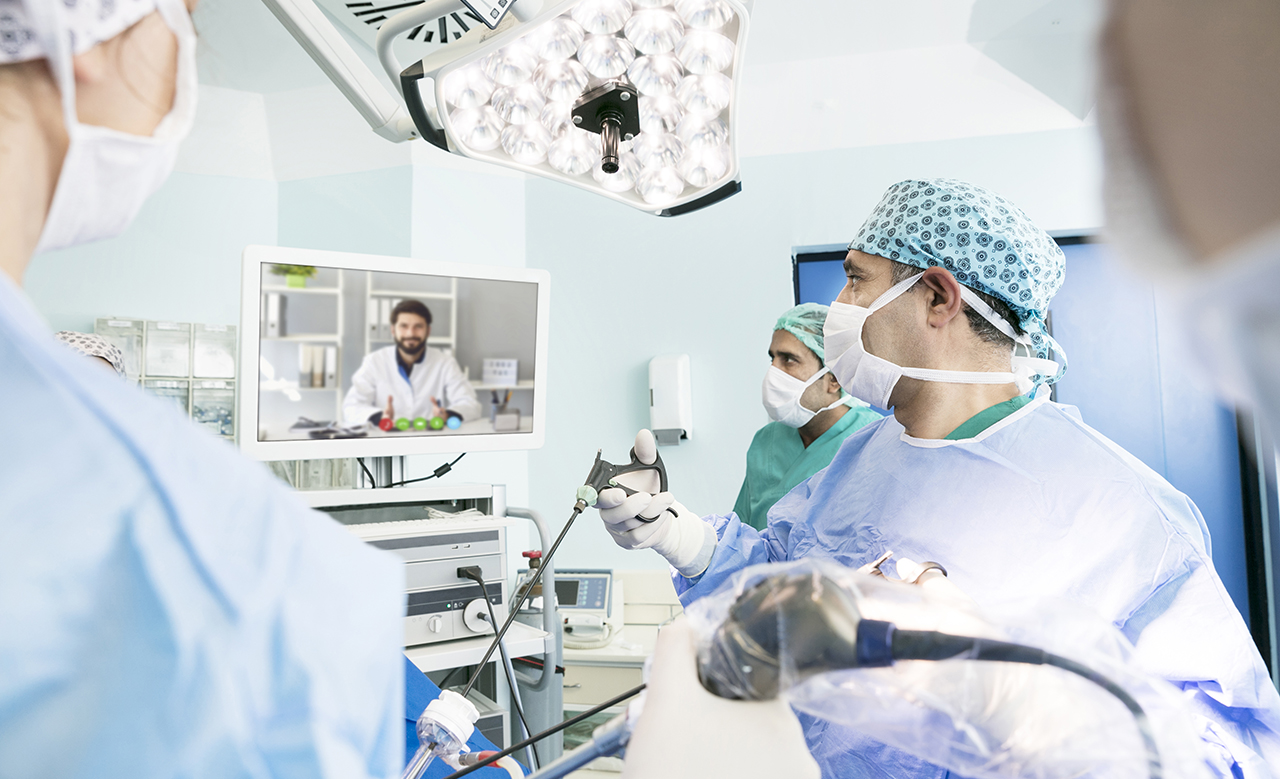
While most hospitals have experienced surgeons, they typically do not have every surgical specialty on staff. Often, they will consult physicians with specialized knowledge. Experts in specific surgical fields have been using video and audio to support the surgical team during the operation.
With medical advances, more and more surgeries are depending on technology. For example, a small surgical microscope can be inserted inside the body, and, using a high definition 4K display such as that of the Olympus Visera, clearly reveal the details of the area to be operated on.
A 5G connection will mean that the same information viewed by the surgical team can be livestreamed in real-time to the supporting expert team, and in the future in even higher 8K resolution. This real-time connection will enable the experts to advise the team as the surgery takes place.
Better Emergency Support in a 5G Smart City

During the pandemic, many hospitals became overwhelmed due to Covid-19. In some cases, hospitals had to turn away patients for lack of ICU space. Being unable to admit a patient to an ICU promptly endangers patients and disrupts normal hospital routines.
Some cities have started to experiment with smart cities technologies to support better healthcare. In a smart city, after an ambulance picks up a patient who needs urgent care, a nearby hospital would be informed automatically about the patient’s condition and the estimated arrival time.
That information would enable the hospital’s emergency team to quickly get ready. If there is no ICU bed available, the ambulance would have been warned, and the system would automatically route the ambulance to the next available hospital without stopping. If electronic health records (EHR) are installed, the hospital would know the patient’s condition before arrival and have the right medical setup ready. By knowing information in advance about any allergies to medicines or materials, the medical team can prepare with less last-minute scrambling.
Furthermore, in a smart city the ambulance is guided through traffic using Computer Aided Dispatch (CAD) and Advanced Vehicle Location (AVL). Smart traffic lights – today controlled with 4G LTE adaptive traffic control and ultimately controlled by 5G – will automatically be synchronized to allow the ambulance to go through while stopping all other traffic, saving time and increasing safety.
The Future of 5G and Medical Technology
We are only seeing a glimpse of what 5G will be able to do for telehealth and healthcare. It will improve home healthcare and remote patient monitoring and surgeries. In smart cities 5G will advance the way emergencies are handled. Critical information, available in near real time, will let teams react much more quickly to deliver better care.
Looking ahead, it is expected that many of these decisions and functions can be performed with AI. Machine learning, AI and robotics will play a greater role in procedures to improve precision. And caregivers and emergency teams will have more time and be better prepared to deal with unexpected situations caused by sickness or accidents as well as natural disasters.
Planning for the future? Contact us to help you determine how and when to deploy next generation connectivity.