With 5G deployments underway, many people have questions about 5G applications and use cases, and what connected life will be like after the roll-out. The fact is, 5G will be transformational. It will enable many new applications that are not viable today, particularly in urban areas and cities. This is relevant, because according to the UN, over two thirds of the world’s population will live in an urban area or city by 2050.
Today, there is a lot of news and hype about 5G. As thought leaders in this industry, we regularly share knowledge about developments in the deployment of 5G, and what you can expect, particularly if you are involved in the commercial and industrial IoT space. Compared to the consumer space, commercial 5G is traveling a distinctly different but concurrent path.
Here are some of our past articles:
In this article, we will look at some of the anticipated applications for 5G.
5G IoT Applications and Use Cases
As 5G rolls out, what new IoT applications will we see? What 5G use cases will be enabled by the higher bandwidth and faster throughput? Will life change as we know it?
Yes, life will change with 5G and the anticipated applications it will enable, but not ubiquitously. There will be a growing divide of network connectivity and services between urban and rural areas because it is impractical to deploy 5G everywhere right away.
The fundamental idea behind 5G is a single network that is flexible enough to handle a variety of different use cases. In order to deliver the promise of 5G, mobile network operators (MNOs) have to build a dense network with a massive amount of network nodes that will form the 5G infrastructure.
Each node costs money, and MNOs will invest into 5G through network upgrades and densification first in cities, where they can reach many paying customers and get a faster return on their investment. In rural areas the 5G rollout will happen at a slower pace.
Categorizing the Applications for 5G
The rollout of 5G will provide benefits in three major areas, also known as the “5G triangle”:
- uRLLC: Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication use cases
- mMTC: Massive Machine Type Communication (IoT) use cases
- eMBB: Enhanced Mobile Broadband – high speed use cases
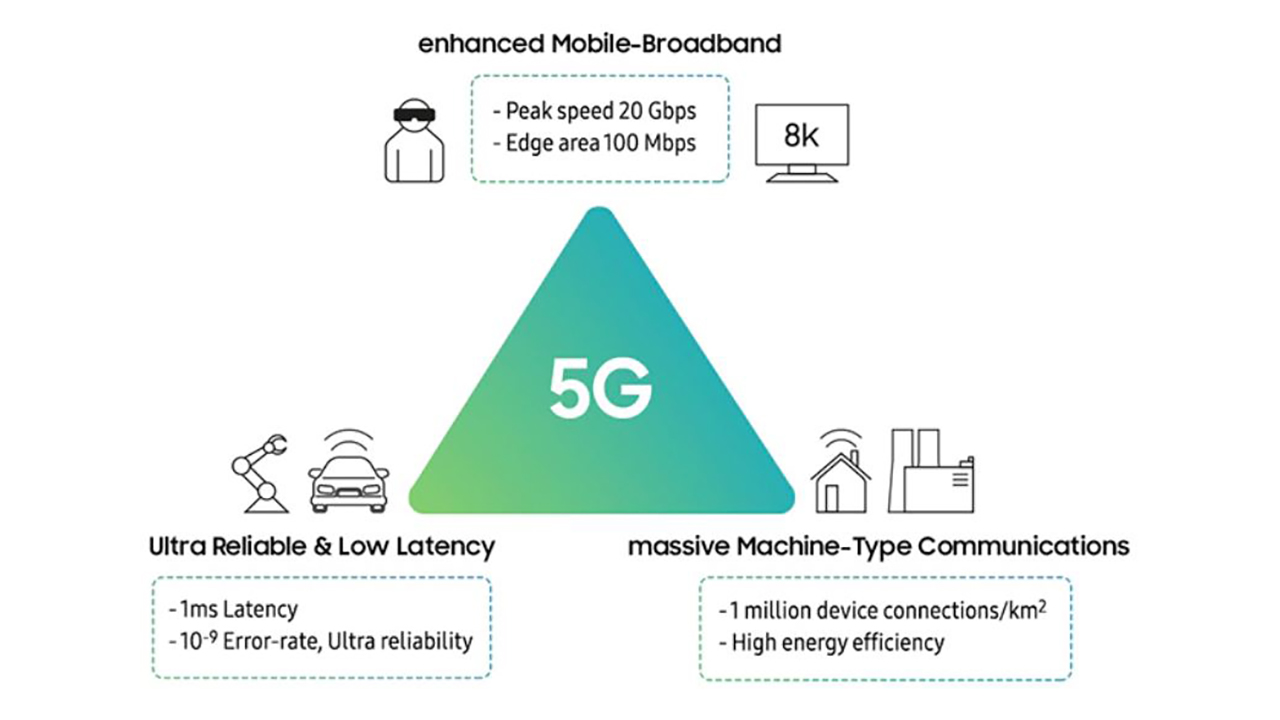
Image source: Samsung.com
uRLLC – High availability, Low Latency Use Cases for 5G
Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication (uRLLC) will be one of the biggest game changers once 5G is fully deployed. Here, we will see new applications that require response in fractions of a second.
Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are one of the most anticipated 5G applications. Vehicle technology is advancing rapidly to support the autonomous vehicle future. Onboard computer systems are evolving with levels of compute power previously only seen in data centers.

We hear about autonomous vehicles today, and many people wonder what the barriers are to making this future technology a reality. Many different developments in vehicle technology, network speed, data throughput and machine learning must come together for the fully autonomous vehicle future to materialize.
5G networks will be an enormous enabler for autonomous vehicles, due to the dramatically reduced latency, as vehicles will be able to respond 10-100 times faster than over current cellular networks.
The ultimate goal is a vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication network. This will enable vehicles to automatically respond to objects and changes around them almost instantaneously. A vehicle must be able to send and receive messages in milliseconds in order to brake or shift directions in response to road signs, hazards and people crossing the street.
Let’s compare 4G and 5G latency: Presume a car traveling down the road at 30 miles per hour needs to receive a signal to avoid hitting an object. With current 4G latency at around 100 milliseconds, a car would travel about 4 feet or 1.2 meters. With 5G latency around 10 milliseconds, the vehicle would only have traveled 5 inches or 12 centimeters. The difference is significant and could mean life or death.
Discover Digi 5G Solutions
The future is here, and Digi go-to 5G solutions are ready to take you there!
Watch Video
5G IoT in Smart City Infrastructure and Traffic Management
Many cities around the world today are deploying intelligent transportation systems (ITS), and are planning to support connected vehicle technology. Aspects of these systems are relatively easy to install using current communications systems that support smart traffic management to handle vehicle congestion and route emergency vehicles.

Connected vehicle technology will enable bidirectional communications from vehicle to vehicle (V2V), and vehicle to infrastructure, (V2X) to promote safety across transportation systems. Smart cities are now installing sensors in every intersection to detect movement and cause connected and autonomous vehicles to react as needed.
The communications backbone to support connected vehicle technology can be phased in today, well before 5G is fully deployed, dramatically improving pedestrian and vehicle safety.
Note: Digi offers these communications systems, and is now partnering with major U.S. cities to deploy them as part of strategic planning for congestion and disaster management. The Digi WR54, with FirstNet™ Ready options, is designed to support traffic management and emergency response use cases, while pre-certified Digi XBee 3 Cellular modules are deployed in traffic and parking sensors, metering applications, city lighting and more.
The USDOT website provides an excellent introduction to this initiative:
The U.S. Department of Transportation’s (USDOT’s) Connected Vehicle program is working with state and local transportation agencies, vehicle and device makers, and the public to test and evaluate technology that will enable cars, buses, trucks, trains, roads and other infrastructure, and our smartphones and other devices to “talk” to one another. Cars on the highway, for example, would use short-range radio signals to communicate with each other so every vehicle on the road would be aware of where other nearby vehicles are. Drivers would receive notifications and alerts of dangerous situations, such as someone about to run a red light as they’re nearing an intersection or an oncoming car, out of sight beyond a curve, swerving into their lane to avoid an object on the road.
5G IoT Applications in Industrial Automation
The key benefits of 5G in the industrial automation space are wireless flexibility, reduced costs and the viability of applications that are not possible with current wireless technology.

Industrial automation is in use today, and most likely you have seen videos showing synchronized robotics at work in factories and supply chain applications. Today these applications require cables, as Wi-Fi does not provide the range, mobility and quality of service required for industrial control, and the latency of today’s cellular technology is too high. With 5G, industrial automation applications can cut the cord and go fully wireless, enabling more efficient smart factories.
As stated by the 5G ACIA, “Industry 4.0 integrates the IoT and related services in industrial manufacturing, and delivers seamless vertical and horizontal integration down the entire value chain and across all layers of the automation pyramid. Connectivity is a key component of Industry 4.0 and will support the ongoing developments by providing powerful and pervasive connectivity between machines, people and objects.”
For example, with Industry 4.0, humans and robots will be able to interact and work together; a machine can lift heavy parts and the worker can attach them. For this to work, the robot needs to be in constant communication with the factory and its surroundings. It has to be mobile, have complete physical range of motion, and environmental sensors. These advances will enable symbiotic human-machine partnerships where each plays the role it does best.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The low latency of 5G will make AR and VR applications both immersive and far more interactive. In industrial applications, for example, a technician wearing 5G AR goggles could see an overlay of a machine that would identify parts, provide repair instructions, or show parts that are not safe to touch. The opportunities for highly responsive industrial applications that support complex tasks will be extensive.
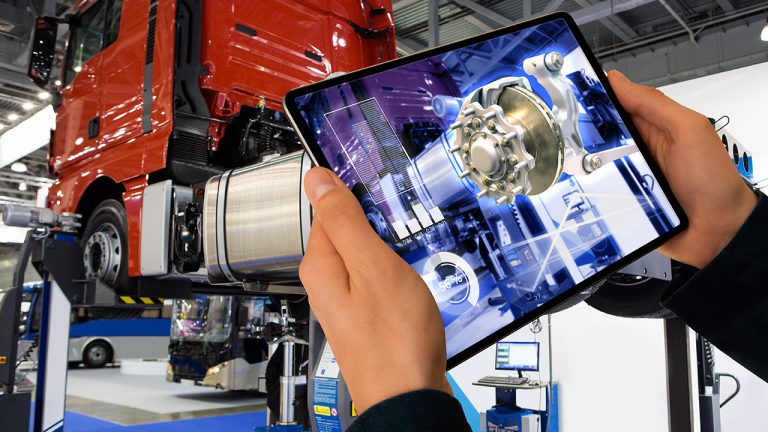

In business environments, you can have AR meetings where it appears two people are sitting together in the same room, turning boring phone or 2D video conferences into more interactive 3D gatherings.
Sporting events and experiences will likely be some of the top applications for 5G in the consumer space. Anytime you need to react quickly to a stimulus, such as in a sports training application, it must happen with minimal latency. For example, if two people wearing 4G LTE goggles were trying to kick a a soccer ball back and forth, it would be very difficult to correctly time their response, because by the time their brain has received the input that the ball has come to them, it’s too late. But with 5G goggles, the lower latency enables the receiver to see the ball and kick it back before it passes.
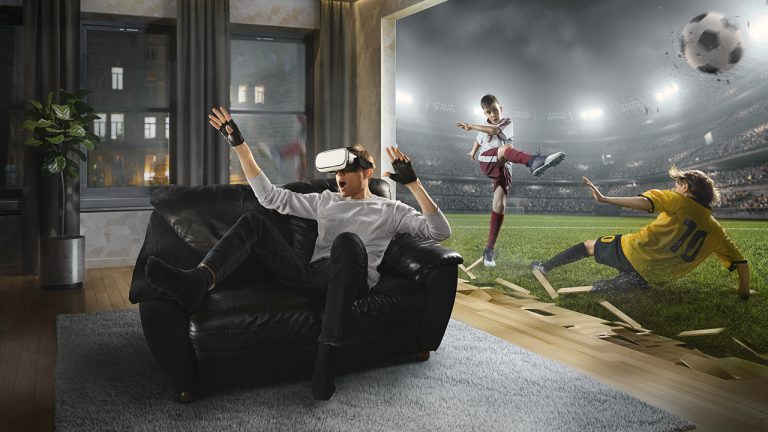

We will also see more immersive experiences with AR in sports arenas. If you have a 5G phone and AR, virtual players will welcome you and cheer you up as you walk in. And during the game, you will be able to see larger-than-life replays and player stats.
In entertainment, expect to see more hologram entertainers and greeters. For example, we will be able to bring Elvis Presley or Patsy Cline back to life via holograms. Or you can create your personal AR dance partner.
5G IoT Applications for Drones
Drones have a vast and growing set of use cases today beyond the consumer use for filming and photography. For example, utilities are using drones today for equipment inspection. Logistics and retail companies are looking at drone delivery of goods. The trend will continue, and together with 5G we will be able to push limits of drones that exist today, especially in range and interactivity.
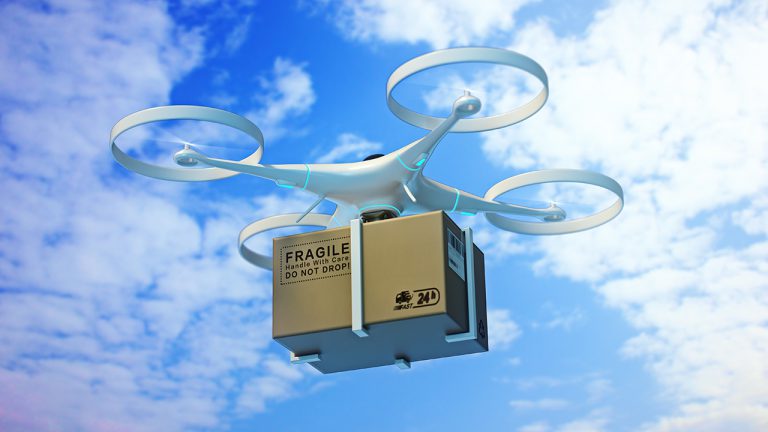

Today drones are limited to line of site and distance of the controller. If you can’t see the drone or it is out of range, you cannot see where it’s going and maintain control. With 5G, however, you will be able to put on goggles to “see” beyond current limits with low latency and high resolution video. 5G will also extend the reach of controllers beyond a few kilometers or miles. These advances will have implications for uses cases in search and rescue, border security, surveillance, drone delivery services and more.
Massive IoT Use Cases for 5G
One of the upcoming challenges of IoT will be its explosive growth. Statistica/IHS predicts that the ratio of worldwide, IoT connected devices per human on the planet will increase from the 2 per person today to 10 per person by 2025. The projected number of connected devices requiring a data connection places significant demands on the communications infrastructure – e.g. cellular towers. While 4G is addressing this need pretty well today in areas with relatively good cell density, this will improve even more with 5G.
The minimum requirements documentation for the IMT-2020 standard — the standard that is associated with 5G — requires minimum connection density of 1 million devices for square kilometer (roughly 0.38 square miles). In comparison, the 4G LPWA standard supports 60,680 devices at the same size of coverage—a far cry from what 5G can deliver.
Applications That Will Benefit from Massive IoT – Wearables and Mobile
What would trigger such a growth in connected IoT devices? Wearables, trackers, and sensors will be a big market for the Massive IoT aspect of 5G. Consider when all of your gadgets, appliances and machines you are interacting with on a daily basis are directly connected over a cellular connection, in addition to phones, tablets and laptops that are already connected today. 5G will enable far more devices to operate seamlessly (without perceived delays, dropped signals, and so on) in any given area.

High Speed Use Cases for 5G
In the high speed uses cases, we will see a range of applications that currently are hampered by slow speeds. Fixed wireless access (FWA) will provide ultra-fast Internet for consumers and businesses.
Higher bandwidth applications like 4K and in the future 8K streaming, or 360 degree video will enable high-quality, immersive experiences at real-time speeds for consumers. As the viewer you will be able to control the angle you want to take. For example in a video car race, you can look around and see who is next to or behind you.
Businesses will be able to store more information in the cloud and access it over fast, low-latency 5G as if it were stored locally. This reduces the need for expensive on-premise servers. And instead of needing a fast laptop for rendering information locally, you render in the cloud and have it streamed to you. It will be just like local but you can use your phone for these high-end apps.
5G will also change how companies think about business connectivity. Today you might have a fiber, DSL or cable modem line to connect your business for primary connectivity, and cellular backup in case your primary connection goes down. But with 5G, cellular can become your primary connection, with its high bandwidth, reliability and low latency. You won’t have to worry about building wiring and the related installation costs. With cellular, you receive the equipment, you plug it in and it works.
Summary
5G will be transformational and enable many new applications that are not viable today, particularly in urban areas and cities. 5G use cases will not be limited to a particular area: consumers, businesses, industries, and cities will benefit from one or multiple dimensions of the “5G triangle”:
- uRLLC: Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication
- mMTC: Massive Machine Type Communication (IoT)
- eMBB: Enhanced Mobile Broadband
However, instead of waiting for the fully 5G rollout, we can start building the future now with 4G LTE technology and validate applications and business models. And then refine and expand when 5G becomes more widely available.