Industrial conditions require solutions that include failure-proof industrial connectivity, industrial IoT devices and powerful remote monitoring and management. Without the most robust solutions, commercial enterprises and government entities struggle to provide continuity of critical services, which can result in costly downtime and lost productivity.
Industrial use cases for connected Internet of Things (IoT) platforms underpin many of the services and processes that play an integral role in our local and global economies — from utilities to municipal services, traffic management, mining, manufacturing and agriculture.
What is industrial connectivity and why is it so vital? Industrial connectivity refers to the integration of various connected devices, machines, sensors, and systems within an industrial environment to enable seamless data exchange and communication. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of processes, improving efficiency, productivity, and decision-making. It typically involves technologies such as IoT wireless networks, as well as cloud computing and/or edge computing, enabling industries like manufacturing, energy, and logistics to automate operations, monitor assets, and enhance overall performance.
Unlike connectivity devices located in climate-controlled environments like offices or residential buildings, industrial wireless routers are frequently placed in tough, variable environments like oil fields, factories and remote utility installations, making them difficult to access for repair or maintenance. Additionally, industrial use cases require reliable, uninterrupted connectivity in challenging environments.
Remote installations depend on solutions that are built to withstand unpredictable and even hazardous conditions. Especially in industries like oil and gas, water/wastewater management, mining and agriculture, organizations need rugged connectivity solutions with hardened enclosures designed and tested for these harsh environments.
Essential Capabilities for Industrial Connectivity Use Cases

With the right connectivity solutions, industrial organizations can implement technologies that help them achieve profit-driving digital transformation. Services like digital signage, predictive equipment maintenance and environmental monitoring can increase safety, efficiency and productivity — supporting long-term cost savings and business growth.
To achieve these industrial connectivity goals, organizations must implement an industrial IoT (IIoT) platform that can maintain reliable, stable connections despite variable or extreme environmental conditions.
Industrial organizations are recognizing the value of holistic digital transformation, turning to technology to cut operational costs, improve productivity and lower risks to on-site personnel and equipment. To achieve these benefits, these organizations are implementing IIoT solutions to improve their operations in multiple ways:
- Process automation
- Cloud and edge computing
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML)
- Green and sustainable technology
- Industry 4.0 or smart, automation-driven manufacturing
Get Our White Paper Teaser: Learn about new solutions for upgrading SCADA systems
Get Our White Paper Teaser: Learn about new solutions for upgrading SCADA systems
Download PDF
Digital Transformation at Work in Industrial Settings

The way these solutions are implemented in the field can vary significantly, depending on the specific use case, the needs of the business and the data security implications. However, what they all have critical requirements in common:
- Equipment designed for reliability and longevity. When placing industrial wireless routers in variable environments, organizations need to be confident that they’ve chosen solutions that will be able to withstand difficult and hazardous conditions. Not only does that ensure access to critical data from the field, but it also reduces the expense involved in maintenance of equipment at remote sites.
- Fast, consistent data transmission. Industrial routers can easily be connected to hundreds or thousands of IIoT devices at once. In fields like oil and gas, manufacturing, transportation and urban traffic management, millions of data points about environmental conditions or equipment performance can be generated every second. Managing devices and processes in the field requires rapid, remote visibility, which means industrial wireless routers must be designed to handle high volumes of data and have sophisticated remote monitoring and management capabilities.
- Improved operational efficiency. Ultimately, cellular routers used at edge sites need to be capable of improving operational efficiency. Often, industrial use cases for connected devices are focused on process automation that can improve productivity and decrease the risk of equipment damage, on-site accidents or injuries to workers. Organizations and the applications they deploy at the edge need ready access to data to inform applications controlling predictive maintenance, which is why reliable industrial connectivity is essential.
Multiple Verticals Require Industrial Connectivity

Robust connectivity and industrial-rated devices are required for the expected industrial sectors, as well as multiple operations in environments that experience challenging conditions:
- Industrial operations such as oil and gas, mining. Organizations in the oil and gas sector need industrial wireless connectivity and remote management solutions that allow them to continually monitor and maintain a variety of equipment in hazardous locations. Having timely data is essential for compliant operations that are safe for workers and the environment. This is also true for companies in multiple verticals with remote sites:
- Manufacturing and Industry 4.0. With the rise of Industry 4.0 processes, manufacturing organizations are building smart factories to take advantage of advances in AI/ML technologies. Deploying smart applications on the factory floor allows organizations to automate the use of industrial equipment based on control data (I/O) while eliminating the need for operator intervention.
- Traffic and safety. Another industrial use case for connected devices is smart transportation, which includes both public mass transit options like buses and subway systems as well as traffic management systems for city streets and highways. In both categories, devices deployed in these environments are subject to variable weather. These scenarios also make routine maintenance like software updates challenging, time-consuming and expensive. Robust connectivity options that support remote updates can help solve these difficulties.
- Outdoor digital signage. Outdoor signage can be an effective way to implement smart traffic management strategies, as operators can change dynamic, high-resolution content easily and often. But to use these tools effectively, the municipalities and organizations that control them need trustworthy outdoor performance, remote monitoring and management of highly distributed deployments. All these essentials depend on reliable industrial connectivity through redundant primary or secondary cellular connections.
- Kiosks, outdoor vending, and outdoor retail. Although you might think of kiosks or vending machines as something you’d find in a mall or store, point-of-sale transactions are deployed in a wide range of locations including outdoor events and pop-up retail. They can be used to track transactions and equipment or supplies used at remote industrial sites, temporary outdoor venues like festivals or for smart city metered parking, all while providing secure financial transactions with Payment Card Industry (PCI) certification.
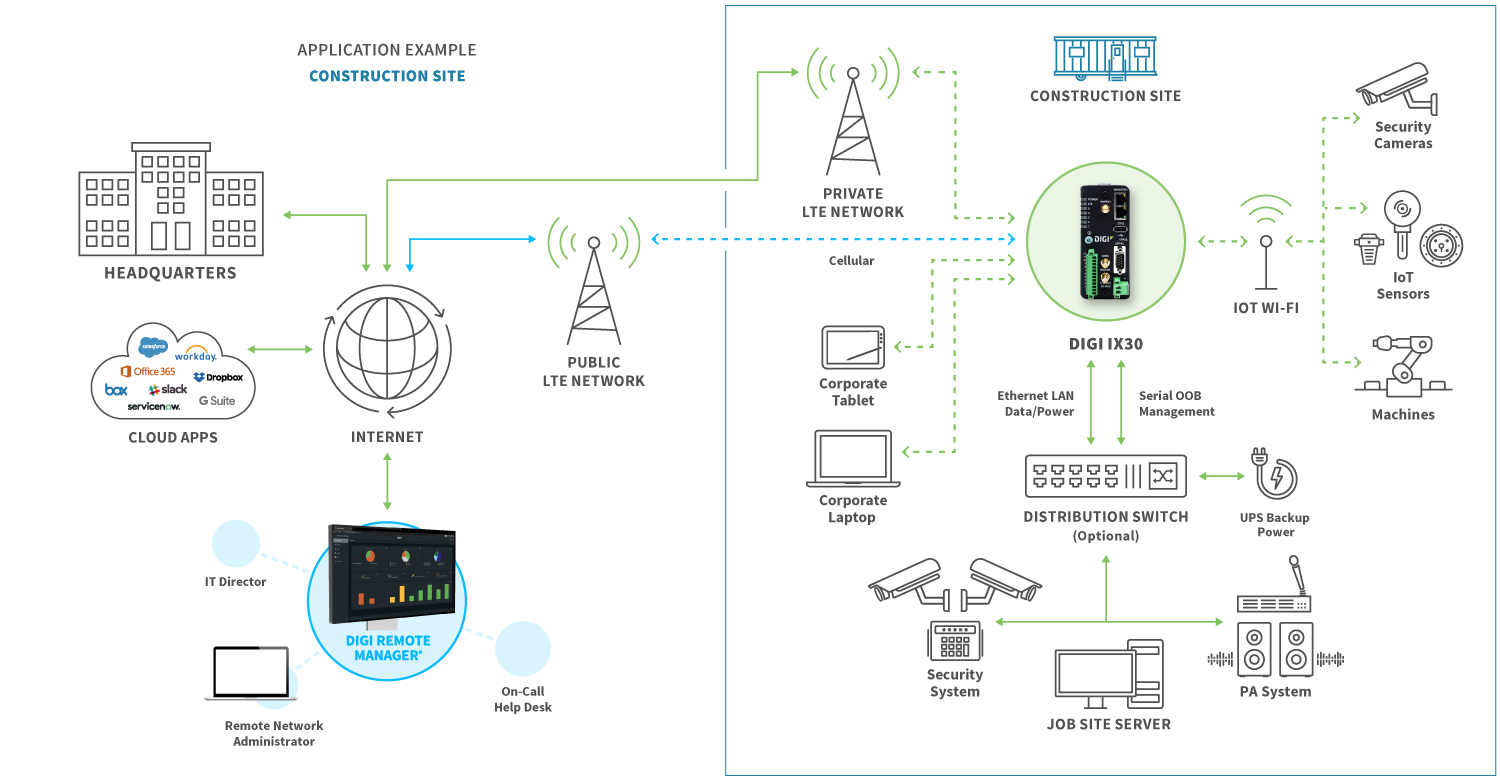
The following application diagram illustrates a configuration in the construction industry, with Digi solutions driving connectivity, cloud integration and edge computing.
Industrial Connectivity for the Harshest Environments

Maintaining reliable network connections under extreme conditions requires physically tough solutions. Features like hardened, fire-resistant and temperature-resilient enclosures and components can make a significant difference in the longevity and reliability of your organization’s routers.
To select the right options for your specific industrial use case, each organization must identify the challenges they face. Industrial cellular routers often need to withstand variable conditions where they are exposed to extreme temperatures (ranging from -20 °C to 74 °C), accidental leaks, equipment breakdowns or flammable substances, including gases and vapors.
Once you’ve identified the likely scenarios that may affect your organization's remote sites, what’s next? How can you gain confidence in the devices you deploy in these environments?
Fortunately, there are widely recognized design standards for devices that need to function in hazardous sites commonly found in industrial operations. You’ll need to find solutions that are specifically tested and rated for reliable operation in the toughest environments, and that provide the critical management and visibility tools to access your deployed devices.
Digi designs 4G LTE and 5G routers that are rated for use in Class I, Division 2 (C1D2) environments, as defined by the National Electrical Code (NEC) in the United States. Devices with the C1D2 rating can provide reliable operation under hazardous conditions. These may include:
- The presence of flammable vapors or gases under normal operating conditions.
- Other hazardous materials normally contained within closed canisters, equipment, or systems. (During abnormal conditions, such as when systems or containers fail, and leaks or ruptures occur, these materials may become exposed.)
Meet Digi’s Toughest Industrial Routers
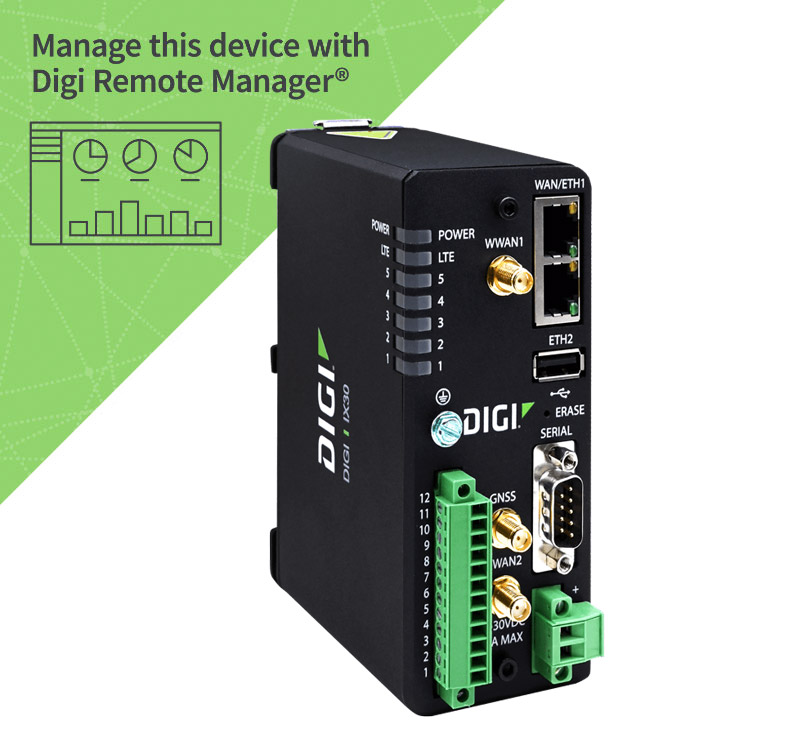 Digi's line of industrial wireless routers is growing. Digi IX30 — which can be rapidly configured, deployed and managed remotely via Digi Remote Manager® — is a rugged, robust 4G LTE cellular router in our IX family. This C1D2-certified router has an IP30-rated aluminum enclosure designed to withstand the harsh environmental conditions found in industrial use cases across verticals including manufacturing automation, oil and gas, mining, water/wastewater management, utilities, manufacturing, agriculture and the many and varied use cases that require industrial connectivity for monitoring and control.
Digi's line of industrial wireless routers is growing. Digi IX30 — which can be rapidly configured, deployed and managed remotely via Digi Remote Manager® — is a rugged, robust 4G LTE cellular router in our IX family. This C1D2-certified router has an IP30-rated aluminum enclosure designed to withstand the harsh environmental conditions found in industrial use cases across verticals including manufacturing automation, oil and gas, mining, water/wastewater management, utilities, manufacturing, agriculture and the many and varied use cases that require industrial connectivity for monitoring and control.
 Digi IX40 is an industrial 5G edge computing solution designed for the needs of utilities, oil and gas applications and Industry 4.0. This ruggedized router integrates Digi Remote Manager for remote configuration and management, and offers global 5G and LTE support, as well as certification on major carriers. With integrated industrial edge computing capabilities, Digi IX40 supports hosting of containerized applications as well as global private 5G networking deployments.
Digi IX40 is an industrial 5G edge computing solution designed for the needs of utilities, oil and gas applications and Industry 4.0. This ruggedized router integrates Digi Remote Manager for remote configuration and management, and offers global 5G and LTE support, as well as certification on major carriers. With integrated industrial edge computing capabilities, Digi IX40 supports hosting of containerized applications as well as global private 5G networking deployments.
Digi IX30 and IX40 support connections via Ethernet, serial I/O, Analog and Digital I/O. USB, and Modbus bridging and includes a GNSS receiver supporting GPS, GLONASS, BeiDou and Galileo. These solutions are available in FirstNet Capable™ models designed to meet the demands of first responders for priority, pre-emptive communications in the event of a public emergency. And they include Digi SureLink, our proprietary software that monitors router connections to ensure continuous uptime and data transmission.
An End-to-end IIoT Solution that Lets You Connect with Confidence
 Digi IX30 also offers the advantage of the Digi TrustFence® security framework, which ensures that Digi routers only connect with secure protocols, right out of the box. And if there’s ever an attempt to make unauthorized changes in your device settings, Digi Remote Manager blocks the attempted configuration change and automatically sends you a security alert, enabling you to address the problem without requiring on-site troubleshooting.
Digi IX30 also offers the advantage of the Digi TrustFence® security framework, which ensures that Digi routers only connect with secure protocols, right out of the box. And if there’s ever an attempt to make unauthorized changes in your device settings, Digi Remote Manager blocks the attempted configuration change and automatically sends you a security alert, enabling you to address the problem without requiring on-site troubleshooting.
Together, Digi Remote Manager and our full line of industrial wireless routers — which includes Digi IX10, Digi IX20, Digi IX30 and Digi IX40 — comprise an end-to-end solution for all your industrial connectivity needs. This complete solution can be fully managed from configuration to security monitoring and rapid system-wide firmware updates across the network with just a few clicks.
Simplifying Industrial Connectivity for Challenging Applications
 Today’s organizations need industrial connectivity solutions that can adapt to meet varying technology requirements, with flexible options for network redundancy, security configurations and remote monitoring and management. Digi offers robust solutions — which can all be centrally managed with Digi Remote Manager — that are designed for easy configuration, deployment and management of your industrial devices and applications.
Today’s organizations need industrial connectivity solutions that can adapt to meet varying technology requirements, with flexible options for network redundancy, security configurations and remote monitoring and management. Digi offers robust solutions — which can all be centrally managed with Digi Remote Manager — that are designed for easy configuration, deployment and management of your industrial devices and applications.
See how you can take advantage of our end-to-end industrial connectivity solutions — fully managed by Digi Remote Manager — for connectivity in the toughest, most remote environments.
Industrial Connectivity in Harsh Environments FAQ
What does “industrial connectivity in the toughest environments” mean?
It refers to deploying networking, communications, and sensor devices (routers, gateways, etc.) in extreme conditions—places exposed to heat, cold, vibration, moisture, corrosive materials, explosive atmospheres, or other hazards—while maintaining reliable operation, remote access, and data flow.
Why is rugged connectivity critical for industrial operations?
Industrial operations (e.g. oil and gas, mining, utilities, water/wastewater, traffic) often span remote sites or harsh terrain. Connectivity equipment in these settings must resist environmental stress, reduce maintenance visits, and ensure uptime. Failures or downtime in these settings can lead to costly outages, safety hazards, and lost productivity.
What capabilities and design features should industrial connectivity solutions include?
To succeed in extreme environments, connectivity solutions should have:
- Rugged hardware and enclosure: hardened enclosures, fire/temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, ingress protection
- Environmental ratings / certifications: e.g. Class I Division 2 (C1D2) certification for use near flammable gases or vapors
- Redundant and failover connectivity: primary and secondary links, multiple carriers, fallback paths
- Remote management and monitoring: ability to push firmware, monitor health, diagnose issues without physical access
- Wide temperature range support: components rated for extreme low/high ambient conditions
- Robust security: secure protocols, device identity, tamper protection — because remote sites are attack targets
What is Class I Division 2 (C1D2), and why does it matter?
C1D2 is a U.S. certification standard that indicates equipment is safe to operate in environments that may contain flammable gases or vapors under abnormal (fault) conditions. C1D2-rated routers or devices are designed to avoid ignition risks even when internal faults or external hazards occur. In industrial environments, using C1D2-rated gear is a key safety requirement.
Which industrial use cases most demand rugged connectivity?
Some of the high-demand scenarios include:
- Oil and gas / remote wells and pipelines
- Mining operations and remote extraction sites
- Water and wastewater treatment plants in rural or exposed settings
- Utilities, transmission, and distribution infrastructure
- Smart infrastructure and traffic management systems deployed outdoors
- Outdoor digital signage, kiosks, or vending machines in exposed locations
- Agriculture / precision farming across large, open fields
These use cases often require devices to function autonomously, maintain connectivity, and survive harsh weather or physical stress.
How should organizations approach selecting connectivity hardware for these environments?
- Assess site hazards: Identify temperature extremes, exposure to chemicals, explosive gases, dust, moisture, vibration, etc.
- Choose rated devices: Select gear certified for the environment (e.g. C1D2, IP ratings, etc.)
- Plan for connectivity resilience: Use multiple carriers, redundant paths, cellular fallback, or hybrid links
- Ensure remote management: Pick equipment compatible with remote monitoring platforms so updates, diagnostics, health checks can be done remotely
- Ensure modular interfaces: Support Ethernet, serial, I/O, USB, and bridging to accommodate legacy systems
- Plan for security: Ensure devices include robust security frameworks, identity, and firmware protection from day one
What are the benefits of deploying rugged industrial connectivity in harsh settings?
- Reduced site visits and operational cost: Remote management reduces the need for on-site staff in hazardous zones
- Higher uptime and reliability: Robust systems resist failures under environmental stress
- Faster data-driven decisions: Continuous connectivity supports real-time monitoring, analytics, and control
- Safer operations: Fewer in-person interventions in dangerous settings
- Scalability and flexibility: Once rugged connectivity is in place, adding sensors, endpoints, or new applications becomes easier
Connect with Digi
Seeking next-generation solutions and support? Here are some next steps:
Note: This blog post was first published in August, 2022, and updated in June, 2025.