What do mining operations, wind and solar farms, construction operations and manufacturing facilities have in common? They are just a few of the many complex environments that depend on robust, secure and cost-effective IoT connectivity to keep track of valuable equipment location and status and prevent equipment failures before they occur and cause business downtime. Specifically, IoT asset monitoring and predictive maintenance solutions work together to provide real-time insights and notifications when equipment and other assets are on the move, are not operating properly, or begin to show signs of failure.
Digi supports industrial asset management and predictive maintenance use cases with high-performance connectivity solutions and remote monitoring and management tools that integrate with business intelligence and cloud software to provide comprehensive, robust asset tracking, monitoring and maintenance solutions. Let’s talk about these systems and how IoT connectivity and remote management solutions support them.
What Is Asset Monitoring?

Asset monitoring can be defined as remotely tracking the location and condition of equipment in a factory, warehouse, or industrial site using connected hardware and software. For example, in the case of manufacturing operations, assets might include equipment, parts and production lines. The industry is on the rise with the adoption of the Internet of Things. In fact, the IoT asset monitoring market in the manufacturing industry is projected to grow to $1.52 trillion by 2030.
How Does Asset Monitoring Work?
Sensors are at the core of asset monitoring. Depending on the application, sensors measure everything from location and speed to vibrations or temperature in the operating environment. Using IoT connectivity, sensor data is processed and transmitted to a cloud solution or processed at the network edge wherever assets are deployed. Remote global teams can then use this data to monitor equipment in or near real-time. These same technologies can even remotely send firmware, security and functionality updates to equipment without disrupting normal operations.
As network speed and other technologies advance, these applications increasingly take advantage of AI and Machine Learning capabilities to utilize this data for automated decision making.
Why Do We Need Asset Monitoring?

Any industry that requires complex machinery and systems as part of its infrastructure or operations can benefit from IoT asset monitoring. In the manufacturing industry, asset monitoring and predictive maintenance can reduce unplanned downtime. With the cost of unplanned downtime ten times higher than planned downtime, the value is obvious.
The wind energy industry is another great example. According to the Global Wind Energy Council Global Wind Report 2021, new wind capacity in 2020 increased by 53 percent over the previous year. With unscheduled downtime accounting for over 60 percent of land-based turbine operation and maintenance costs and continued industry growth, asset monitoring of these complex systems is essential.
A great example of asset monitoring in action comes from Eaton, a power management company that offers solutions for effectively managing electrical, hydraulic and mechanical power more efficiently, safely and sustainably. Eaton tapped Digi to design a predictive monitoring system to predict hydraulic hose failure before it occurs. By proactively monitoring the health of the hydraulic hoses on widely deployed assets, Eaton not only avoided costly unscheduled repairs, but they also extended visibility into their customers’ machine assets.
What Is Meant by Asset Tracking?
Asset tracking helps companies keep tabs on high-value equipment in real time, who is using it and how it is being handled. It is especially useful in industries that manage large amounts of equipment such as in construction and farming operations.
For example, IoT enabled asset tracking can streamline supply chain performance. Businesses can reliably track asset and inventory location and condition, providing real-time updates to help prevent equipment failures, asset loss or poor handling.
Asset Tracking Uses
Asset tracking and monitoring enables the management of equipment and company assets, regardless of their location. Use cases include:
- Integrating GPS into products, equipment and transportation for more accurate IoT asset tracking and monitoring
- Improving production line, distribution processes and transportation route efficiency
- Enhancing predictive maintenance based on patterns identified from supply chain data collection over time
- Performing critical asset monitoring for high-value and mission-critical assets using IoT connectivity and management software
What Is the Difference Between Asset Tracking and Asset Management?
Beyond asset management tracking to monitor the location and usage of assets such as fleet vehicles or farm tractors, asset management refers to the overall software system that controls information about the assets. Industrial asset management tools help companies manage maintenance schedules, audits, purchase information, end-of-life equipment disposal and more.
What Is the Best Way to Monitor Assets?
There are several technologies that support key business objectives, including remote asset monitoring in industrial applications, IT asset management for enterprises, and asset monitoring and control in hospitals and the healthcare industry. These include:
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) – Tags that store and communicate information about an object or inventory, including location information
- Global Positioning System (GPS) – Devices that transmit through cellular networks or satellites and can be integrated into equipment and tracked through software
- Barcode – A label that is physically attached to an object and scanned with a mobile device
- Bluetooth Low Energy – A short range wireless technology that can exchange data with nearby devices
- Near Field Communication (NFC) – Two-way communication capability commonly used in mobile wallet and other contactless payment systems
IoT Asset Monitoring Benefits:
- The IoT enables smart asset monitoring and remote inspections, which replace or reduce on-site visits. Sending truck rolls out to monitor assets or identify problems can be time-consuming, costly, and hazardous to workers.
- IoT sensors can measure almost any aspect of the system, which can be input into asset management applications for predictive maintenance.
- Continuous monitoring increases system reliability by reducing unplanned downtime.
- Asset monitoring significantly reduces costs of unplanned failure.
What Is Predictive Maintenance?

Predictive maintenance is a critical part of IoT asset monitoring. For a predictive maintenance definition, think of a system of sensors and intelligent edge devices that identify anomalies and predict system failures before they happen, then alert operators so that service personnel can perform preventive maintenance.
How Does Predictive Maintenance Work?

Predictive maintenance technology monitors equipment status and performance in real time, analyzes sensor data and compares it to normal operational data in order to identify potential problems in advance. This allows operators to schedule maintenance around production schedules so as not to disrupt normal operations. The results are improved maintenance practices, reduced costs and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Traditional methods can be very expensive because operators can miss clues that equipment is malfunctioning. Manual equipment checks often require multiple trips to remote sites. By contrast, an automated predictive maintenance solution uses sensors to monitor and detect irregularities 24/7/365, and the system sends an alert that a problem is developing. Repair teams can then troubleshoot and fix an issue before the end customer is even aware of the problem.
Increasingly, AI and Machine Learning play a key role in creating a seamless and automated workflow that improves speed, efficiency, reliability, while also moving toward full automation and the promise of Industry 4.0.
What Are Examples of Predictive Maintenance?
Let’s look at some predictive maintenance IoT examples. Wind and solar energy make up valuable parts of the renewable energy equation. During the summer of 2022, the U.S. reached an important milestone by generating 20 percent of power from wind and solar. As the world transitions toward renewable energy, availability and reliability become crucial as they increasingly contribute power to the grid.
Unplanned failures can create production outages while new parts are ordered, leading to thousands of dollars of lost energy per day. If unplanned failures occur during times of peak demand, blackouts could leave citizens without power at a time when they might need it most – like increased air conditioning usage during a heat wave. As summers become longer and hotter due to climate change, this situation is likely to continue.
Predictive maintenance also reduces costs. According to U.S. Department of Energy research, a predictive maintenance solution can create savings of up to 40 percent over reactive maintenance.
For Otis elevator, with over 2.1 million elevators in operation globally that move one billion people every day, predictive maintenance delivers optimal customer service. Otis’ IoT solution rapidly detects issues and sends data to the cloud where it can be distributed to applications utilized by customers and field technicians. By proactively learning about potential issues before its customers experience problems, Otis’ 30,000 field technicians can conduct maintenance that prevent elevator service disruptions.
Other Predictive Maintenance Examples
- Manufacturing – IoT connectivity fuels predictive maintenance in manufacturing and supply chain applications, and is improving quality, uptime and worker safety
- Railway sector – The railway sector employs predictive maintenance to detect problems with assets and track irregularities
- Oil and gas industry – IoT connectivity allows predictive maintenance on facilities not easily accessible, especially in remote, offshore and deep-water locations
- Mining operations – Mining operations save millions of dollars in lost revenue by avoiding unexpected conveyer belt failure while transporting rock over long distances
What Is the Difference Between Preventative and Predictive Maintenance?
While both methods are proactive approaches to maintenance, there are specific differences between the two. Preventative maintenance is scheduled, routine maintenance performed on equipment periodically to minimize failures, whether the equipment is functioning properly or not. Preventative maintenance is usually based on time or usage over the expected lifespan of the equipment. Predictive maintenance isn’t based on a routine schedule.
Instead, predictive maintenance uses asset condition monitoring to predict a failure before it happens. Then, maintenance can be scheduled before a failure occurs. Ultimately, a combination of both approaches works best to reduce the potential for unplanned maintenance.
What Is the Next Step to Implementing IoT Asset Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance?
Whether your goal is to create better customer experiences, reduce unplanned maintenance costs, obtain better insights into your equipment location and usage, IoT asset monitoring and predictive maintenance solutions can help. The right technology partner can make predictive maintenance and asset monitoring solutions seamless while also significantly reducing the time to impact and investment required. Digi is your technology partner.
How Digi Can Help
Digi solutions provide the robust, secure connectivity and remote monitoring tools needed to deploy asset management and predictive maintenance applications anywhere across the globe, with visibility and control at your fingertips.
Digi offers a full suite of equipment, devices and remote management tools to conduct asset monitoring, gain insights and conduct predictive maintenance on critical assets, whatever your industry. And Digi’s solutions readily integrate with business intelligence applications from asset tracking IoT companies and system integrators.
Digi Solutions for Asset Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Here is an overview of some of the Digi solutions and services available to help you deploy complete asset monitoring and preventative maintenance solutions for your operation.
Digi Remote Manager
Digi Remote Manager® (Digi RM) is the command center of your distributed network. It keeps tabs on your devices and provides automated notifications and security monitoring (preventing intruders from changing device configurations) and enables IT and system managers to control and update large numbers of devices quickly from a dashboard.
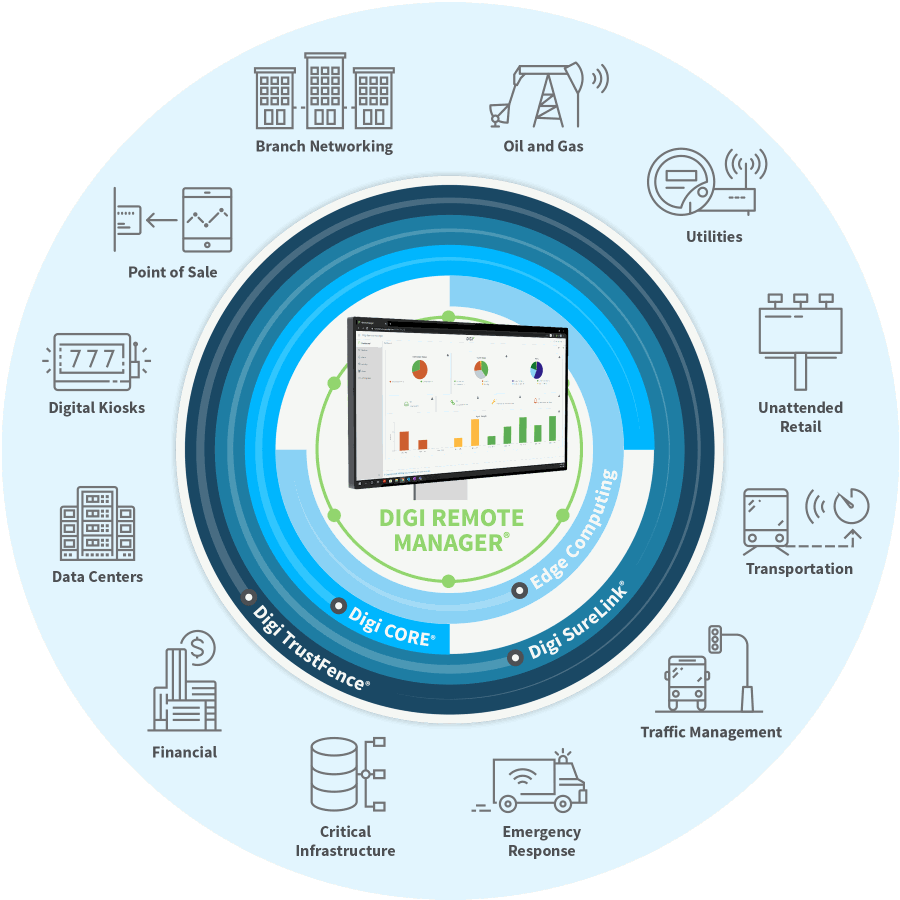
In addition to managing Digi devices, Digi RM provides a console for 24/7 remote access and out-of-band management of any serial-based devices on the network. Quickly and easily integrate Digi RM with third-party cloud services such as Microsoft Azure, AWS and the Google Cloud Platform. Digi RM can act as facilitator between edge devices such as cellular radios, gateways and routers and many different third-party services. It can then simplify the ability to get your data where you want it to go. Add edge intelligence, reduce latency and enhance your network efficiency.
Digi Cellular Solutions
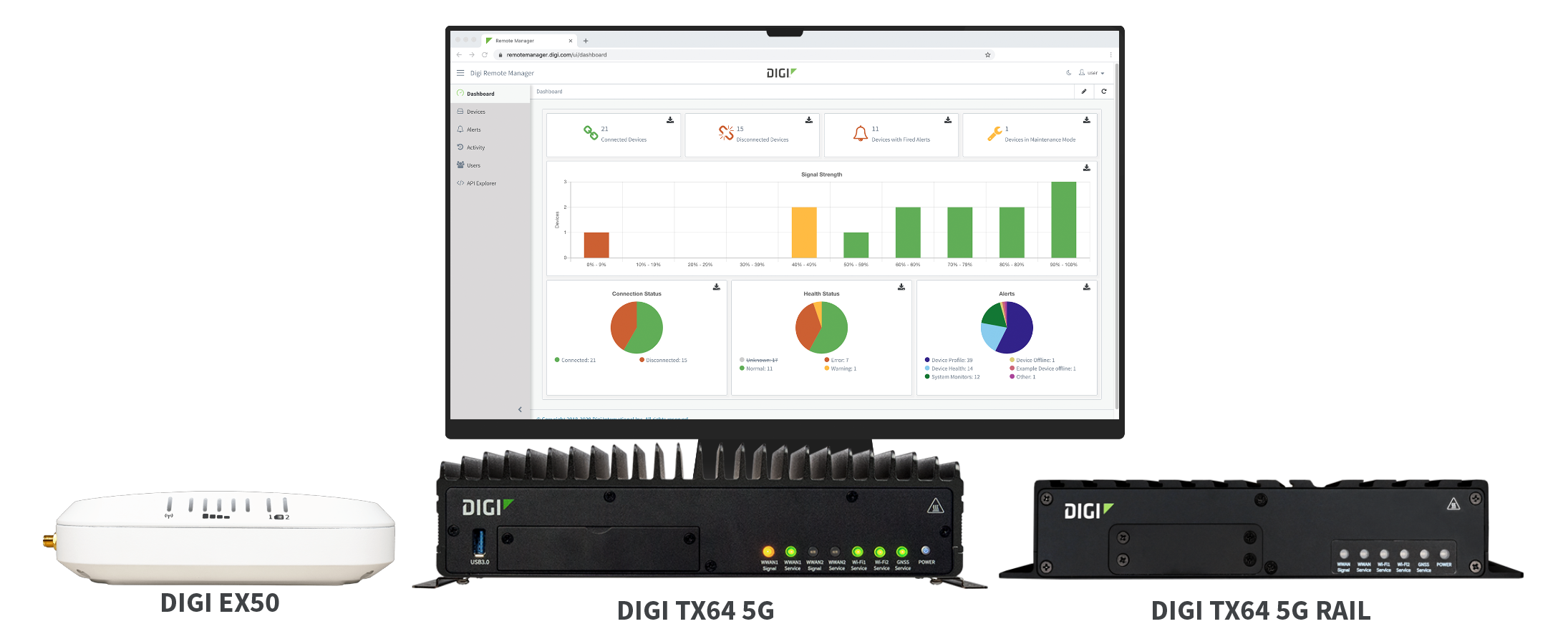
Digi cellular routers and extenders provide enterprise and industrial connectivity for any connected application, anywhere. Enterprise routers provide connectivity for indoor and light industrial applications. Industrial connectivity solutions meet the needs of applications in challenging and hazardous environments.
With the advances in network speed and the technologies associated with digital twins and Industry 4.0, Digi offers industrial 5G router solutions including Digi IX40 that support mission critical use cases in manufacturing automation, with mission-critical speed and edge intelligence.
Digi also offers transportation connectivity for traffic management, public transit and heavy rail applications, for asset tracking and predictive maintenance. Our cellular routers are fully integrated solutions, dedicated to supporting the most mission-critical needs, with rapid deployment, secure edge computing capabilities, and highly resilient connections.
All of these solutions integrate Digi RM for remote monitoring, firmware updates, functionality enhancements and out-of-band management.
Digi Embedded Solutions
Digi's extensive offering of embedded solutions for developers and system integrators include:
Sensor Connectivity
 Digi Connect Sensor enable applications to gather data from sensors and route it to cloud-based apps via Digi Axess.
Digi Connect Sensor enable applications to gather data from sensors and route it to cloud-based apps via Digi Axess.
User-friendly interfaces allow you to automate and rapidly deploy across many industrial applications.
Serial Connectivity and Infrastructure Management
Digi offers a wide range of connectivity solutions for IT asset management, as well as connectivity and management of remote devices with a wide range of protocols.
These include USB connectivity solutions such as Digi AnywhereUSB® Plus, which provides secure, flexible and scalable connectivity for peripherals and handheld assets anywhere on a Local Area Network (LAN) via Ethernet or Wi-Fi without a locally-attached host computer.
Digi's infrastructure management solutions also include serial device servers like the Digi Connect® EZ family, which supports robust secure access and management for servers, network devices and critical equipment.
Next Steps