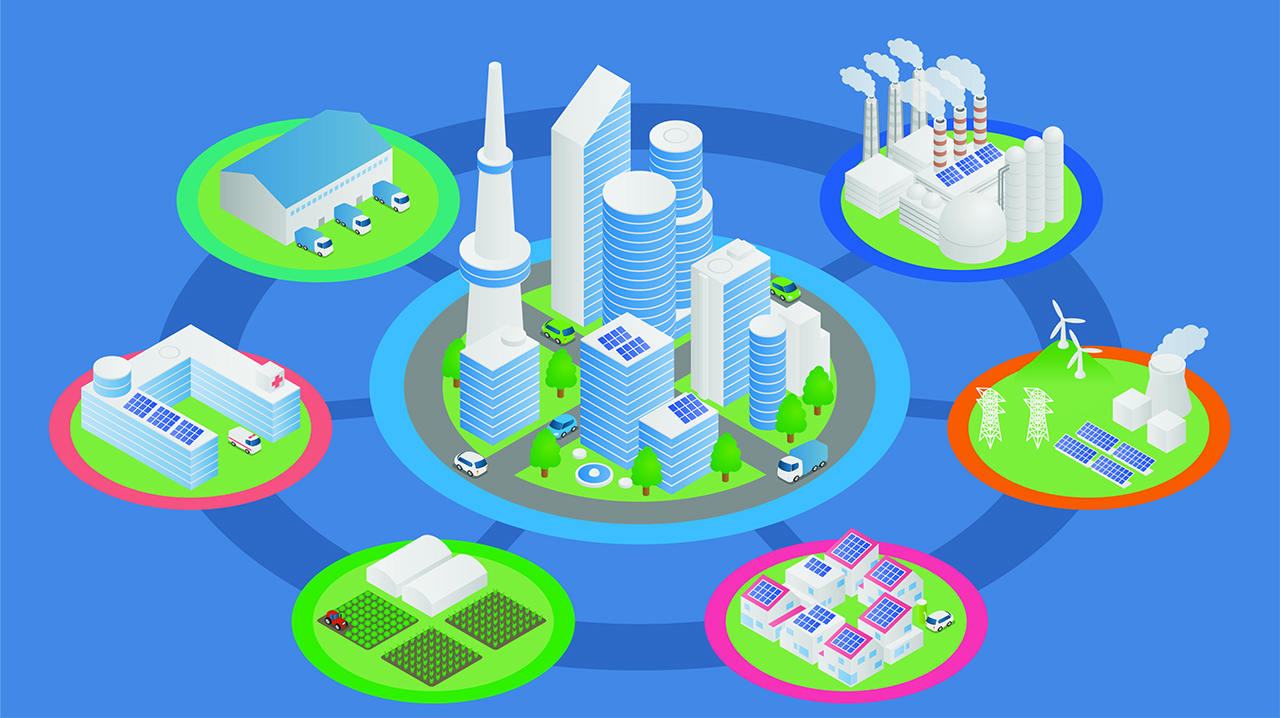
Welcome to the IoT smart city — where connected devices are driving massive change. More than ever, cities must meet numerous challenges — from reducing traffic congestion and managing sanitation and waste to protecting the environment and reducing energy consumption. That’s why, across almost every aspect of the modern municipality, the Internet of Things (IoT) is playing an increasingly important role in industrial applications, public transit, public safety and emergency services, city lighting, and other applications.
IoT and smart cities go hand-in-hand today, with sophisticated IoT technology enabling municipalities to leverage connectivity and data-driven intelligence in everything from smart buildings to connected vehicles and EV charging stations, to rideshare, public transit and municipal utilities. IoT for smart cities enables urban centers to increase the efficiency of their infrastructure, improve reliability and responsiveness of emergency services, improve urban livability, cut costs and more. We can expect to see many more instances of the application of IoT in smart city initiatives.
The Market for IoT in Smart Cities
According to Expert Market Research, the global smart cities market was valued at approximately US$1.14 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow to US$4.14 trillion by 2032 – a CAGR of 15.3%. What’s more, the smart infrastructure segment of this market — including smart grids, energy management systems, water management systems, and waste management solutions — accounted for more than 35% of the market share in 2023.

Key Drivers for IoT Applications in Smart Cities
What’s driving investments in the application of IoT in smart city initiatives?
- Cost is a significant factor driving the shift from wired to wireless solutions due to the high expense of installing and maintaining landlines. Moreover, declining cellular data plan costs, along with enhanced wireless communication capabilities, are enabling previously cost-prohibitive use cases.
- Efficiency also plays a critical role. Wired solutions often require on-site visits for infrastructure audits and maintenance, leading to costly and inefficient "truck rolls." In contrast, wireless communications allow for remote monitoring and management of IoT deployments, enabling firmware updates, security patches, and automated issue notifications.
- Resource reduction is another key motivator, particularly in applications like smart street lighting and asset monitoring. These IoT smart city solutions utilize sensors and wireless modules to control resource use, significantly reducing energy consumption.
- Smart energy usage and sustainability are crucial as cities seek new and efficient ways to reduce resource consumption, lower carbon footprints, and enhance urban operations. These practices promote long-term environmental health and cost savings, ensuring cities remain livable and resilient.
The IoT Infrastructure for Smart Cities
A scalable, secure, and future-proof IoT infrastructure for smart cities encompasses a range of hardware and software components.
- Sensors — Across the IoT smart cities landscape, sensors capture massive numbers of data points for automation, decision making, reporting and compliance. These include:
- Environmental sensors in smart cities monitor air quality, noise, temperature, and other conditions in real time to enhance public health, optimize urban planning, and support data-driven decision-making.
- Traffic sensors in IoT smart cities applications monitor vehicle flow, congestion, and speed in real time to optimize traffic signal timing, reduce delays, improve road safety and pedestrian safety, and reduce emissions.
- Utility sensors enable real-time monitoring of water, gas, and electricity usage to detect leaks, prevent outages, and support efficient resource management in smart cities.
- Surveillance sensors such as cameras and motion detectors improve public safety by detecting security threats or unauthorized activities.
- Infrastructure sensors monitor the conditions on bridges, roads, and buildings to identify structural issues and prevent failures.
- Parking sensors can detect the availability of parking spaces to reduce the time and emissions associated with searching for parking.
- Connectivity — By leveraging cellular, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi-enabled devices, smart city infrastructure delivers intelligence and insights — enabling coordination of services and agencies, as well as waste reduction, and enhanced operational efficiency.
- Instrumentation — Using rule-based conditions and sensor alerts, smart city operations can remotely and automatically activate infrastructure such as opening gates and viaducts, reconfiguring traffic light patterns, modifying street lighting, and more.
- Data repositories — A central database (e.g., a data warehouse or data lake) stores transactional data and performs sophisticated analyses, enabling predictive models that leverage AI and statistical algorithms to identify patterns and correlations.
- Central management — A sophisticated management application enables administrators to remotely and centrally provision, diagnose, troubleshoot, and repair connected devices across the municipality — such as cellular routers deployed at intersections for traffic monitoring and V2X applications.

IoT and Smart Cities in Action
Smart cities IoT initiatives span everything from traffic management to public transportation to city lighting and more. Let’s look at some examples from Digi’s customer deployments.
Public Transit

Transit systems are an ideal use-case for IoT smart cities applications, which can significantly reduce costs, strengthen safety, optimize routes, and enhance the rider experience.
Many municipalities, previously facing declining ridership, now see growth thanks to enhanced visibility into bus and rail routing, as well as improved passenger Wi-Fi connectivity, utilizing dual-cellular 5G transportation routers. By analyzing embedded sensors, transit operators can identify public usage patterns, ensuring safety, and improve timeliness.
Digi IoT Smart City Transit Solutions in Action
- TriMet (Tri-County Metropolitan Transportation District of Oregon) operates a fleet of over 700 buses on 85 routes with thousands of stops across the Portland metro area. A Digi TX64 transportation router on each bus, managed by Digi Remote Manager, enables TriMet to utilize CA/AVL technology and perform electronic fare collection, among other connected applications. Additionally, Digi routers power the agency’s award-winning Transit Signal Priority initiative to optimize bus routing, expand capacity, and improve the rider experience.
- With Digi Remote Manager paired with Digi’s purpose-built transportation routers mounted on hundreds of buses, Pittsburgh Regional Transit gives riders have real-time information about schedules, location, and passenger density information, as well as free Wi-Fi service — all part of the goal to improve public transit ridership.
- In Greater Boston, the Massachusetts Bay Transit Authority (MBTA), one of the world’s largest and longest-running transit agencies, refuels, cleans, inspects, and periodically maintains more than 1,000 buses in an organized, methodical, and documented way. That’s courtesy of S&A Systems’ Fleetwatch, a powerful hardware/software solution – driven by a Digi XBee 3 Zigbee 3 RF embedded module on each bus that connects via 2.4 GHz to transmit and receive data. The result: reliable and accurate, real-time control and data acquisition for vehicles, employees, fuel/fluids, and tank monitor systems.
Read more about smart city IoT applications for busing and light rail in our customer stories.
Smart Traffic Management
 With IoT sensors in vehicles, smartphones and traffic lights as well as roadway cameras, cellular transportation routers can collect data about traffic conditions, congestion, and accidents and help identify longer-term patterns based on time of day and time of year.
With IoT sensors in vehicles, smartphones and traffic lights as well as roadway cameras, cellular transportation routers can collect data about traffic conditions, congestion, and accidents and help identify longer-term patterns based on time of day and time of year.
These sophisticated solutions enable traffic management teams to re-route traffic to prevent or resolve unexpected congestion spots and improve public transit and emergency vehicle routing.
A Digi IoT Smart City Traffic Management Solution in Action
- The New York City Department of Transportation oversees one of the most complex urban transportation networks in the world, with 6,300 miles of streets and highways, over 12,000 miles of sidewalk, nearly 14,000 signalized intersections and 800 bridges and tunnels. Through a collaboration of multiple vendors and agencies, the city upgraded its citywide traffic system using Digi Remote Manager® (Digi RM), a Digi dual cellular router at each intersection, and customized Digi software and services. This large-scale deployment was completed in nine months and under budget.
Download our Solution Brief
Learn about intelligent transportation and emergency preparedness
Download PDF
Water Management
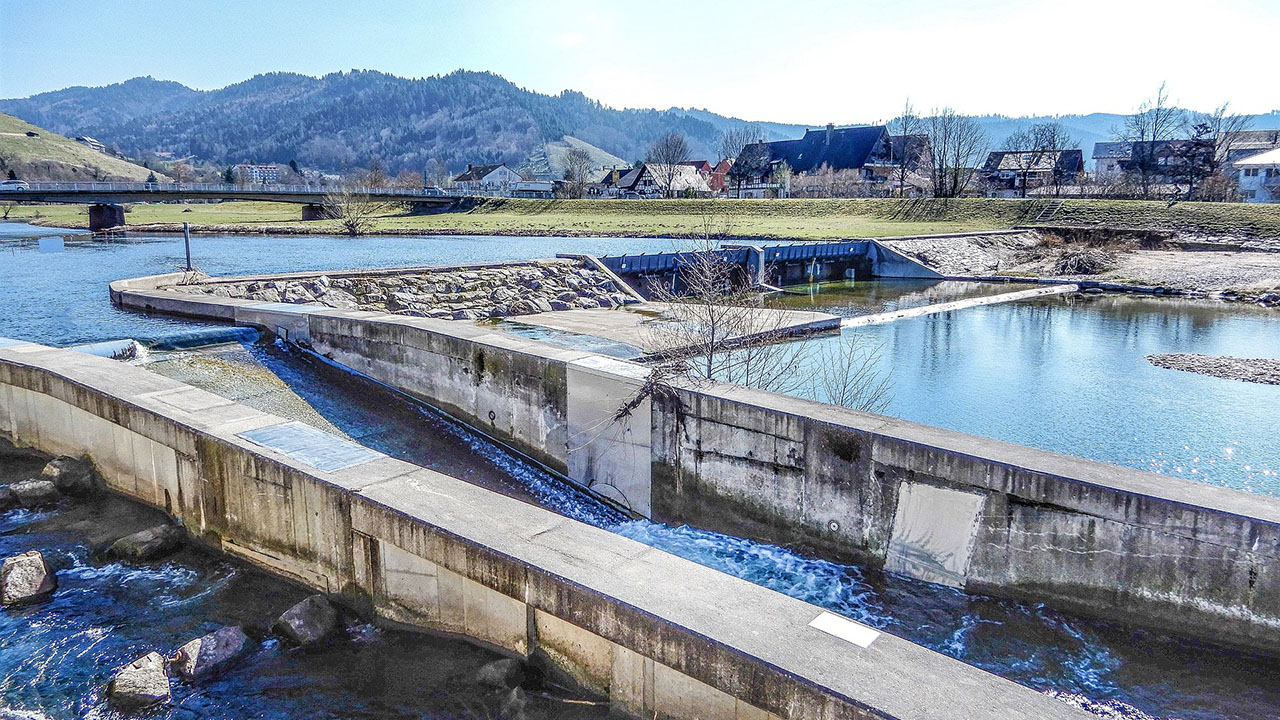 Water management is a high-priority activity, and the IoT is playing an increasingly important role in IoT smart cities initiatives.
Water management is a high-priority activity, and the IoT is playing an increasingly important role in IoT smart cities initiatives.
Governmental organizations and local municipalities need to upgrade aging infrastructure with high-performing industrial cellular routers and infrastructure management solutions, increase efficiency, improve visibility into remote tanks and water management processes, and reduce the cost of monitoring and servicing their assets.
Digi IoT Smart City Water Management Solutions in Action
- In Georgia, the Augusta Utilities Department provides water and sewer service across 230 square miles for a population of more than 160,000 – including approximately 1,200 miles of water mains. Digi Connect® Sensor XRT-M helps keep a careful eye on this vital infrastructure, bringing intelligence, visibility, and efficiency to the crucial monitoring and maintenance processes.
- Across North America and the Pacific, Brown and Caldwell deploys creative solutions to help municipalities, private industry, and government agencies successfully overcome challenging water and environmental obstacles. Using Digi Remote Manager and Digi Connect Sensor XRT-M, the firm brings greater insights and innovation to water infrastructure.

Waste Management
IoT solutions in smart cities enhance waste management through real-time monitoring and data analytics. Wireless sensors and cellular connectivity devices enable cities to track waste levels in bins, optimize collection routes, and reduce operational costs. This ensures timely waste removal, lowers fuel consumption, and minimizes environmental impact.
A Digi IoT Smart City Waste Management Solutions in Action
- Through its iSmart IoT system, Metro Compactor Service Inc. helps its municipal customers proactively manage and extend the life of their waste equipment infrastructure, ensuring productive and efficient operations. Digi industrial cellular routers and Digi RM play a critical role by keeping equipment connected at all times. That translates into fewer compactions, less energy usage, lower maintenance, and fewer instances of frustrating over-capacity situations.
See more water management and wastewater management solution stories in our customer case studies.

EV Charging
The infrastructure for smart city IoT solutions enables efficient electric vehicle (EV) charging networks. Wireless connectivity, sensors, and remote management platforms all combine to enable cities to monitor and manage EV charging stations in real-time. This ensures optimal energy distribution, reduces downtime, and prevents overloading of the power grid.
Additionally, data analytics help cities plan the strategic placement of charging stations, ensuring accessibility and convenience for citizens. These solutions support the growth of sustainable transportation, reduce carbon emissions, and contribute to a more efficient, future-ready urban infrastructure.
Digi IoT Smart City EV charging Solution in Action
- FLO, Canada’s largest EV charging network, operates a comprehensive charging ecosystem that meets drivers’ needs wherever they are — at home, at work or on the go. Its stations rely on Digi XBee wireless modules, as well as industrial cellular gateways and embedded system-on-modules. FLO has sold more than 80,000 charging stations across North America and its network enables more than 1 million monthly sessions.

City Lighting, Digital Signage and Cameras
Lighting, signage and security cameras are some of the best examples of implementing IoT applications for smart cities, and many municipalities today are turning to wireless communications for efficiency, cost savings and energy reduction.
Digi solutions for city lighting, digital signage and security applications can incorporate a range of solutions, depending on the specific application. One organization, for example, developed a smart pole, using ruggedized Digi industrial cellular routers, which provide drop-in connectivity and data routing for multiple device nodes on the smart pole. Cities can also use embedded solutions like Digi industrial cellular gateways paired Digi XBee® modules. These solutions offer complete flexibility to support a range of applications:
- LED lighting controls
- Surveillance cameras
- Environmental sensors
- Electronic billboards
- Charging stations
- Wi-Fi coverage
Digi IoT Smart City Lighting Solutions in Action
- Dimonoff, an innovator in wireless controls and remote-monitoring technologies for street and area lighting, combines embedded hardware and back-end management software into a solution designed to reduce energy consumption, lower operating and maintenance costs and increase citizen safety. By integrating Digi XBee DigiMesh 2.4 modules into their solution, the company creates a secure mesh network that communicates with a master control center for data logging and scheduling. This enables administrators to configure and control streetlights through sensors, switches, or remotely. The system tracks real-time fixture data, including power consumption, voltage, current, power factor, and operating status, and issues automated alerts.
- In Chile, Sicom Electronics offers municipalities CityMesh®, a scalable smart cities network to intelligently control thousands of streetlights and traffic lights with greater precision. The result: lower costs, a better eco-footprint, and greater citizen safety. Digi XBee® RF modules provide the wireless connectivity to make it happen.
- Using Digi connectivity hardware, Owlet Nightshift — developed by Schréder and headquartered in Mainz, Germany — enables cities to retrofit aging lighting infrastructures with long-lasting intelligent technology. Each intelligent light is equipped with a high performance LED array and a Digi XBee ZigBee module. Digi XBee modules allow groups of lights to form a ZigBee Mesh network that connect to a cellular WAN through a Digi cellular gateway.
Smart Buildings
A smart building uses advanced technology and IoT devices to automatically control and optimize various building systems, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, and more. These systems are interconnected and can be managed centrally, often through cloud-based platforms, to enhance efficiency, comfort, security, and sustainability.
Digi IoT solutions provide edge computing, reliable connectivity, scalability, security, and cloud integration. That lets you collect data and monitor conditions in real time, automate and control building systems, reduce energy consumption, strengthen security and safety, and enhance occupant comfort.
Digi IoT Smart Building Solutions in Action
- NuOz helps building administrators manage their energy usage in real time, with continuous access to energy metrics that help them make timely decisions to reduce costs, improve operational efficiency, and strengthen their commitment to sustainability goals. To meet these goals NuOz selected Digi enterprise cellular routers and Digi Remote Manager for connectivity and management of sensors in current transformers on building electric panels. This enables them to collect precise data at the circuit level. Those sensors communicate via LoRaWAN® to a local server gateway where the data is aggregated and backhauled through the cloud to NuOz servers where customers can browse and drill down on usage metrics and trends.
- Infinitum Electric is aiming to reinvent the electrification landscape with its patented PCB stator technology that creates smarter, lighter, quieter and more environmentally responsible electric motors and generators. Digi XBee® cellular modems play a key role in that mission as the company targets major opportunities in HVAC systems that offer superior efficiency and durability.

Utilities, Smart Grid and Smart Metering Applications
Smart grids utilize Digi's reliable and secure solutions, including industrial connectivity and edge computing routers, to optimize energy distribution, integrating renewable sources and responding dynamically to demand. Smart metering, powered by Digi's secure networking devices, provides real-time data on energy usage, enabling efficient resource management and personalized consumer insights. These technologies not only enhance energy efficiency but also support sustainability goals, reduce operational costs, and empower citizens with greater control over their energy consumption, making smart cities more resilient and environmentally friendly.
Digi IoT Smart Energy Solutions in Action
- E-GEAR’s proprietary Energy Management Controller (EMC). This device uses a range of voltage and current-measurement sensors to monitor and control the storage of solar power into a local battery and then subsequently manages the release of that energy into the residence or back into the electrical grid in the smooth, controlled manner that utilities desire. With this smoothing function, entire neighborhoods can act as distributed generation and storage sources for the electrical utility. This reduces the utility’s need for excess generation capacity and variances in voltage on the grid. Digi Remote Manager provided E-GEAR with a highly functional cloud interface right away. And the way the EMC leverages Digi system-on-modules, also accelerated the hardware and software development.
- Digi designed a completely new, custom software application to meet the requirements of E-DeMa a joint pilot project between SWK, RWE, Siemens, Miele, ProSyst, the universities of Bochum, Duisburg/Essen and Dortmund and the University of Applied Sciences and Arts, Dortmund. This creates a sustainable model for utility companies to employ that allows consumers to become active participants in the market by controlling their consumption. The communication links between all the components and the consumers in the project are managed by the Digi Extended Grid Solution platform, which utilizes Digi Remote Manager and Digi cellular gateways.
- ElectriCities of NC, a not-for-profit organization, provides a range of technical services to support power services throughout North Carolina, South Carolina and Virginia. Moving away from outdated network infrastructure (T1 and 56k modems), ElectriCities selected Digi industrial cellular routers because they provided the right combination of reliability, security, control and flexibility.
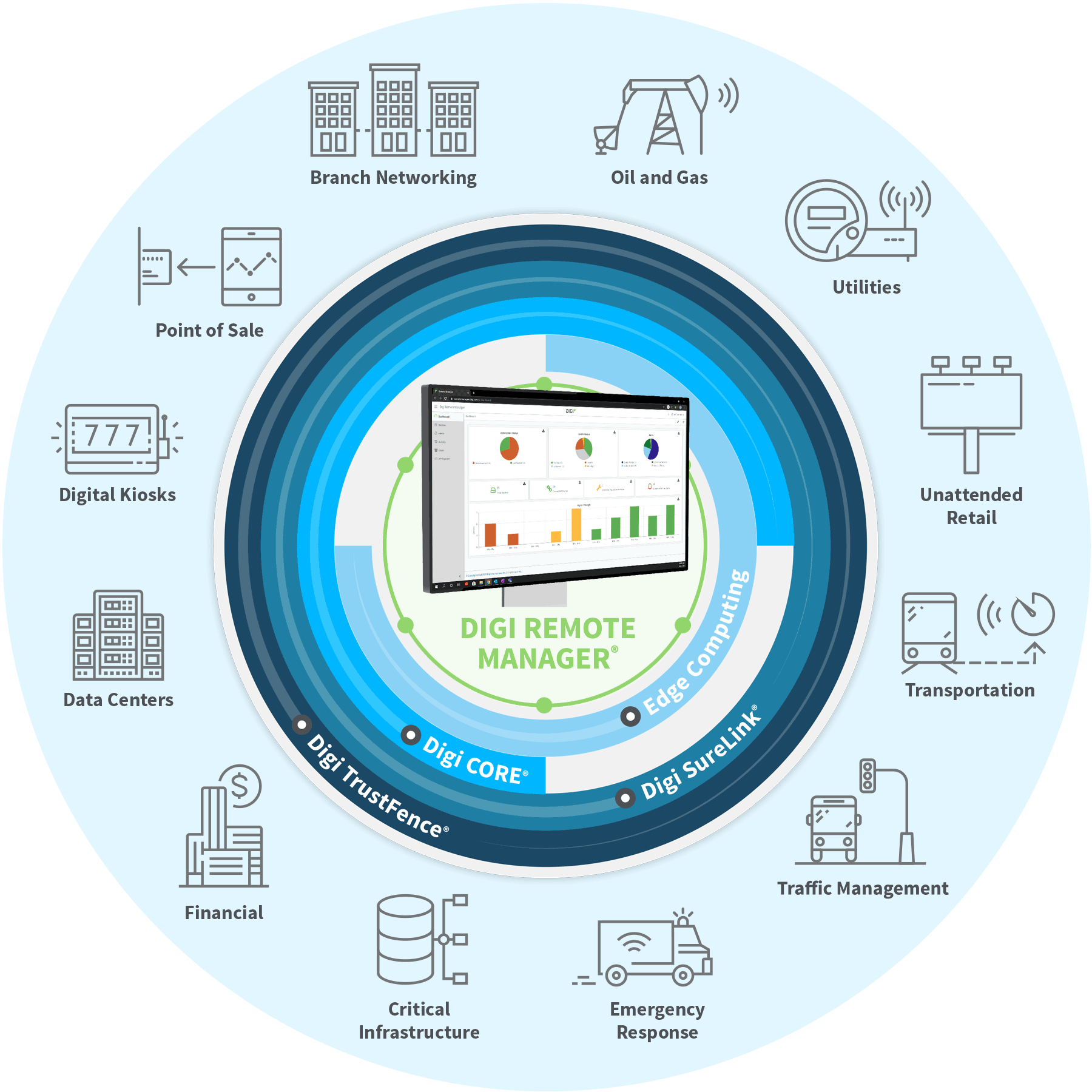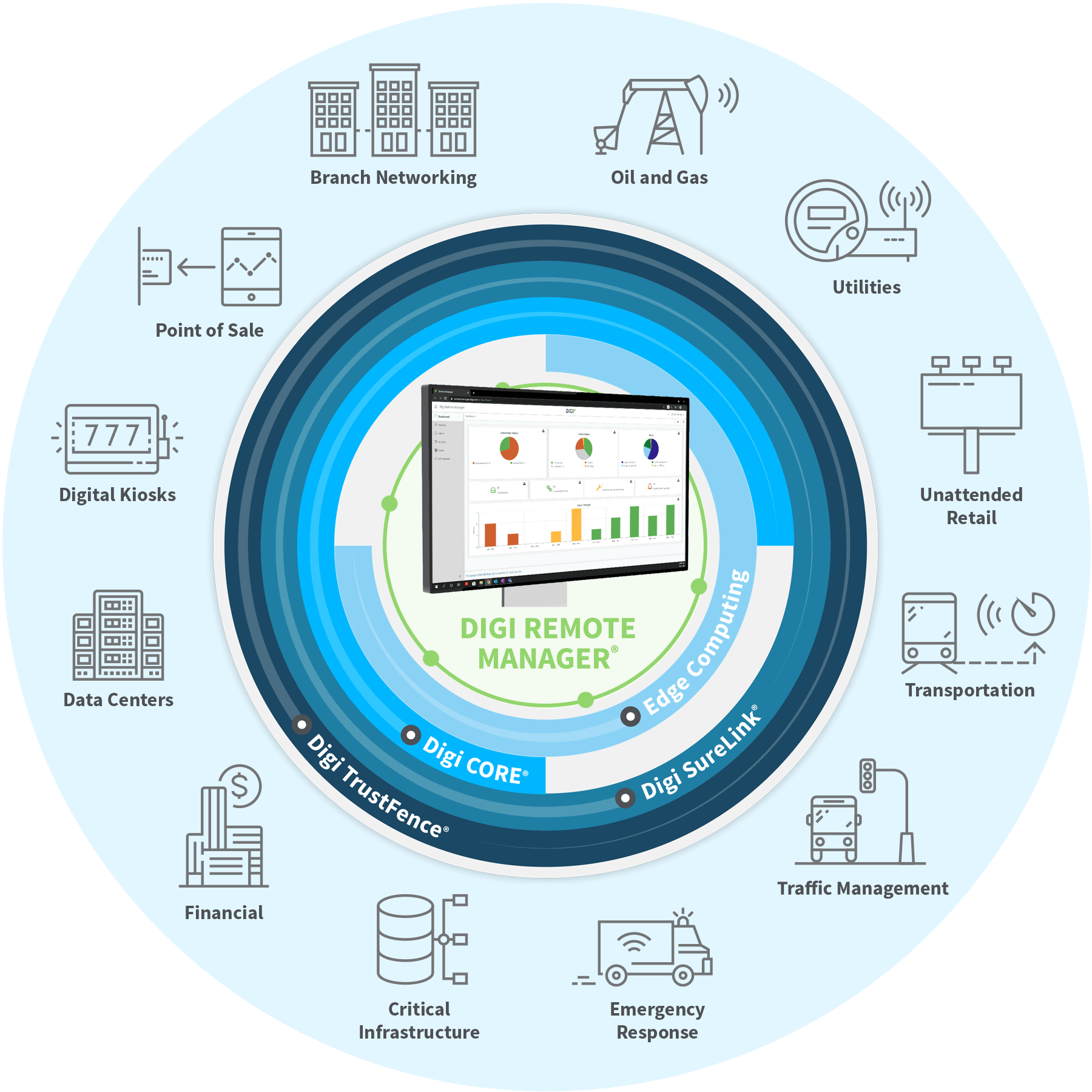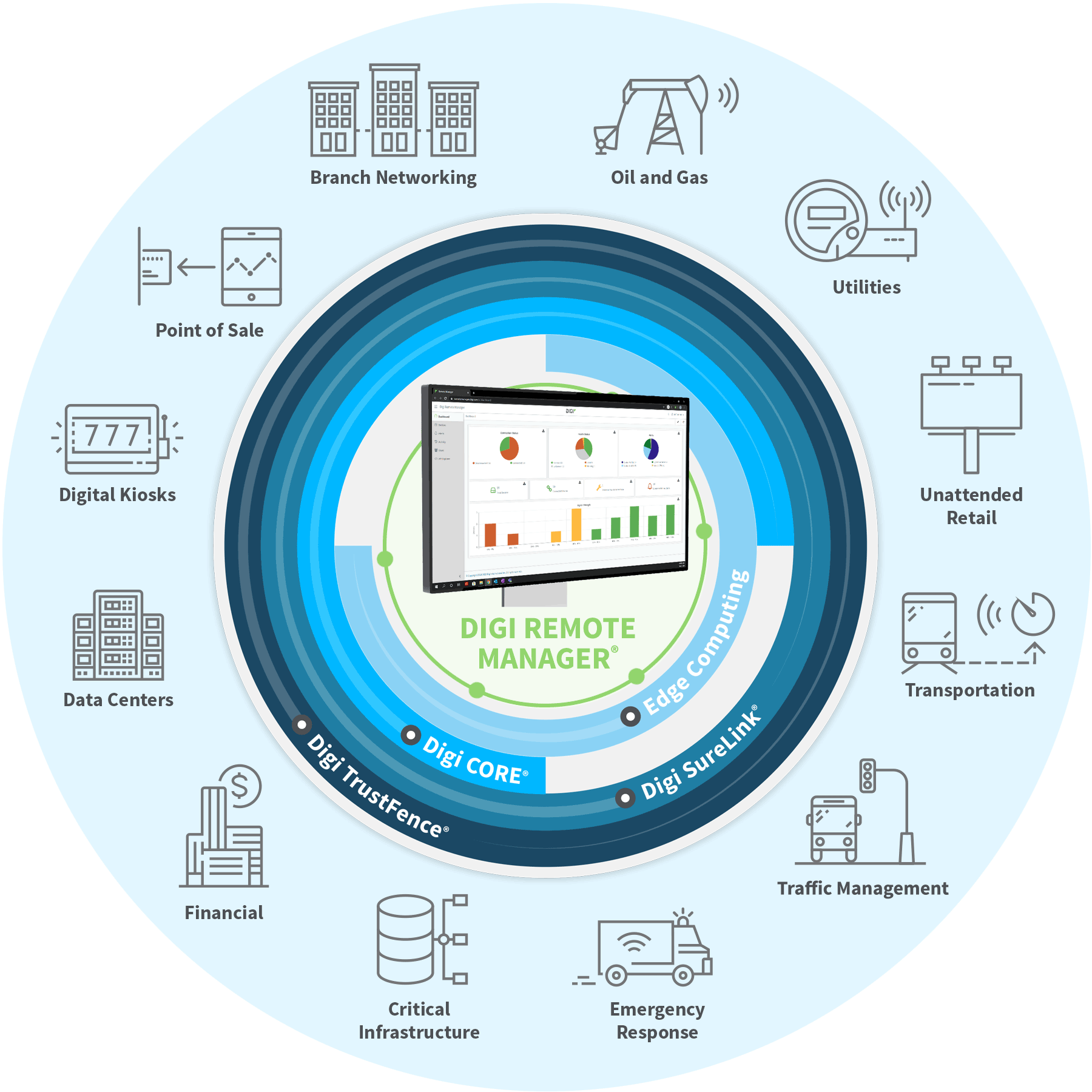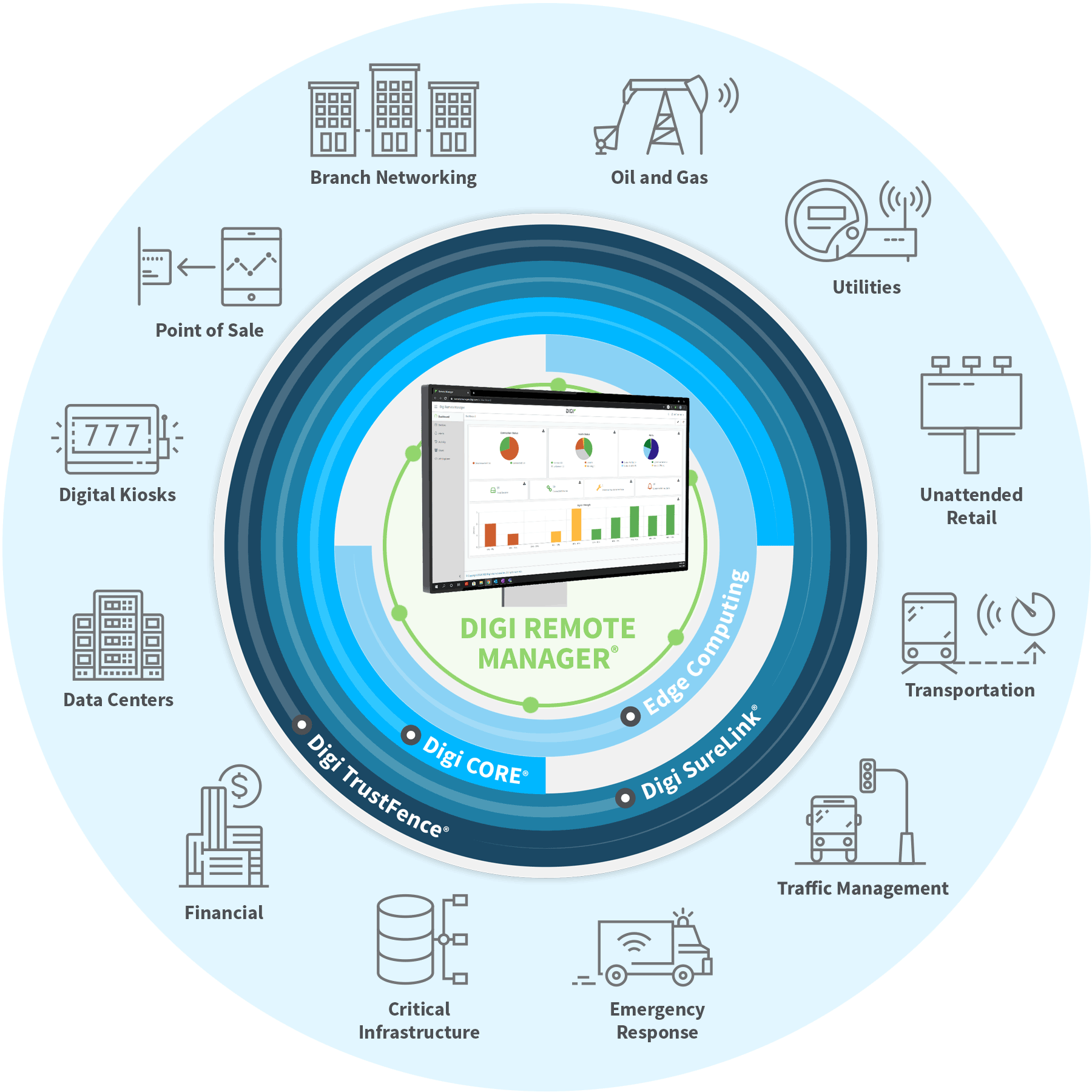
How Smart Cities Benefit from the IoT
The application of IoT in smart city projects has ushered in a new era of urban renewal that empowers cities to improve efficiency, gain greater control over resource use and improve life for its citizens. For example, these improvements include:
Enhanced management of municipal resources: Smart cities leverage the IoT, AI, and big data analytics to improve the way they manage their transportation, water, and energy resources. The result: cost savings, reduced waste, and improved efficiency.
Greater sustainability: IoT smart cities aim to be more sustainable by cutting energy usage and encouraging the use of renewable energy. Sustainable city initiatives help reduce waste, increase the city’s resilience, and promote green energy strategies.
Cleaner air: As a whole, smart city applications and green tech initiatives not only promote sustainability but reduce greenhouse emissions that contribute to pollution and air quality issues. From smart buildings, which dramatically reduce energy usage, to traffic management systems that optimize traffic flow and reduce idling of transit buses, to micro-mobility projects that encourage commuters to travel by human and electric-powered vehicles instead of gas-powered cars, all of these initiatives reduce emissions and carbon footprint, release less pollution and improve air quality for city residents.
Economic growth: Smart cities drive economic growth by creating a better environment for new businesses – and jobs.
Better quality of life: In a smart city, citizens enjoy a much higher standard of living thanks to data and technology. That translates into better healthcare, education, and public safety services. What’s more, these enhanced services create greater civic engagement.
Applications of IoT in Smart Cities are a forward-thinking strategy to create more livable, sustainable, and efficient urban environments that meet current and future citizen needs.

IoT in Smart Cities FAQ
What is the Internet of Things (IoT) in the context of smart cities?
In smart cities, the Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of connected devices—such as sensors, meters, streetlights and cameras — that gather and transmit data to enhance city operations. These devices communicate over wireless networks, enabling real-time monitoring, automation and analytics to support more efficient, sustainable and livable urban environments.
What are the applications of IoT in smart cities?
IoT applications in smart cities optimize traffic management, improve waste collection, monitor environmental conditions, enhance public safety, and enable smart grids for energy efficiency.
Smart city leaders are turning to IoT technologies to address long-standing urban challenges. Examples include:
- Smart transportation and mobility — Real-time traffic management, connected public transit, smart parking systems and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication help reduce congestion and improve travel times.
- Smart energy management — Connected grids, smart meters and intelligent lighting systems optimize electricity use and lower operational costs.
- Environmental monitoring — Air and water quality sensors track pollutants, enabling more responsive and informed policy decisions.
- Smart waste management — IoT-enabled bins and route optimization reduce fuel use and streamline collection schedules.
- Public safety and security — Smart surveillance, gunshot detection systems and connected emergency response networks enhance response times and situational awareness.
- Smart infrastructure — Sensors embedded in roads, bridges and buildings support predictive maintenance and extend the lifespan of critical infrastructure.
- Smart water systems — Automated leak detection and water quality monitoring conserve resources and help protect public health.
These innovations lead to more sustainable, efficient, and livable urban environments.
What is the advantage of IoT in smart city initiatives?
The primary advantage of IoT in smart city initiatives is the ability to enhance efficiency across various sectors, such as infrastructure, public safety, inner-city mobility and energy management. IoT enables real-time monitoring, data-driven decision-making, and automated processes, leading to more sustainable, responsive, and livable urban environments.
What are the key technologies in smart cities?
Key technologies in smart cities include IoT devices for connected infrastructure, AI for data analysis and automation, 5G for fast, reliable communication, cloud computing for data storage and processing, and smart grids for efficient energy management. These technologies collectively enhance urban sustainability, efficiency, and quality of life.
How does IoT support ROI and measurable benefits?
IoT deployments deliver a range of quantifiable benefits for municipalities:
- Operational efficiency — Automating functions such as lighting and waste collection reduces manual work and costs. For instance, smart streetlights can lower energy use by up to 70%.
- Lower emissions — Intelligent mobility and energy systems reduce fuel consumption. Adaptive traffic signals have helped some cities cut CO₂ emissions from idling vehicles by as much as 25%.
- Improved air quality — Cities such as Barcelona and London have used IoT-based air quality monitoring to reduce particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide levels.
- Enhanced mobility — IoT data powers real-time traffic updates and transit scheduling, improving both reliability and user satisfaction.
- Quality of life — Citizens benefit from cleaner air, faster services and safer streets. Mobile apps provide residents with updates on traffic, air quality and public services — enabling more informed decisions.
What is smart city IoT architecture?
Smart city IoT architecture involves a layered framework, including sensors for data collection, network connectivity for data transmission, cloud computing for storage and processing, and AI-driven analytics for real-time decision-making. This architecture enables efficient management of city resources and services, enhancing urban living.
Can smart city IoT solutions scale and integrate across municipal organizations and agencies?
Yes. Many municipalities are investing in unified IoT platforms that consolidate data from transportation, utilities and emergency services. These integrated systems provide a central analytics dashboard, improving collaboration, reducing redundancy and supporting long-term ROI through shared insights.
What are the common challenges involved in smart city IoT implementations?
Cities may encounter challenges such as:
- Data privacy and cybersecurity concerns
- Interoperability among vendors and systems
- Upfront investment and funding constraints
- The need for skilled personnel and sustainable maintenance models
However, phased rollouts and defined KPIs can help municipalities realize value within the first few years of deployment.
Additionally, organizations like Digi offer integrated solutions that facilitate efficiency in planning and deployment. For example, Digi worked with New York City traffic management personnel, carriers, and other agencies to support the rapid planning and deployment of a citywide traffic management system upgrade, developing a scalable deployment workflow for implementation of cellular routers at 14,000 traffic intersections.
Next Steps