Your industry relies on mission-critical communications. The last thing you want to worry about is the reliability, security and flexibility of your network. That is where a software defined network (SDN) shines.
One thing that first responders, financial institutions, utility service providers and transportation services have is common is their reliance on networks. And the quest to improve their performance, reliability, security and management — while keeping costs under control is constant.
Continue reading to learn more about software defined networks. We’ll explain why they are important and how you can get started with an SDN solution for your application.
What Is Software Defined Networking?
Software Defined Networking Definition
What is SDN? The Digi SDN definition for Software-Defined Networking is a software-based network architecture where software applications intelligently control and manage the network. However you define a software network, it is important to understand that this approach simplifies network management. It makes it easier to update, test or even monitor the security of your network, regardless of the underlying hardware.
Here are additional reasons why SDN is an important networking architecture solution:
- Automation improves reliability — Automatically reroute networks in the event of an outage
- Reduced need for hardware reduces costs — Instead of installing costly redundant equipment, an SDN allows you to automatically reroute to other equipment on your network
- Dynamically increase or decrease bandwidth — Automatically provides reliability to key equipment without going over your data plan
Functions of Software Defined Networking:
- WAN failover — When a single SDN router handles many Internet connections and a connection fails, SDNs automatically reroute the traffic to another cellular router.
- Maintain connectivity — SDNs automate connectivity validation and can reroute to backup Internet connections. With this feature, a single router can support multiple carriers to significantly reduce downtime.
- Network health monitoring — Intelligently routes network traffic to reduce data usage overages and ensure faster connection.
- Customizable — SDN intelligent software controls hardware from many different vendors through a common interface. This allows organizations to monitor their equipment in a way that makes the most sense for the devices.
How Does SDN Work?
Software Defined Networking Explained
If you are thinking, “help me decide between SDN and traditional networking,” continue reading. We’ll explain the differences later in this article.
How does SDN work? The software part of the network is separated from the hardware. The software decides how to route traffic through the network. This way, a centralized software interface controls the entire network. Otherwise, each device would need individual management.
SDN Components
SDN components exist in three distinct layers for greatest network agility. The bottom layer is the infrastructure layer and contains the forwarding equipment. The middle layer or control layer maps service requests from the top or application layer to the infrastructure layer (such as an SDN Wi-Fi controller).
- Applications: The application layer consists of applications and services running on the network that communicates requests or information about the network.
- Controllers: The control layer is the part of the software defined network architecture that routes network traffic flow and makes decisions based on network activity.
- Networking devices: The infrastructure layer contains the network's actual switches and routers.
Types of Software Defined Networking
Software Defined Network solutions dynamically handle network traffic. They use intelligence to optimize performance. As a result, they significantly reduce costs. There are 4 SDN architectures available. Each one works differently and provides different benefits.
- Open SDN: Open SDN uses open-source software protocols such as OpenFlow to control and route network traffic.
- API SDN: API SDN uses something called southbound APIs, to control data flow for each device.
- Overlay model SDN: Overlay Model SDN creates tunnels to run multiple separate networks on top of existing network.
- Hybrid model SDN: A Hybrid Model SDN combines SDN and traditional networking as a step into SDN meaning it allows for a gradual transition.

SDN vs Traditional Network: How Are They Different?
In traditional networks, the three layers (Application, Controlling and Networking) all reside in the same network device. With SDNs, network functionality exists in three different layers. Each manages a part of operating the network. In a traditional network, each device must be individually managed and controlled. But in SDN, separate layers operate through a unified interface.
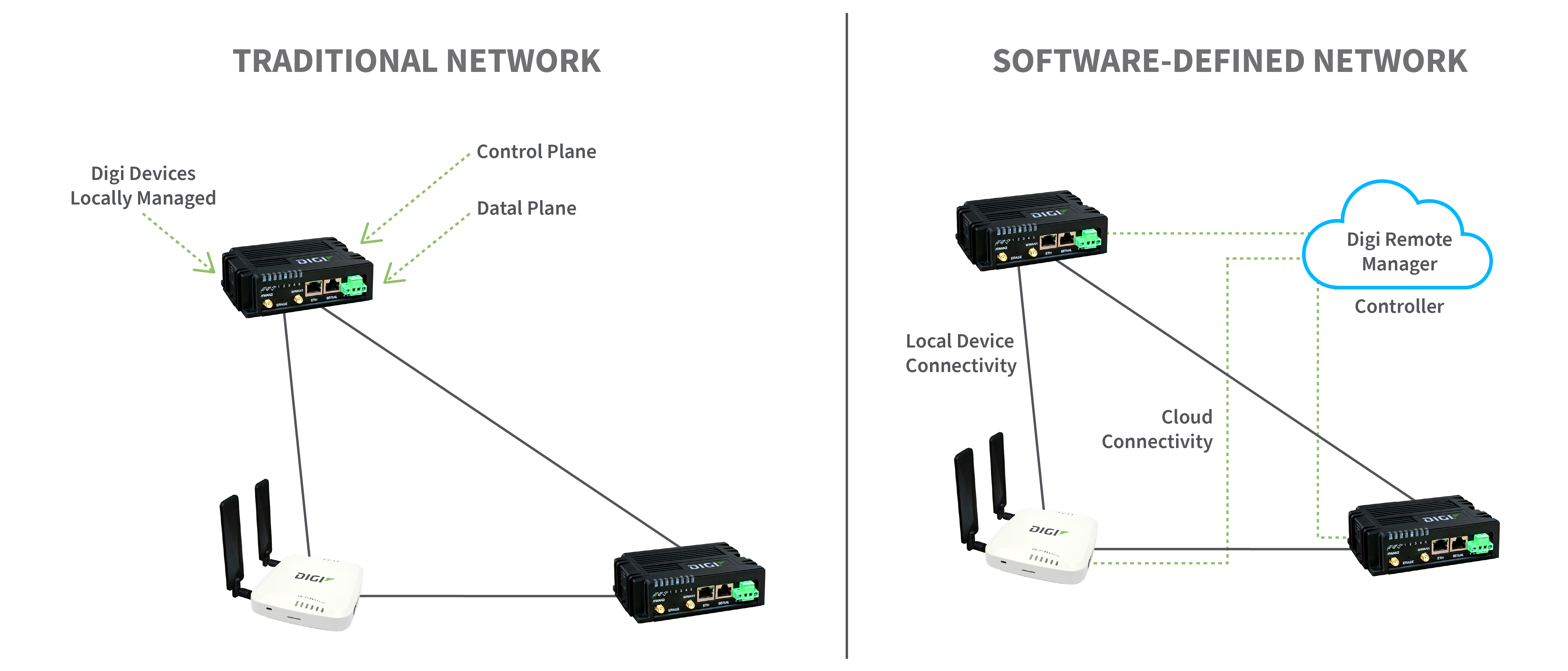
Here's a summary of an SDN vs traditional networks:
- SDNs separate networking functions into three separate layers. Traditional networks combine all functions in one device.
- Traditional network devices get managed individually. SDN IoT devices can be managed from a central software platform.
- SDNs use dynamic software to reroute traffic in the event of a failure while traditional networks need extra hardware for redundancy.
Benefits of Software Defined Networking
SDN can help organizations manage and safeguard their Internet traffic for critical digital communications, especially for equipment installed in remote locations. Managing thousands of IoT devices and routers individually is not scalable or even workable without automation and software solutions that perform remote connectivity testing.
Flexible
Software Defined Network features provide a way for engineers to instantly re-route networks. In the event of an outage, an SDN can automatically reroute to another network to maintain connectivity.
With many automation configurations, network traffic can be dynamically managed to balance the load during peak activity. Alert messages notify engineers about approaching data usage limits or overages.
Secure
Network automation enabled by SDN architecture means more visibility into network traffic. An SDN can detect suspicious activity more quickly. Once an anomaly has been detected, SDNs act quickly to divert suspicious network traffic to firewalls and intrusion detection systems. In fact, software defined network security applications may block suspicious actors before they access critical parts of the network.
Cost-Effective
By automating device monitoring and software updates, SDNs can simplify updating and monitoring of thousands of cellular routers. This reduces maintenance costs by limiting on-site staff needed.
Additionally, because software defined networking technologies can automatically reroute communications during an outage, extra hardware is not needed. SDNs ensure reliability while also reducing hardware costs.
Digi’s Software Defined Networking Solutions

Digi understands that commercial and government organizations alike need reliable, automated, intelligent and customizable SDN solutions. That’s why Digi created a new generation of cellular routers and infrastructure management solutions that support all SDN capabilities. Digi also developed the Digi Accelerated Linux operating system (DAL OS). DAL OS creates seamless integration with all Digi routers, servers and connected devices.
Digi Remote Manager
One of the biggest benefits of SDNs is the ability to automate at scale through a single interface. With Digi Remote Manager®, Digi routers automatically sync to the cloud portal for status checks and updates. The platform also supports carrier switching. Organizations can integrate connection redundancy from their routers that use many SIM cards from different carriers.
Here is a quick summary of some of the biggest Digi Remote Manager benefits
- Supports carrier switching — Integrate connection redundancy/failover via routers that support multiple SIM cards from different carriers.
- Access Point Name (APN) detection and connectivity — Once connected, the carrier SIM card is automatically detected and issues the correct credentials and loads the correct firmware.
- Automatic router syncing — The routers also automatically sync with the Digi Remote Manager cloud portal for updates to the device and monitoring of the device.
- A single pane of glass — A centralized interface to remotely provision, deploy, automate, and integrate all your network assets.
Digi Cellular Routers
Digi created a new generation of cellular routers and infrastructure management solutions that all include SDN capabilities. Digi also created a dedicated operating system, the Digi Accelerated Linux operating system (DAL OS), to deliver the critical capabilities that commercial and government organizations require: reliability, automation, intelligence and customization.
- Always-on Connectivity — Digi SureLink® is a custom feature developed by Digi specifically to maintain persistent network connections.
- Automatically sync to Digi Remote Manager — Routers also automatically sync with the Digi Remote Manager cloud-based portal.
- Out-Of-Band Management — Digi cellular extenders enable out-of-band (OOB) management and network resilience for a range of use cases.
Watch our webinar to learn more about the advantages of Digi Cellular Routers for Software Defined Networking.
Run Your Business Smoothly with Digi’s SDN Solutions
 As you transition your network to a software defined network architecture, you need a partner that can help you every step of the way. After all, your network is mission-critical, and every poor decision could cost money or lives.
As you transition your network to a software defined network architecture, you need a partner that can help you every step of the way. After all, your network is mission-critical, and every poor decision could cost money or lives.
Digi is a complete IoT solutions provider, connecting IoT devices since 1985. We support every aspect of design and deployment services for your project. We purpose-build our solutions for end-to-end functionality.
Because Digi is SDN vendor agnostic, our secure LTE and 5G devices can support virtually any existing SDN deployment. Partner with Digi to find the right solution, customized to your exact requirements.
Next Steps