Organizations are leveraging the benefits of IoT (Internet of Things) in many different ways today — such as improving efficiency and safety,
monitoring remote and hard-to-access equipment, automating processes,
reducing the environmental impact of operations, ensuring equipment and goods maintain regulatory compliance, and saving money.
Imagine, for example, if a municipality could simultaneously improve the energy efficiency of their city lighting system, reduce carbon emissions, and save costs, simply by switching to IoT-enabled smart lighting. That is one of many examples of how organizations and municipalities are achieving results with IoT.
In this post, we’ll look at a number of real-world examples to help shed light on IoT advantages such as the operational enhancements the Internet of Things offers in process, visibility, time management, cost savings and more.
IoT in the World Around Us
The Internet of Things largely goes unnoticed in everyday life, as it is mostly “behind the scenes.” Yet the IoT — comprised of millions of connected devices communicating with one another via radio frequency and cellular signals — is always at work, handling a vast range of critical processes and delivering data and insights to decision makers.

We all know about IoT in smart home applications, and the ability to remotely monitor your residence or automate your home’s climate. Here are some IoT examples in the commercial, industrial, government and medical realms:
- Monitoring tank levels in industrial and agricultural applications
- Automating processes in industrial operations for safety, efficiency and cost savings
- Upgrading to Industry 4.0 technologies that combine edge computing, AI and real-time connectivity in applications like factory automation
- Remotely monitoring and managing meters, reclosers and other equipment in utilities
- Detecting gas leaks in oil and gas operations
- Tracking the location of goods in transit
- Monitoring the temperatures of perishable goods in trucking and refrigeration
- Managing processes and payments in electric vehicle charging stations and parking meters
- Monitoring train and bus locations, as well as keeping watch on railroad tracks for obstructions
- Detecting soil moisture and conditions for watering and crop management
- Patient monitoring in medical clinics, as well as automating infusions and other medical processes
These are just a few examples of the vast and growing use cases for the Internet of Things in commercial and smart cities applications. But what are the benefits of IoT projects? We will cover that next.
7 Advantages of IoT
The advantages of IoT in commercial and industrial applications are many. Most of them center around efficiency — not only because efficient operations help lower costs and reduce our impact on the planet, but because in some cases, the efficiency of a given process, or the delivery of information and process automation, is mission critical. In many cases, lives depend on it.
Automation
 The world is moving to IoT-enabled automation in many different sectors. This is especially important in applications such as industrial systems and manufacturing.
The world is moving to IoT-enabled automation in many different sectors. This is especially important in applications such as industrial systems and manufacturing.
Consider, for example, the critical importance of detecting overheating of flammable or explosive systems which can be automatically shut down if certain conditions are detected. Another key example is the manufacturing of automotive parts and medical devices, which must be built with precision to work flawlessly in real-world operation.
The advantages IoT solutions bring to the table in the area of manufacturing automation include several capabilities that humans can’t offer:
- Machines can assemble parts with more precision and speed, resulting in fewer errors during assembly
- Automation also enables a factory to work longer hours without fatigue
- Robots can very rapidly detect faults that may not be detected by the human eye
Other examples of automation include smart traffic management to improve flow and quickly route emergency vehicles through the city; connected vehicle technology, which automates vehicle behavior and braking for safety; and automated frost fans in agriculture when frost is detected.
IoT Automation Use Case Spotlight
The benefits of IoT in agriculture are many, and adoption is rapidly growing because of the many opportunities for automating processes. Bin Sentry is a company that develops farming solutions to improve efficiency.

They observed that the manual process of checking on feed bins to make sure they are stocked is a cumbersome and error prone manual process. Inaccurate orders and delays in checking the bins until they are nearly out causes feed mills to scramble to handle rush orders. The downside was inefficient truck rolls as well as loss of livestock.
The solution was the first battery-operated, solar-powered feedbin monitor that is designed to replace the mundane and error-prone task of checking feedbins with automation for improved accuracy. The system involves setting up a network of low-cost, Internet-connected, energy-efficient sensors.
The ROI is excellent. Previously, most feed mills were getting feed data only once a week. But the BinSentry application can send data and diagnostics from the device six times a day, and even if there’s a total power solar-cell failure, there’s 90 days of backup battery power.
For additional automation examples, see our smart city lighting case study with Sicom Electronics, and the use cases described in our blog post, 5G Applications and Use Cases.
Predictive Maintenance
 One of the key benefits of using IoT is predictive maintenance, which involves ongoing monitoring of systems and processes to identify key indicators of problems before they result in downtime or system failure.
One of the key benefits of using IoT is predictive maintenance, which involves ongoing monitoring of systems and processes to identify key indicators of problems before they result in downtime or system failure.
Traditionally, the notification that a machine or system needed maintenance would occur when equipment broke down, operations came to a halt, or a system disaster occurred — resulting in everything from lost revenue, to environmental damage, fines, PR nightmares and loss of public trust.
The advantage of IoT is automated sensing and reporting, as personnel simply cannot manually monitor every process. With IoT-enabled predictive maintenance, IT and operations teams get notified when certain conditions indicate the need to send personnel to a site for maintenance. And in many cases, that service team can arrive on site with the exact tools and equipment required.
Predictive Maintenance Use Case Spotlight
Digi supports predictive maintenance in a wide range of applications in industrial IoT by delivering robust connectivity solutions that connect sensor data to business intelligence, integrated with Digi Remote Manager® — the command center for IoT systems, visualization, and remote management.
Otis Elevator is a global organization with elevators installed in hundreds of thousands of locations. The company has nearly 33,000 field professionals around the globe to service elevators, keep them running smoothly, and ensure their customers are happy.

To that end, the company developed Otis ONE, an IoT solution to help them continually optimize their response rates. The holy grail for this company was to convert from fast response to predictive response. Otis ONE turns customer equipment data into predictive insights so technicians can stay ahead of potential issues.
They are also better able to pinpoint the problem. The IoT solution delivers important information about all of the elevator’s components — what’s working and what’s not. Therefore, when service is required, service professionals can arrive on site with the right parts and return the elevator to service faster than ever before.
For additional excellent predictive maintenance examples from Digi customers, see how FLO built predictive maintenance into their electric vehicle charging stations, and how Wake, Inc. built a predictive maintenance solution to monitor concrete curing for rapid response, remediation and reporting.
Process Improvement
 Improving processes is one of the essential advantages of Internet of Things deployments, as process improvement affects every aspect of an operation’s bottom line. Consider precision agriculture, for example, in which sensors and connected systems support more efficient irrigation systems that can be automated based on sensor readings for soil conditions and weather.
Improving processes is one of the essential advantages of Internet of Things deployments, as process improvement affects every aspect of an operation’s bottom line. Consider precision agriculture, for example, in which sensors and connected systems support more efficient irrigation systems that can be automated based on sensor readings for soil conditions and weather.
Utilities offer excellent opportunities for process improvement as well, enabling companies to reduce truck rolls to remote sites and more quickly identify the precise location where service is needed.
Process Improvement Use Case Spotlight
Here is one example of how remote monitoring can improve processes, as well as predictive maintenance and other key IoT benefits.
A manager of an unattended oil field needs to make sure distributed oil tanks have adequate dosing chemicals. An IoT solution designed to report on the oilfield dosing can allow personnel to monitor the tanks from an iPad, from anywhere.
The figure below shows the example application, in which sensors on the tanks communicate via radio devices through a gateway to the cellular network and then to applications that collect and display the data so personnel can monitor the tanks remotely and receive alerts for specified conditions.
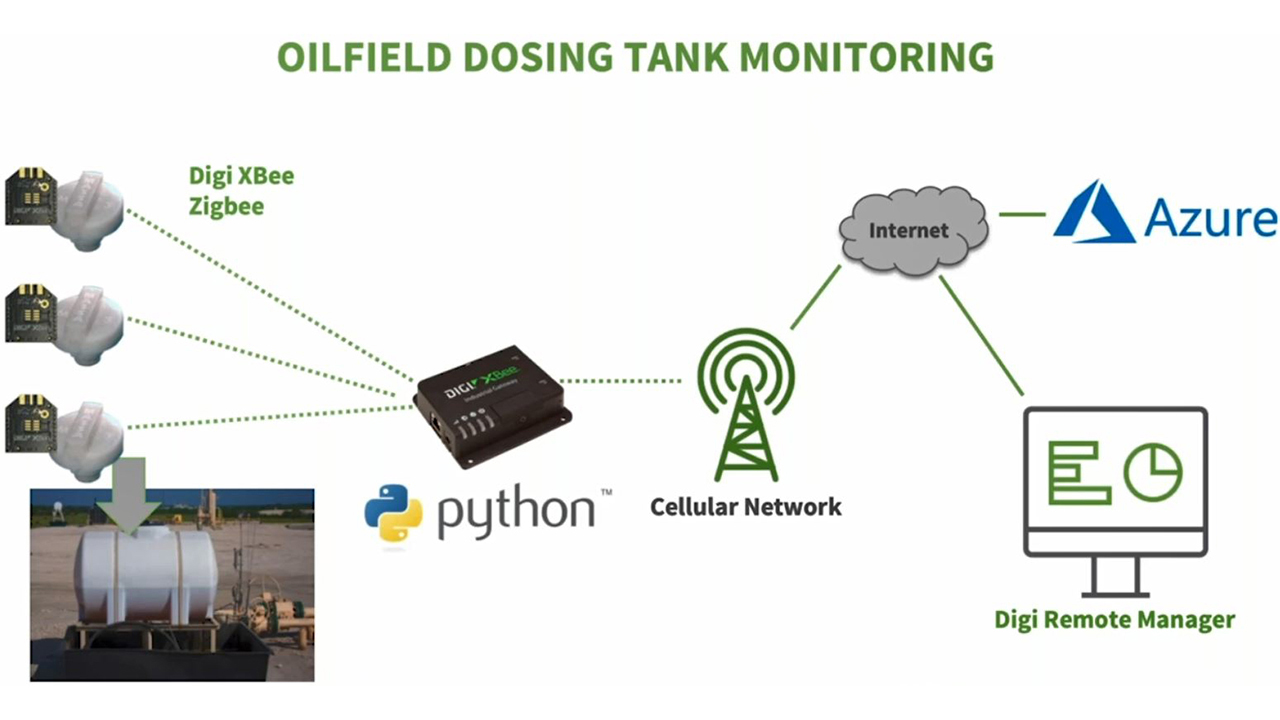
For additional examples of process improvement from Digi customers, see how WiseConn developed DropControl to improve irrigation systems to save farmers money and help reduce water usage, and how Nobel Systems developed a water management system that enables customers to centrally orchestrate and monitor water systems to prevent costly leaks.
Cost Reduction
 Cost reduction is perhaps one of the surprising benefits Internet of Things projects deliver, across all sectors. When an organization can improve system uptime, automate processes, reduce the risk of failure and loss of revenue, gain insights that support better decision making, and reduce resource usage and the time demands on personnel, the result is efficiency and cost savings.
Cost reduction is perhaps one of the surprising benefits Internet of Things projects deliver, across all sectors. When an organization can improve system uptime, automate processes, reduce the risk of failure and loss of revenue, gain insights that support better decision making, and reduce resource usage and the time demands on personnel, the result is efficiency and cost savings.
Of course, achieving these goals involves an upfront cost to procure, configure and deploy the IoT system. So, the key for any organization is to review the return on investment — meaning how soon the time and cost to develop and deploy the system will pay off.
Digi customers often see a rapid ROI from their deployments through reduced operational overhead, fewer wasted work hours spent doing tasks that could have been automated or tackling problems that could have been averted with earlier or more precise data, as well as the ability to rapidly address challenges — anywhere in the network — due to notifications and intelligence from the edge.
Cost Reduction Use Case Spotlight
Digi supports cost reduction in multiple ways. Let’s take a look at how bioFeeder helps shrimp farmers improve processes and lower the cost of doing business.
For shrimp farmers, a key challenge is feeding shellfish dispersed across hundreds or even thousands of hectares of ponds. The feeders are traditionally handled manually and are very labor intensive. It is both costly and difficult to keep to schedules that are optimal for shrimp production; the ideal feeding schedule is every half hour around the clock, which is impossible with manual feeding systems.
The solution was a network of intelligent, solar-powered, and cloud-connected feeders that leverage algorithms designed to optimize the feeding cycle of shrimp, all of which can be managed from a central location.
The ROI is demonstrated very quickly. Because the feed accounts for more than 40 percent of the cost of production on shrimp farms, the efficiency of the system is a game changer. bioFeeder customers are achieving a 100-percent payback in six to 12 months. And meanwhile, workers can redirect their time to other important activities on the shrimp farms.
For more examples, read how ElectriCities deployed wireless routers and Digi Remote Manager for reliable connections and remote management capabilities that saved over $300,000 in the first year alone, and how AFCEC saved an enormous amount and saw ROI in six months by converting from land lines to cellular.
Improved Insights
 IoT systems often act as the eyes and ears on remote, hard-to-reach, or widely distributed equipment and processes. For this reason, some of the key Internet of Things benefits include network-wide visibility, and quickly getting critical data from edge computing-enabled systems, resulting in improved insights.
IoT systems often act as the eyes and ears on remote, hard-to-reach, or widely distributed equipment and processes. For this reason, some of the key Internet of Things benefits include network-wide visibility, and quickly getting critical data from edge computing-enabled systems, resulting in improved insights.
In any deployment of connected devices, network managers need a sophisticated remote monitoring and management system such as Digi Remote Manager, which can aggregate data from the network edge, provide notifications and insights into the health of the entire network, and send alerts in the event of attempts at security breaches. These insights enable administrators to proactively respond to conditions and manage issues.
Use Case Spotlight on Improved Insights
Digi solutions support improved insights with IoT systems across many verticals, including industrial processes, water and wastewater management, agriculture and transportation.
Evoqua Water Technologies developed a system where a cellular module connects to Microsoft Azure and uses machine learning to gain insights into the operation of the distributed systems. The system gathers monitoring results and presents them on Evoqua’s cloud-based platform.
The solution was a response to their customers’ needs for greater insights. They wanted to know the actual analog readings, and they wanted pressure sensors and other data across all of their water systems. And Evoqua wanted to ensure that they could provide predictive insights and respond to customers quickly.
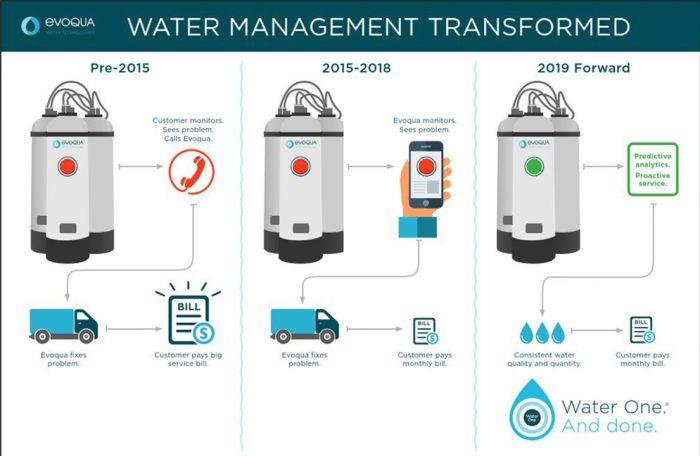
The new system delivers all of these insights, which enables customers to better manage their systems, improves customer satisfaction, and provides the opportunity for Evoqua personnel to proactively maintain equipment.
For more examples, see how New York City DOT monitors and manages traffic via Digi devices at 14,000 intersections, how Journeo uses IoT-enabled video monitoring to gain visibility into railroad track conditions, and how Fleetwatch keeps tabs on their fleet of hundreds of buses.
Adaptability
 In a changing world, it is critical for organizations to be able to pivot when needed. One of the most important IoT benefits for business enterprises is the ability to adapt to new business requirements, customer needs, and changing conditions, or scale the deployment in response to business growth or customer requirements.
In a changing world, it is critical for organizations to be able to pivot when needed. One of the most important IoT benefits for business enterprises is the ability to adapt to new business requirements, customer needs, and changing conditions, or scale the deployment in response to business growth or customer requirements.
With the right tools, an organization can roll out a connected device deployment — whether it’s digital signage, EV charging stations, lottery kiosks, connected vehicles or an environmental monitoring application — and then use the connectivity to those deployed systems to manage additional upgrades over time. For example, they may need to enhance functionality, send a new configuration to a device, or improve security when new threats are detected.
The key to each of the needs described above is a sophisticated remote management system like Digi Remote Manager that enables managers to update firmware across an entire fleet of connected devices quickly, and quickly configure and deploy new devices.
>
Use Case Spotlight on Adaptability
Digi supports predictive maintenance in a wide range of applications in industrial IoT, with robust connectivity solutions that connect sensor data to business intelligence, and with Digi Remote Manager® — the command center for IoT systems, visualization, and remote management.
Heating and air conditioning systems must work seamlessly in public buildings and office buildings, and HVAC systems are excellent examples of systems that require predictive maintenance. Infinitum Electric took on the challenge, with the goal to reinvent the electrification landscape with its patented PCB stator technology that creates smarter, lighter, quieter and more environmentally responsible electric motors and generators that offer superior efficiency and durability.
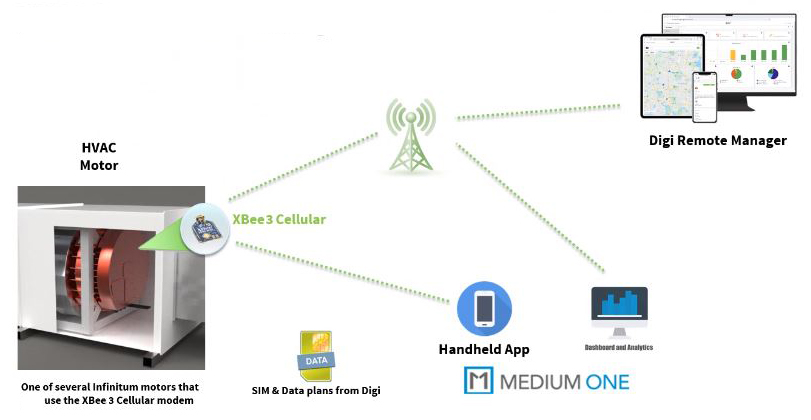
They developed their connected PCB-based motor with integrated Digi XBee communication modules, designed to improve size, weight, and durability, then added sensors to monitor various aspects of the motor’s performance. Then they pushed that data to the cloud to enable customers to collect operational data and run analytics across a portfolio of thousands of devices to predict failure or optimize maintenance protocols.
For additional use cases showcasing how IoT supports adaptability, read how Reborn Electric converts diesel-fueled buses to electric powered vehicles in Chile, and how Valmont Industries, Inc. took their cutting edge technology for IoT-enabled irrigation pivots for agriculture and modified the design to enter a critical new market with smart poles.
Compliance
 In any compliance-heavy industry, such as the medical device and food management sectors where human health is a critical concern, data and insights are mission critical. This is an area where the Internet of Things shines.
In any compliance-heavy industry, such as the medical device and food management sectors where human health is a critical concern, data and insights are mission critical. This is an area where the Internet of Things shines.
With the use of sensors, gateways, edge intelligence and the ability to rapidly deliver the right data at the right time, IoT systems enable teams to visualize their systems and get notifications whenever measurements are out of range. Further, they can produce reports quickly, without performing manual data entry.
Use Case Spotlight on Compliance
“Cold chain” is a term that refers to supply chain systems that must be monitored and managed within specified temperature ranges. This aspect of supply chain spans the continuum from production to packaging, shipping, delivery, processing and final sale, and includes everything produced in the food industry as well as pharmaceuticals.

All along the way, the items must be maintained within those required temperature ranges, and each location where the items are stored or processed must log the temperatures on a specified schedule to remain in compliance.
Because of the huge need in the cold chain industry for solutions that support compliance and safety, and the problems involved in manually logging processes, Digi established the SmartSense by Digi division, which provides solutions for monitoring and automated logging for the food, pharmaceutical and trucking industries.
Check out the video on the SmartSense grocery page page describing the experience of professionals at Schnuck’s grocery. Having installed SmartSense solutions in their stores, they reduced the time devoted to the monitoring and logging tasks from hours to minutes a day, and also obtained peace of mind that their logs were accurate and in compliance.
For another example of the benefits of IoT for compliance, see how the Southern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA), which provides light rail, subway and bus service in and around Philadelphia, turned to Digi for robust railway connectivity to meet federal positive train control (PTC) — a sophisticated train-signaling system designed to prevent crashes, derailments and track worker injuries resulting from speed and signal violations.
Mobility
 Mobility means many things, so to harness our discussion around the benefits of IoT, we will focus on smart mobility, which means mobility in smart cities applications.
Mobility means many things, so to harness our discussion around the benefits of IoT, we will focus on smart mobility, which means mobility in smart cities applications.
A great definition of smart mobility can be found on Geotab: Smart mobility refers to using modes of transportation alongside or even instead of owning a gas-powered vehicle. This can take on many different forms, including ride-sharing, car-sharing, public transportation, walking, biking, and more.
Today, we see IoT-enabled mobility in multiple use cases:
Wireless connectivity enables all of these applications in different ways, from monitoring public transit vehicles, to tracking the locations of rented scooters to providing emergency vehicle routing through a city, managing adaptive traffic control and more.
Watch Our Pre-Recorded Webinar on Optimizing Public Transit
In this webinar, our presenters address the challenges of public transportation, and how municipalities can address them with the right technology, such as next-generation transit signal priority.
Watch Video
Use Case Spotlight on Mobility
An excellent example of mobility is New York City DOT’s IoT implementation, which provides city-wide visibility into traffic flows and traffic incidents, from the department of transportation’s traffic management center. When the city's wired infrastructure needed upgrading, the NYC DOT team worked with a cross-functional vendor team, including Digi and AT&T, to architect a wireless intelligent transportation system to modernize their traffic management operations.
This system, which involved deployment of Digi cellular routers at 14,000 intersections across all five NYC boroughs, provides full visibility citywide. Across the city, adaptive control automates traffic lights, based on the conditions, and enables personnel to work with emergency response teams and proactively divert traffic whenever needed. An intelligent software application operating at NYC DOT’s Traffic Management Center (TMC) in Long Island City accommodates changing traffic patterns and eases traffic congestion.
Using Digi Remote Manager, the deployment team was able to preconfigure each router prior to deployment in the field to complete the deployment in record time. Digi RM not only supports visibility into the changing conditions across the city, but also enables the team to rapidly configure and add new routers to the system as needed, and roll out network-wide firmware updates.
Next Steps