Utility industry trends revolve around the theme of digital transformation in utilities and smart cities. Today, utilities are working to upgrade their infrastructures in anticipation of numerous initiatives in renewable energy and decarbonization. A key trend today is the electrification of almost every aspect of our world, from our cars, trucks, and buses, to heat pumps to lawnmowers and leaf-blowers — all aiming to reduce our dependence on fossil fuels.
At the rate of transformation from gas to electrical power, it is projected that our transmission systems will need to increase their capacity by 60% by 2030. Yet, 70% of today’s grid infrastructure is at least 25 years old, so a difficult challenge is on the horizon.
Another of the utility industry trends lies in the shift toward renewable energy resources. In 2020, almost one-fourth of all electricity consumed in the U.S. came from renewable energy sources. By 2028, almost all electric generation initiatives in the U.S. will come from renewables. In a growing number of regions where policies are in place to promote renewable energy, we’re seeing different needs for the grid: solar systems and inverters, battery storage systems, and EVs.
Why Utilities Are Embarking on Digital Transformation
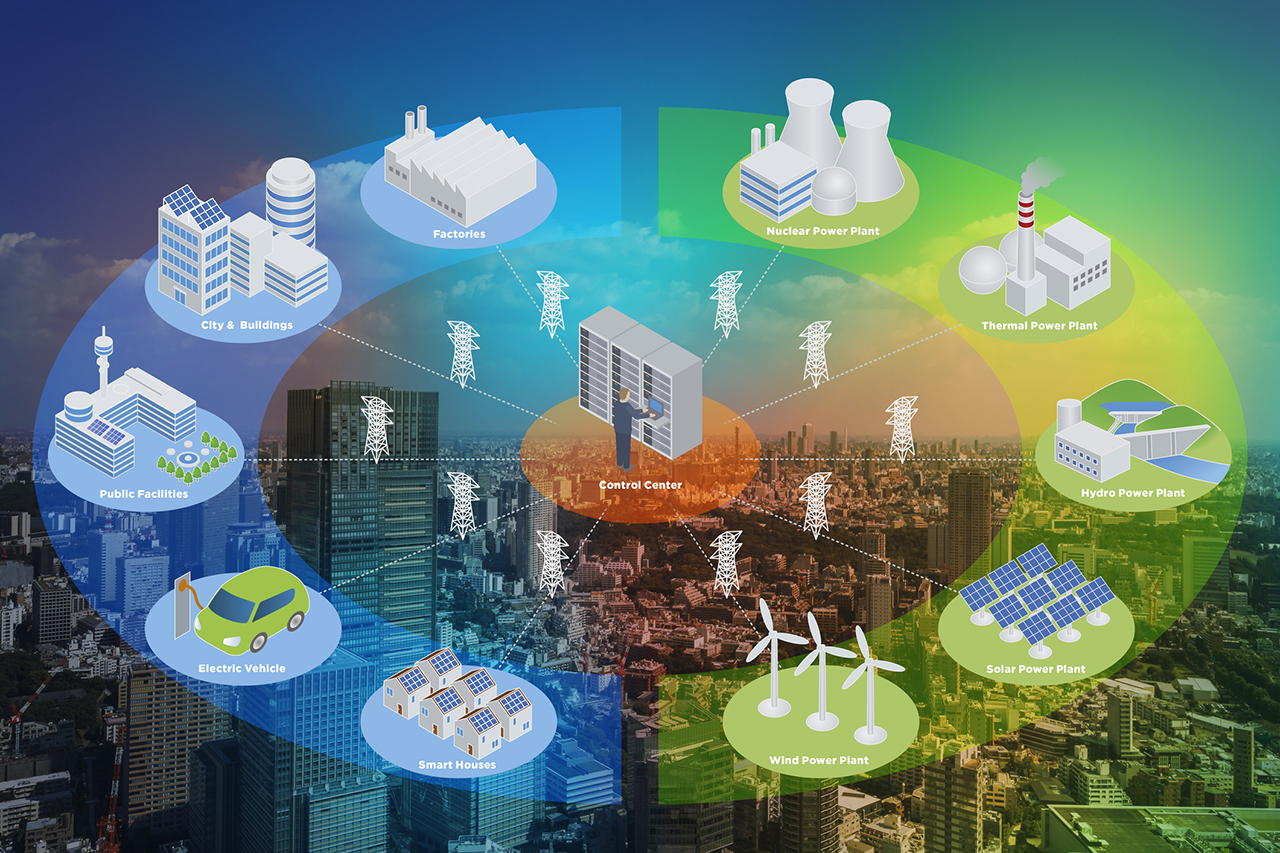

Unfortunately, the electrical grid wasn't designed for today's distributed energy requirements, nor was it designed to harness the power of greener energy sources. It was designed for large, centralized generation. It needs to become more robust and scalable. That’s why we’re seeing many utilities embarking on digital transformation to harness the power of the IoT to gain the adaptability they now need.
The U.S. government has earmarked $65 billion for investment in grid modernization. That’s the good news as digital transformation takes hold and the utilities industry shifts from central station baseload power toward more distributed power. To manage this shift, we expect a strong movement to digital transformation in utilities using IoT technologies and network strategies such as private networks.
IoT, Utilities, and the Next Generation of Networking FAQ

The utility industry trends we’ve discussed create both challenges and opportunities. Digital transformation in utilities relies on a range of technologies and services. It requires partnering with companies like Digi that can provide industrial connectivity solutions with integrated remote monitoring, as well as key carrier and technology partnerships and expertise in capabilities like private networks, emergency response systems and edge intelligence. Here are some answers to some frequently asked questions.
What Is Digital Transformation in Utilities?
Digital transformation isn’t simply about adding new technology to existing processes. Successful digital transformation requires new ways of working across four focus areas and a commitment to transformation.
- Technology — Advanced communications and network connectivity technologies make up any digital transformation. With IoT, power utilities are modernizing.
- Business — To meet consumer demand for how services get delivered, determine how and what services to deliver digitally.
- Process — Use digital technologies to automate or streamline business processes. This might include anything from automating alerts to using a centralized digital platform to track and manage smart devices across facilities.
- Organizational Change — Create greater worker agility by integrating data and analytics across the organization.
What Is Digitalization in the Energy Industry?
Electrification represents one of the most significant utility industry trends as the entire energy industry transitions to more flexible, decentralized power generation. For example, digitalization transforms energy grids that transport and distribute electricity. Smart meters connect to renewable sources such as wind or solar to enable smart grids that manage and balance intermittent electricity flows efficiently. This helps integrate renewable energy into the grid and opens opportunities for small producers to share energy back into the grid.
What Are Some Examples of Digital Transformation in Utilities?
Any utility can achieve a digital transformation. Here are several examples of how utilities can create value from digital transformation.
- Remote monitoring improves worker efficiency and safety — Thanks to smart sensors, workers can remotely check turbines, dams, or plant conditions in real time. Utilities can make important decisions without sending personnel to remote or dangerous sites.
- Smart meters easily integrate into a smart grid — Smart meters gather real-time data to determine energy usage, voltage fluctuations, and outages. This helps utilities buy and distribute electricity more efficiently.
- Networked IoT sensors — Utilities can track energy production more safely in areas prone to natural disasters and receive alerts when conditions change.
How Does the IoT Help the Energy Sector?

With the IoT, power utilities gain new abilities in tracking, automation, and predictive maintenance. Sensors that connect securely through private networks form the foundation of digital transformation. Here’s how some utilities companies use the power of the IoT:
- Energy storage — Remotely track, manage, troubleshoot, and improve the operation and performance of energy storage systems that use fire-prone lithium-based batteries.
- Smart grids — Smart grids rely mainly on IoT-based components to function.
- Vehicle-to-grid management — IoT solutions enable important analytics on vehicle-to-grid smart-charging technology. For example, they allow electric car batteries to return electricity to the grid.
Are Private Cellular Networks Viable for Utilities?
Many utilities find that private cellular networks provide better data speeds, improved flexibility, opportunities for signal prioritization and extra security As funding flows into utility infrastructure projects, there’s a need for investments in better networking. Reliable, secure, two-way communication systems integrate all the assets into a single system.
What Are the Benefits of Private Cellular Networks for Utilities?
As utilities embrace next-generation wireless network connectivity to support grid modernization, grid resiliency, and digital transformation initiatives, many seek alternatives to common carrier options. Utilities need solutions that collect and apply data from many grid devices, such as smart meters, gas sensors, voltage regulators, distributed energy resources and other emerging technologies. This a greater need for reliable and secure two-way communications to connect these assets. In fact, many large investor-owned utilities already invest large sums into private cellular networks as part of their grid updates. These private networks can cost hundreds of millions of dollars for acquiring expensive licenses for frequency, building out the infrastructure, and ongoing operating costs. Nonetheless, the payoff is compelling:
- Greater Service Quality — Although they don’t require capital investments, public networks can get bogged down during peak traffic loads. Private networks provide faster, more reliable service.
- Increased Security — On a private network, SIMs can be completely controlled—turned “on” or “off” for extra security.
- Prioritized Wireless Network for First Responders — Public carriers include AT&T FirstNet®, a public network built for specific mission-critical applications that do not contend with traffic on a public network. Many investor-owned utilities use these of networks because they’re shared assets that don’t need investment.
- Backups — Utilities that build out private networks often still use public networks for backup and resiliency.
- Hybrid Solutions — Utility cellular networks don’t have to be all-public or all-private. For most utilities, it isn’t workable to build out complete coverage using a private cellular network – some public spectrum makes sense.
Learn More About Private Cellular Network Benefits
How Digital Has Made a Huge Difference for Utilities

Accenture found that companies that invested in digital infrastructure during the pandemic quickly pivoted to new revenue streams. Competitors had to make unplanned technology investments just to survive. In fact, these digital transformation leaders grew twice as fast as laggards during this challenging time. McKinsey research suggests that digital technologies enabled 2-10% improvements in production and yielded 10-30% improvements in cost.
How Digi Supports the Next Generation of Connectivity in Utilities
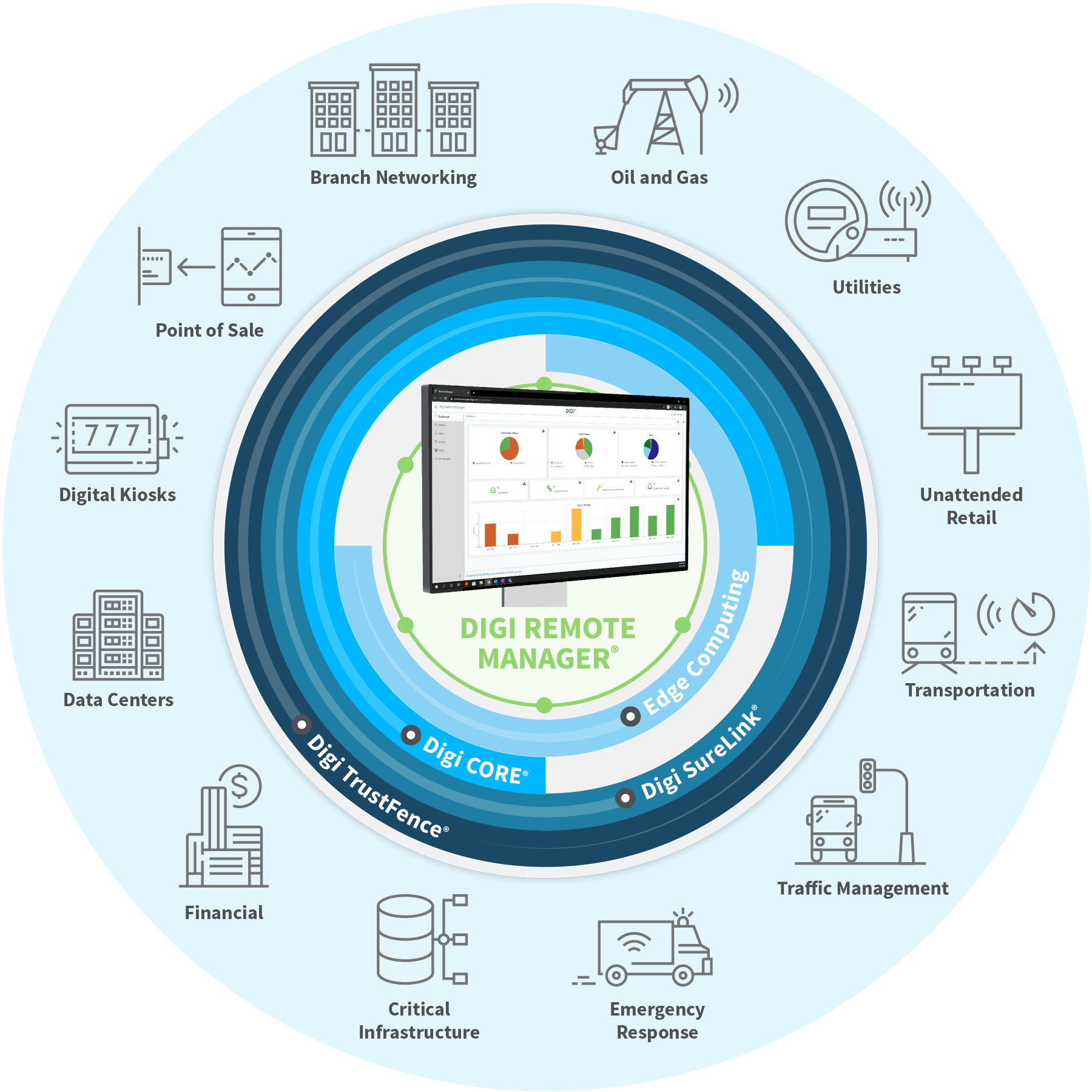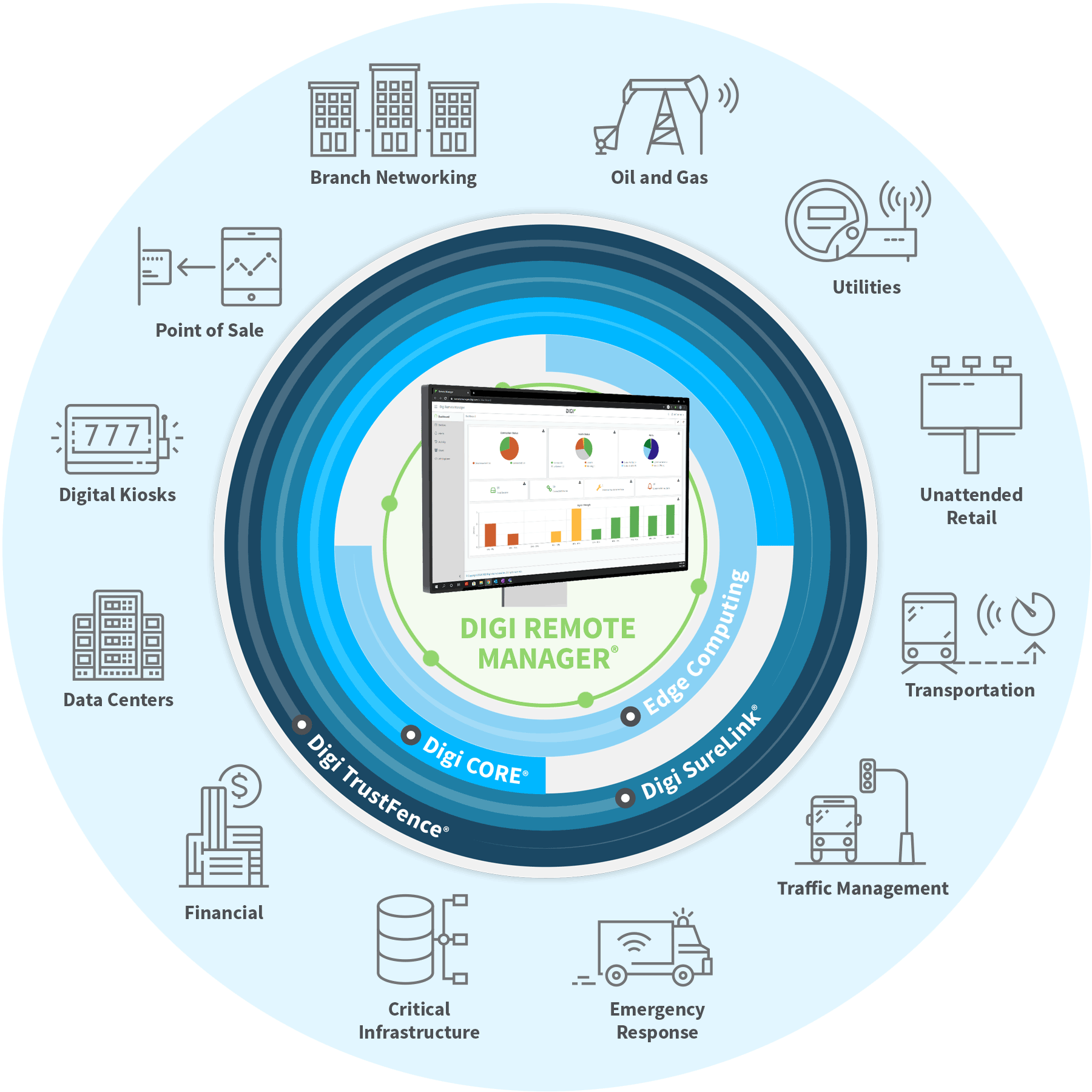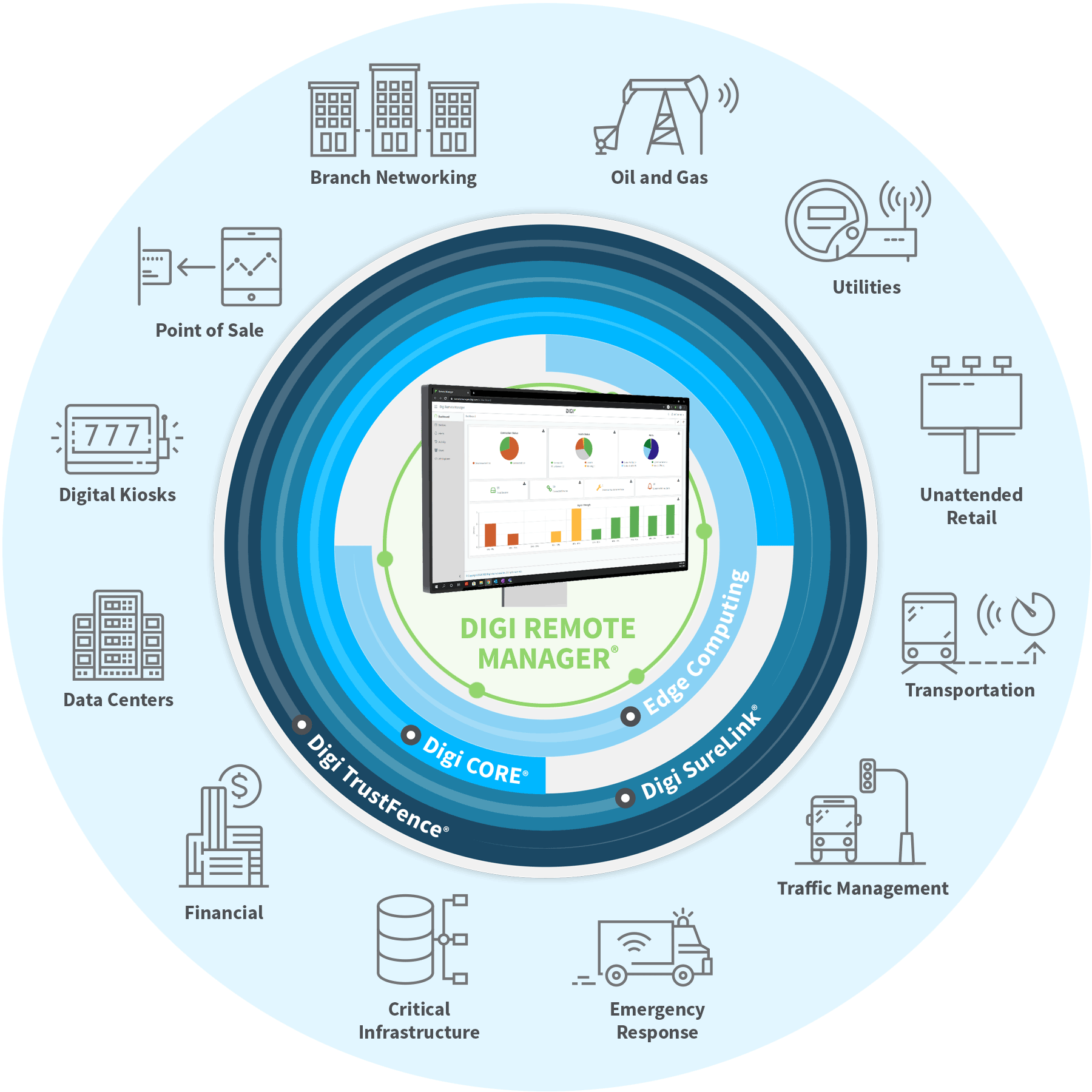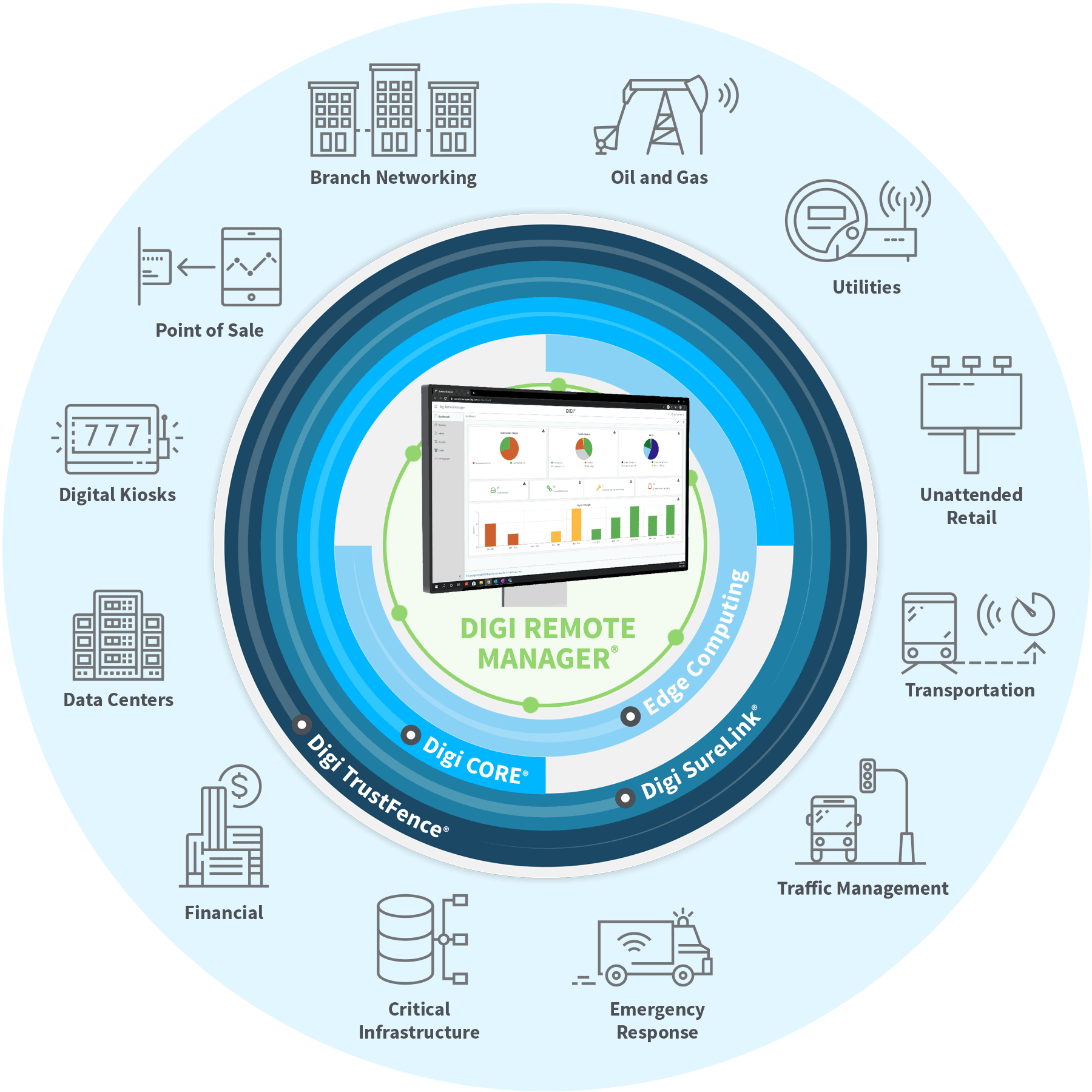
Looking for a technology solution partner to support your digital transformation? Digi can help — with a broad range of industrial cellular connectivity solutions and the professional consulting services you need to plan, procure and deploy your solution. Additionally, Digi's cellular solutions support private networks and are fully integrated with the secure remote monitoring and management platform, Digi Remote Manager®.
Next Steps