Edge computing, AI and machine learning are on the rise in Internet of Things applications. These technologies have evolved from the research and prototype phase and are now being deployed in practical use cases in many different industries. The symbiotic nature of edge compute and artificial intelligence is particularly interesting because artificial intelligence requires the extremely fast processing of data, which edge computing enables; meanwhile AI enables higher performance of compute resources and intelligence at the edge.
In this article we’ll look at edge computing (EC), artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), and how this combination is transforming network infrastructure, enabling new use cases, and creating the next generation of data processing.
The Data Center Paradigm Shift that Led to Edge Compute
 A data center centralizes an organization’s IT operations and equipment. It houses computer systems and associated components such as telecommunications and storage systems. Often included are redundant power systems, data communications connections, environmental controls and security devices.
A data center centralizes an organization’s IT operations and equipment. It houses computer systems and associated components such as telecommunications and storage systems. Often included are redundant power systems, data communications connections, environmental controls and security devices.
The role and composition of a data center has changed significantly over the last decade and continues to evolve. It used to be that building a data center was a long-term commitment with inefficiencies in power/cooling, no flexibility in cabling and no mobility within or between data centers. Today's data centers are about speed, performance and efficiency.
Data center computing has traditionally provided an advantage over dispersed, localized hardware. Data center computation is relatively inexpensive and massive amounts of information can be processed on demand. However, data centers are not perfect either. One of the major disadvantages is that the data has to be sent to a centralized location to be processed, and then send back to display the result or take action. This back-and-forth communication often over limited bandwidth links reduces the speed at which an application can run. We all know this from loading a website that is hosted in a remote datacenter.
With the deployment of next-generation 5G cellular networks around the world, edge computing, machine learning and artificial intelligence have started to gain in popularity. Edge computing processes data locally, near or right where it was generated. This obviates the need to send a large amount of information back and forth between the edge device and a centralized data center.
Intelligence at the Edge
 One of the key enabling factors for intelligence at the edge – or edge AI – is compact, inexpensive and powerful hardware. A few years ago, it would have been impossible to run AI locally, as the hardware size and cost would have been prohibitive. However, as Moore’s law has continued to hold true, and compute power has become cheaper, localized AI is now a reality. In fact, it’s becoming so popular that the consulting firm, Deloitte, predicts 750 million edge AI chips will be built into devices in 2020 alone. Deloitte also believes that this number will continue to grow, with an estimate of 1.5 billion edge AI chips being sold in 2024.
One of the key enabling factors for intelligence at the edge – or edge AI – is compact, inexpensive and powerful hardware. A few years ago, it would have been impossible to run AI locally, as the hardware size and cost would have been prohibitive. However, as Moore’s law has continued to hold true, and compute power has become cheaper, localized AI is now a reality. In fact, it’s becoming so popular that the consulting firm, Deloitte, predicts 750 million edge AI chips will be built into devices in 2020 alone. Deloitte also believes that this number will continue to grow, with an estimate of 1.5 billion edge AI chips being sold in 2024.
In addition to analyzing these numbers in the abstract, it can be informative to look at a real example of how edge AI is being used. The computer chip manufacturer NVIDIA is putting GPUs in security cameras. The GPU allows the camera to run recognition software without having to stream the video back to a data center for processing. In a smart city, which could have thousands of these cameras, not having to stream all that data can be a huge cost saver. Not only can these AI-enabled cameras perform recognition tasks, but with their local intelligence can also help to manage traffic and perform other advanced functions associated with a smart city, another topic we’re passionate about here at Digi.
Siri and Alexa are two other interesting examples of programs that employ edge AI. Rather than using localized hardware, these voice recognition platforms are making use of an edge network. Since an edge network essentially consists of multiple smaller, distributed data centers, that information doesn’t have to travel far to be processed. An edge network is viable for a large corporation like Apple or Amazon. For smaller companies, though, localized edge computing in conjunction with AI offers the best service at an affordable cost.
The Benefits of Edge AI
One of the primary benefits of edge AI is speed. Any task or action can happen faster if the data doesn’t have to be transmitted back and forth for processing. Another is the ability to detect issues by integrating smart devices and analtyics functionality to deploy intelligence at the edge for rapid insights.
These benefits enable key insights and capabilities such as predictive maintenance, where AI and edge compute pair together perfectly to identify the issues that can lead to system failures and rapidly route that data to the personnel who can address it rapidly.
Voice recognition increasingly relies on edge AI, especially as consumers expect an immediate answer. There are also industrial uses where AI-enabled cameras and other sensors can monitor production and adjust without having to be connected to a central processor.
This brings up another important point, edge AI can function without a network connection. In the event that a network connection is interrupted, an edge device can continue to function normally, for example to control traffic lights at a busy intersection.
There is a misconception that edge computing will ultimately replace cloud computing, but this is not necessarily the case. There are still computationally intensive tasks that require a data center. The benefit of a localized AI is that it can be programmed to filter data so that only necessary information gets transmitted to the cloud. That is, instead of sending all local data from a device to the cloud, the AI can ensure only relevant data is transmitted. This can save on bandwidth as well as the cost of paying for the transmission of irrelevant data. The more processing that can be relegated to edge hardware being governed by an AI, the less processing must be done at the data center.
In summary, edge AI computing offers the following benefits:
- Lower latency processing (faster speeds)
- Predictive insights for proactive and pre-emptive troubleshooting
- Higher uptime as information processing can take place even without a network connection
- Local filtering of relevant from irrelevant data
Use Cases for AI and Edge Computing
AI is important because it’s the technology that enables a high level of decision making at the edge. Edge computing wouldn’t have ever taken off if functionality was limited. However, because AI enables so many processes at the edge, it reduces the need for centralized computing power.
Edge AI and Decision-Making
 One of the interesting features of AI is that it can be empowered to make decisions. A great example is a smart camera that’s used for security in a production facility. If the camera notices that an employee is in a hazardous area, or some other potentially dangerous obstruction is present, the AI-enabled camera can shut down all machinery running in that area.
One of the interesting features of AI is that it can be empowered to make decisions. A great example is a smart camera that’s used for security in a production facility. If the camera notices that an employee is in a hazardous area, or some other potentially dangerous obstruction is present, the AI-enabled camera can shut down all machinery running in that area.
An AI-enabled camera can also make decisions about which data to forward to a human operator. For instance, an AI camera in an office building can be programmed to recognize the faces of everyone who works there. If the camera detects someone it doesn’t recognize, it can send an alert to a security guard. This is by far more efficient to monitor foot traffic than having a security guard “watching” a camera feed (or 12 camera feeds) round the clock, looking for suspicious behavior. As IoT infrastructure expands at home and in the workplace, AI-enabled smart devices promise a new level of functionality.
When Edge AI is Mission Critical
 The use cases are actually vast, encompassing a widely diverse set of industries and future applications. As we've discussed, the ability of edge AI to detect and report on the pre-conditions for failure has huge implications for both predictive maintentance and for critical decision making in mission critical applications. For example, consider remote assets such as storage tanks, mining belts, and energy systems that either stand to lose hundreds of thousands of dollars for every hour they are offline for maintenance, or actually have the potential for fire, explosion or meltdown in the event that critical issues are not identified.
The use cases are actually vast, encompassing a widely diverse set of industries and future applications. As we've discussed, the ability of edge AI to detect and report on the pre-conditions for failure has huge implications for both predictive maintentance and for critical decision making in mission critical applications. For example, consider remote assets such as storage tanks, mining belts, and energy systems that either stand to lose hundreds of thousands of dollars for every hour they are offline for maintenance, or actually have the potential for fire, explosion or meltdown in the event that critical issues are not identified.
Edge AI, Machine Learning, 5G and the Autonomous Vehicle Future
 While society may be hankering for self-driving cars, there are more systems and technologies that must mature before this reality can fully materialize. Consider the importance of identifying objects crossing the road, sudden changes in road conditions, and the appearance of street signs on a roadside. Artificial intelligence, along with machine learning and high-speed 5G networks will all enable autonomous vehicles by supporting these critical pieces. For example, a vehicle must be able to identify, in real time, when a road construction worker holds up a Stop, Slow or Yield sign, and act on that information.
While society may be hankering for self-driving cars, there are more systems and technologies that must mature before this reality can fully materialize. Consider the importance of identifying objects crossing the road, sudden changes in road conditions, and the appearance of street signs on a roadside. Artificial intelligence, along with machine learning and high-speed 5G networks will all enable autonomous vehicles by supporting these critical pieces. For example, a vehicle must be able to identify, in real time, when a road construction worker holds up a Stop, Slow or Yield sign, and act on that information.
Are Edge Computing and Artificial Intelligence Secure?
 Edge computing is secure when developed with secure embedded solutions like Digi ConnectCore i.MX 8 modules, and deployed on a secure device, like Digi IX20. You'll want to work with a device manufacturer that takes IoT security very seriously, and integrates security into its solutions to support a multi-layer security approach in deployed applications.
Edge computing is secure when developed with secure embedded solutions like Digi ConnectCore i.MX 8 modules, and deployed on a secure device, like Digi IX20. You'll want to work with a device manufacturer that takes IoT security very seriously, and integrates security into its solutions to support a multi-layer security approach in deployed applications.
With edge computing, much of the data is processed locally. There is less of a risk that this data will be compromised than if it was being sent to a data center, stored for an unknown period of time, processed and sent back to the device. If the edge device and the local network an edge device is connecting to are secured and well protected by a firewall, data is secure.
However, in terms of where security can be compromised, there are a few factors to consider.
- Edge devices may not be receiving updates as often as they should. It’s important to buy devices from a manufacturer that puts out regular updates, and then monitor device security, keep up with industry knowledge on security threats, and proactively keep edge devices in compliance – a key feature of Digi Remote Manager®.
- Because edge devices are readily available for purchase, a hacker can easily buy equipment in order to look for vulnerabilities. It’s important to follow industry news and remain aware of any vulnerabilities that have been discovered in specific devices. Note that Digi has a Security Center that is a valuable resource for those building or deploying IoT solutions.
Where Do Digi Solutions Fit in with Edge Compute and AI?
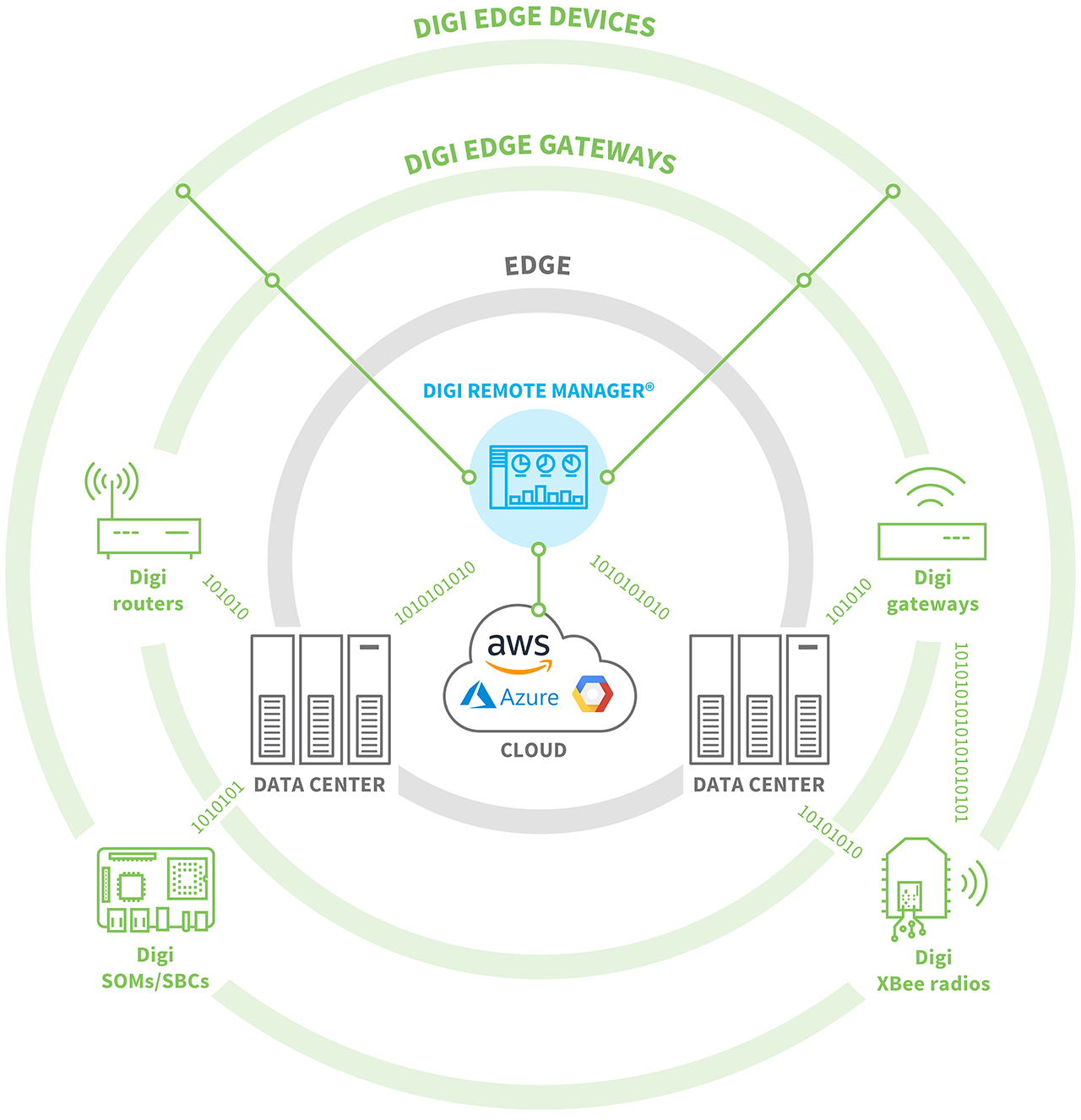 As a provider of IoT solutions predating the Internet of Things, Digi has been helping customers to solve their data connectivity challenges from the data center to the edge for decades. Our cellular gateway and router solutions provide critical connectivity for edge nodes, including sensors, controllers, and RTUs, with processing at the speeds you need to identify and route critical data in mission critical applications. Learn more in our blog post, What Is Edge Compute?
As a provider of IoT solutions predating the Internet of Things, Digi has been helping customers to solve their data connectivity challenges from the data center to the edge for decades. Our cellular gateway and router solutions provide critical connectivity for edge nodes, including sensors, controllers, and RTUs, with processing at the speeds you need to identify and route critical data in mission critical applications. Learn more in our blog post, What Is Edge Compute?
Digi products are also programmable – through Python integration, BASH scripting, and even Native C Linux applications – enabling developers to establish in-node processing and define highly sophisticated processing and intelligence at the edge. Digi edge routers and gateways also support aggregation of edge nodes to enable further processing. Edge devices can then be used to host customer applications to do further edge processing as needed by the specific application. Learn more in our Edge Computing web page.
Additionally, developers have a complete set of developer resources for designing and building the most sophisticated, high-performance, low-latency applications with Digi ConnectCore and Digi XBee solutions. Each of these ecosystems provides complete documentation, code libraries, and built-in security, while also integrating with Digi's remote management solution, Digi Remote Manager. Learn more about Digi embedded solutions for AI, Machine Learning and Machine vision applications of today and tomorrow and in our blog post, Machine Learning and Machine Vision Work Better with Real-Time Edge Processing.
And finally, Digi Wireless Design Services can be your resource for identifying the key requirements, architecture and components of your edge AI solution. This process can help your team with critical decision making throughout development, including any or all of the following:
- Performing a trade-off analysis to optimize each aspect of your design.
- Providing engineering support to augment your engineering team.
- Ensuring you don't miss any critical integration or interoperability requirements (e.g. security, latency, bandwidth, processing speed, battery, certifications, data visualization).
- Providing guidance on how to design, build and deploy your solution for optimal efficiency, functionality and cost savings.
Digi WDS has deep experience in all aspects of designing and engineering edge compute and AI systems and can support your initiative, whether you just need some consulting or you are seeking to augment your engineering team to ensure your project achieves all of its critical objectives, including certifications and time-to-market.
The Future of Edge Computing
 According to IoT Business News, “For every 100 miles data travels, it loses speed of roughly 0.82 milliseconds.” That can quickly add up to a lot of latency. AI-enabled edge computing solves this problem. Latency is annihilated as all processing happens on the spot. Or, in cases where local processing is not enough, AI can decide to send relevant information to a data center while keeping the irrelevant data on its local drives.
According to IoT Business News, “For every 100 miles data travels, it loses speed of roughly 0.82 milliseconds.” That can quickly add up to a lot of latency. AI-enabled edge computing solves this problem. Latency is annihilated as all processing happens on the spot. Or, in cases where local processing is not enough, AI can decide to send relevant information to a data center while keeping the irrelevant data on its local drives.
A review by Gartner found that as of 2018, just 10% of all data was processed at the edge. However, Gartner expects that by 2025 fully 75% of all processing will happen at the edge. This is a tremendous shift, and it is enabled by increasingly powerful hardware and smart AI systems which can process information, communicate across networks and make decisions locally in a split second, faster than ever before.
What's more, with 5G under deployment today, the opportunities for developing and deploying high-speed, low-latency applications that require data transfer in fractions of second, we are on the threshold of fully realizing AI and edge compute.
What are you planning, and how can edge AI help? Digi experts can work with you to identify next steps, design and build your solution, and take advantage of the next-generation benefits of edge computing, machine learning and 5G, and harness the power of the latest technologies.
Contact us to start the conversation!