In a rapidly evolving technology landscape, network managers seek to understand edge computing vs cloud computing to make the best choice for their deployment needs. When it comes to edge vs cloud, each technology has distinct capabilities that also intertwine with one another to revolutionize data processing and storage and offer unique advantages.
Edge computing is the relatively newer technology, compared to cloud computing, but you may be wondering, "what is cloud computing replacing?" Both of cloud and edge computing are gradually replacing traditional computing infrastructure, such as corporate data centers, expensive hardware, and costly software upgrades. Here’s a closer look at edge computing and cloud computing, including how they’re similar and how they stand apart.
The Edge and Cloud Computing Relationship
What is cloud and edge computing and how do they work together? The edge computing and cloud computing relationship redefines modern data management through technology integration and performance optimization. This strategy not only solves network challenges but also maximizes efficiency and scalability.
Edge computing and cloud computing architectures coexist and complement each other to leverage their collective strengths. With this synergy, companies can drive innovations by making the most of both robust solutions, each transforming businesses across various sectors in their own ways.
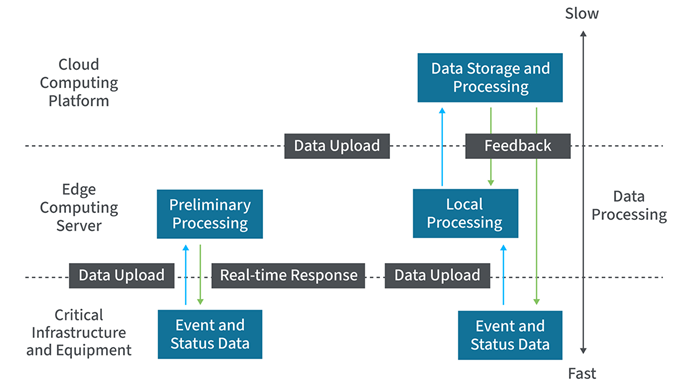
Edge Computing
What is edge computing? It refers to data processing at or near the source of data generation. By deploying hardware at the edge, such as sensors and routers, businesses can augment processing and accelerate computing, all while enhancing security and minimizing data exposure.
For instance, a manufacturing plant might use edge devices to monitor equipment and prevent failures in real time. This proximity to data sources not only accelerates response times, but it also reduces the need for extensive data transmission, saving bandwidth and lowering costs.
For more in-depth information, explore Digi’s edge computing resources.
Cloud Computing
Contrasting edge vs cloud, cloud computing provides immense scalability and cost-effective solutions through enhanced data management. Cloud computing offers vast storage capacities and powerful computational resources beyond what companies can typically implement internally, making it ideal for long-term data analysis and large-scale applications.
In many cases, cloud computing is foundational for Industry 4.0, providing an accessible, scalable platform for data storage, processing, and analytics, taking information generated by IoT devices to enhance productivity and provide additional functionality.
What Is the Edge in Cloud Computing?
In cloud computing, the “edge” is the network infrastructure’s furthest point from the center of the network, where data is exchanged between cloud services and sensor devices, IoT devices and other end nodes.
By processing at the edge, companies can optimize their operations and make quicker decisions based on real-time data analytics. The edge plays a critical role in modern cloud frameworks by accelerating data processing and supporting real-time decision-making. This is vital for creating a more responsive and efficient IoT architecture that works across many vertical industries.
Comparing Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing
Exploring the dynamic between edge computing vs cloud computing reveals a spectrum of capabilities that cater to different technological needs and scenarios. This edge vs cloud comparison delves into the unique strengths and optimal use cases for each, illustrating how they address specific challenges in data processing. By understanding the differences between edge computing vs cloud computing and evaluating their roles in various contexts, businesses can make better decisions about their technology deployments, ensuring they maximize efficiency and innovation.
Core Similarities in Cloud and Edge Computing
While a cloud vs edge computing comparison often highlights the distinctions, both technologies share fundamental objectives that enhance modern computing frameworks. Though their approaches differ significantly, these platforms aim to optimize processing efficiencies and expand computational capabilities by offering:
- Scalability and flexibility
- Enhanced data management
- Cost-effectiveness
It’s important to understand that neither technology is inherently superior. When your evaluation centers on edge vs cloud, it’s important to realize each serves distinct strategic purposes. For instance, edge computing is not just about speed – it plays a crucial role in remote device management. By contrast, cloud computing offers more than storage, such as advanced artificial intelligence capabilities that are transforming industries globally.
Scalability and Flexibility
Both edge and cloud computing architectures offer scalability, though in different dimensions, facilitating tailored responses to diverse technological demands.
Cloud computing excels in handling vast amounts of data and users simultaneously, making it ideal for applications that require global accessibility and massive resource pooling. On the other hand, edge computing scales by multiplying the number of edge nodes to enhance responsiveness and reduce latency in localized contexts when immediate action is required.
For example, in smart city applications, edge devices process and respond to real-time data to optimize traffic flow. At the same time, cloud systems manage broad-scale analytics and software updates that improve system-wide traffic management. This dual approach ensures efficient handling of both immediate and longer-term needs.
Enhanced Data Management
Both cloud and edge technologies significantly improve data management by strategically distributing processing activities to maximize efficiency and effectiveness. Cloud solutions centralize data storage and complex analysis, which is beneficial for long-term strategic planning and compute-intensive tasks that are not time-sensitive. By contrast, edge solutions process data locally on devices at the network's periphery, without the latency of data transmission to centralized data centers.
For instance, in healthcare, edge devices can monitor patient vital signs in real-time during surgery to provide instant data to medical professionals. At the same time, cloud systems can analyze long-term patient data trends to improve overall strategies and outcomes. This complementary approach ensures optimal data utilization and management.
Cost-Effectiveness
Both cloud and edge computing can significantly reduce costs, but they do so through different mechanisms tailored to specific operational needs.
Cloud computing helps businesses reduce upfront capital expenses by leveraging economies of scale with shared resources and infrastructure. That’s ideal for startups and companies that must scale quickly without heavy initial investments. Edge computing, meanwhile, cuts operational costs by saving bandwidth and reducing the volume of data sent over a network. That’s particularly beneficial for applications involving large data volumes or sensitive information that requires local processing to ensure privacy and security.
For example, retail chains rely on edge computing for efficient real-time inventory tracking at individual stores to prevent stockouts and overstock situations. Cloud computing offers centralized inventory management and analytics to optimize the entire supply chain.
Key Differences in Edge and Cloud Computing
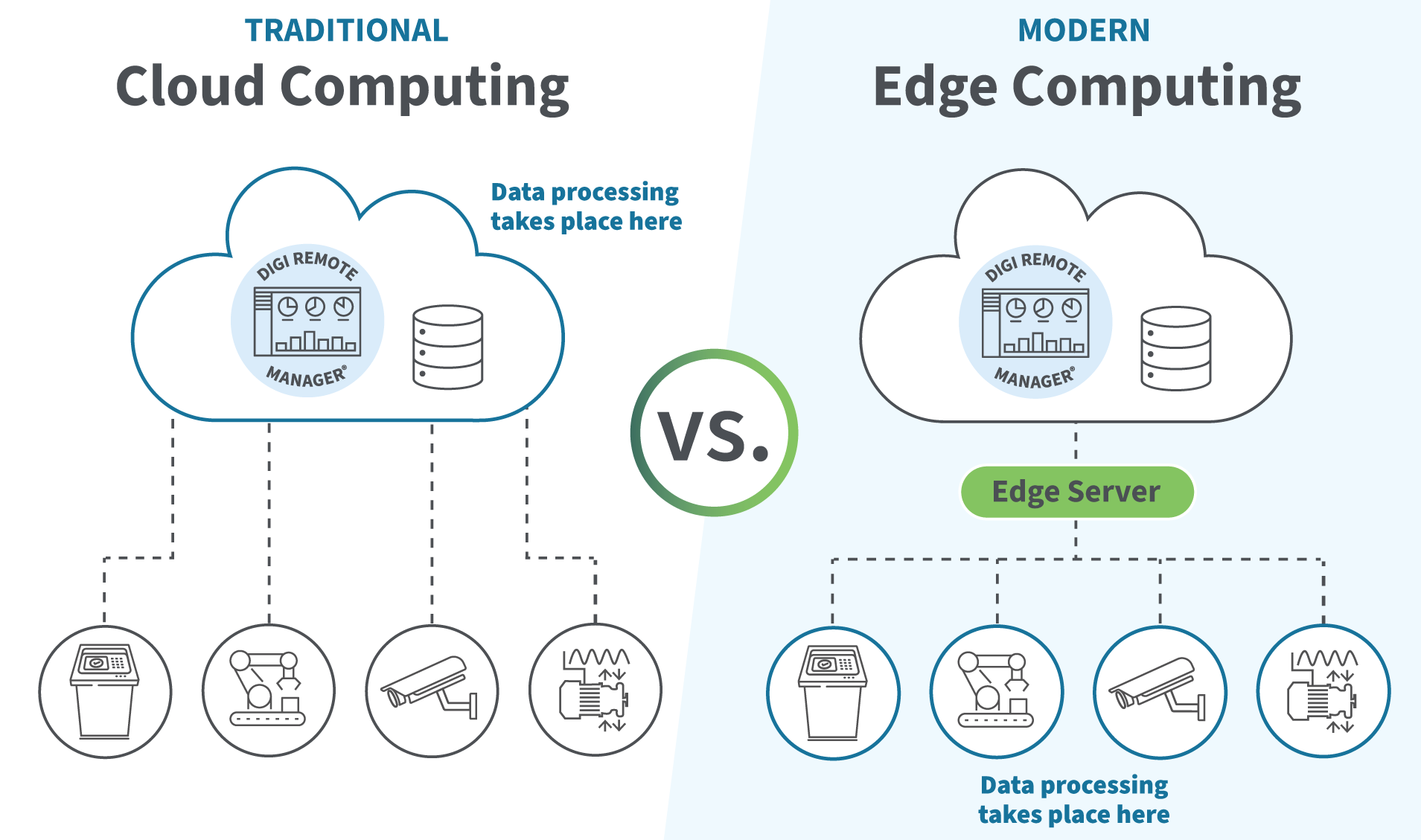
When exploring cloud computing vs edge computing, it's crucial to recognize their fundamental differences in design and functionality. Each technology offers benefits and presents specific limitations that can influence deployment scenarios.
Ultimately, comparing cloud vs edge computing is relatively straightforward. The two technologies differ in fundamental ways, including:
- Data processing location
- Latency and responsiveness
- Data privacy and security
- Core functions
- Connectivity dependency
Here’s a closer look at edge deployment vs cloud deployment and how they compare in each of the abovementioned ways.
Data Processing Location
A key distinction in the cloud vs edge computing debate centers on where data processing occurs. Cloud computing processes data in centralized data centers that are potentially far from the source of data collection. This model is highly efficient for handling vast amounts of data from multiple sources and is ideal for applications that don't require immediate action.
By contrast, edge computing processes data directly at or near the source of data generation, such as on local devices or nearby servers. This proximity allows quicker data access, benefiting applications that rely on real-time decision-making, such as autonomous vehicles or real-time monitoring systems. This difference fundamentally affects the suitability of each computing model for various applications.
Latency and Responsiveness
When evaluating cloud computing vs edge computing, latency and responsiveness are critical factors in the performance of computing systems, particularly in scenarios requiring immediate data processing. Edge computing significantly reduces latency because data does not have to travel long distances to a central server. Instead, it is processed locally on intelligent edge devices. This is especially beneficial for applications such as emergency response systems, where every millisecond counts.
Conversely, cloud computing applications can experience higher latency because data must travel between the remote server and data sources. However, for applications where split-second decisions are not critical (e.g., monthly business analytics), the cloud's centralized processing capabilities provide ample performance without the need for the speed edge computing offers.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy and security concerns are paramount when choosing between edge and cloud computing. Edge computing offers enhanced data privacy by processing data locally on the device, reducing the exposure of sensitive data to external networks. This localized processing is crucial when data sensitivity is high, such as in healthcare or government operations.
However, while initially perceived as less secure, cloud computing has evolved, with robust security measures that rival and sometimes exceed those at the edge. Cloud providers invest heavily in advanced security protocols and infrastructure, benefiting from economies of scale. Regardless, the choice between edge and cloud should consider the specific security needs of the application.
Core Function
The core functions of edge and cloud computing highlight their distinct roles in information technology. Edge computing is primarily about bringing computational power closer to the data source, which is crucial for remote device management and applications that require immediate processing. This is particularly evident in industries like manufacturing, where edge devices control and monitor production lines in real time.
On the other hand, the core function of IoT cloud computing is to aggregate data from across an entire network for comprehensive analysis, storage, and long-term management, which provides businesses with insights that are not possible at the edge alone. Each serves different, often complementary, purposes within an organization's IT architecture.
Connectivity Dependency
Connectivity dependency varies significantly between edge and cloud computing. Edge computing and cellular connectivity allow edge devices to function effectively even with limited or intermittent internet connectivity. This is crucial in remote locations or situations where constant connectivity to a central server is challenging or costly. Edge computing's ability to process and store data locally ensures applications remain operational regardless of network status.
By contrast, cloud computing requires a stable and continuous internet connection to function properly, since access to data and applications depends on real-time data transmission to and from the cloud. This dependency makes cloud solutions less suited for environments where network connectivity is unreliable.
The Future of Edge and Cloud Computing
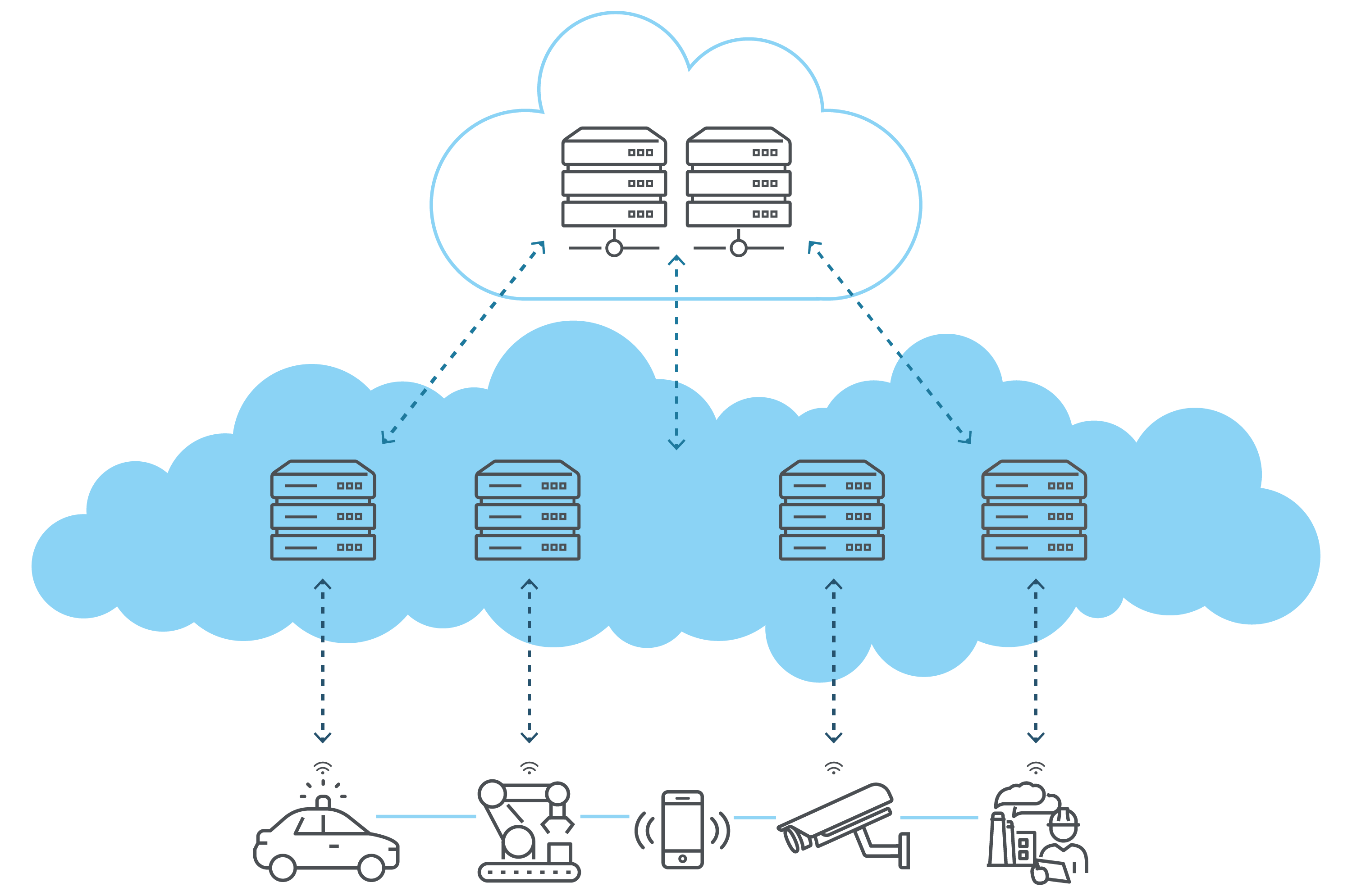
The future of edge-to-cloud computing promises a seamless integration of both technologies, maximizing their strengths to create more robust, intelligent systems.
So, what is edge to cloud computing? In this hybrid model, data flows from the edge, where it's generated and initially processed, to the cloud, where it can be further analyzed and integrated into broader applications.
This model leverages edge to cloud strategies to enhance real-time data processing capabilities at the edge with the expansive computational power of the cloud. By incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) into this framework, systems can predict maintenance needs, optimize operations, and personalize user experiences in real time. The ongoing development of AI algorithms optimized for edge deployment continues to push the boundaries of what's possible, from smarter IoT devices to autonomous vehicles, making edge to cloud architectures fundamental to the next wave of technological innovations.
Hybrid Cloud Edge Computing
Hybrid cloud and edge computing combines cloud environments' computational power and storage capabilities with the real-time processing and localized data handling of edge devices. This approach allows for the distribution of workloads based on latency, bandwidth, and data privacy requirements. Critical data processing and decision-making tasks occur at the edge, close to the data source, reducing latency and improving response times. Meanwhile, extensive data analytics, machine learning model training, and long-term storage are handled by cloud services, leveraging their scalable resources.
By integrating these elements, hybrid cloud and edge computing offers enhanced performance, reliability, and scalability, making it ideal for applications such as IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities, where both rapid local processing and comprehensive data analysis are essential. This synergy allows businesses to extend cloud services to their own data centers or edge locations, supporting applications and workloads that require low latency, local data processing, or data residency, thus facilitating a smooth and efficient operation of their IT environment.
By processing data at the edge, businesses can reduce latency and improve responsiveness, then use the cloud for deep analytics, greater storage capabilities, and comprehensive management tools. This versatile approach supports a wide range of applications, from real-time retail analytics to complex engineering simulations, making it a powerful model for modern enterprises.
Ultimately, the debate surrounding edge computing vs cloud computing highlights a landscape rich with technological advancements, each tailored to meet specific needs and scenarios. While edge computing offers immediacy and locality in data processing, cloud computing provides vast scalability and powerful centralized resources.
The future lies in leveraging both cloud and edge, not choosing one over the other. By understanding the unique strengths of edge computing and cloud computing and how they complement each other, organizations can make informed decisions that optimize their operational efficiencies and drive innovation.
Digi offers cloud, edge, and edge to cloud solutions today. These include:
- Digi Remote Manager®, and its on-premises counterpart, Digi On-Prem Manager: Digi Remote Manager is our flagship remote management solution, providing secure, cloud-based visibility and control across your entire network of deployed devices, including remote out-of-band management. Digi On-Prem Manager is the on-prem counterpart, enabling edge computing and easy asset management fully inside the corporate firewall. These cloud and edge solutions support a wide range of Digi products, including Digi enterprise routers, Digi industrial routers, Digi transportation routers, Digi serial device servers, and Digi AnywhereUSB® Plus connectivity solutions.
- Digi ConnectCore® Cloud Services: These value-added services support Digi ConnectCore system-on-module solutions, enabling OEMs in a wide range of industries to create connected devices with remote-dashboard, remote-service and remote-application capabilities.
- Digi X-ON® Cloud: Digi X-ON Cloud is a scalable management platform, supporting Digi’s complete edge to cloud computing solution for the LoRaWAN® standard, which includes a Digi long-range Digi XBee® module, a gateway, and a deployment tool. Digi X-ON also supports the Digi XBee® intelligent edge controller, a cloud managed smart industrial IoT solution for edge sensors and systems.
- Digi Axess: Digi Axess offers edge and cloud-based monitoring and control capabilities for Digi industrial automation solutions, including Digi Connect® Sensor XRT-M and Digi’s Z45 Industrial Controllers. Whether you prioritize edge-based control or the flexibility of cloud-based monitoring, Digi Axess serves as your unified platform, offering an intuitive interface to streamline data management for enhanced operational efficiency.
As technology continues to evolve, the synergy between edge and cloud computing will undoubtedly shape the next frontier of digital transformation. If you’re ready to embrace edge and cloud computing and all of what these technologies offer, Digi can make the process seamless.
Next Steps