The Internet of Things (IoT) and IoT edge computing have been creating a buzz in the tech world for a number years. And today, IoT and edge computing are on course to see spectacular growth in the next decade, fueled by a range of factors from the desire to gain insights from devices in far-flung places to a need for operational efficiency and ROI.
Want to learn how to leverage IoT in business? You’ve come to the right place. This article explores the transformative power of IoT by delving into ten specific ways it could reshape your business’s digital operations.
Whether you’re strategizing a long-term plan to integrate IoT and edge computing into your business operations, or simply looking to learn something new, we’ve included a range of interesting industries and use cases likely to experience rapid development. Let’s dive in!
How the Internet of Things Connects Our World
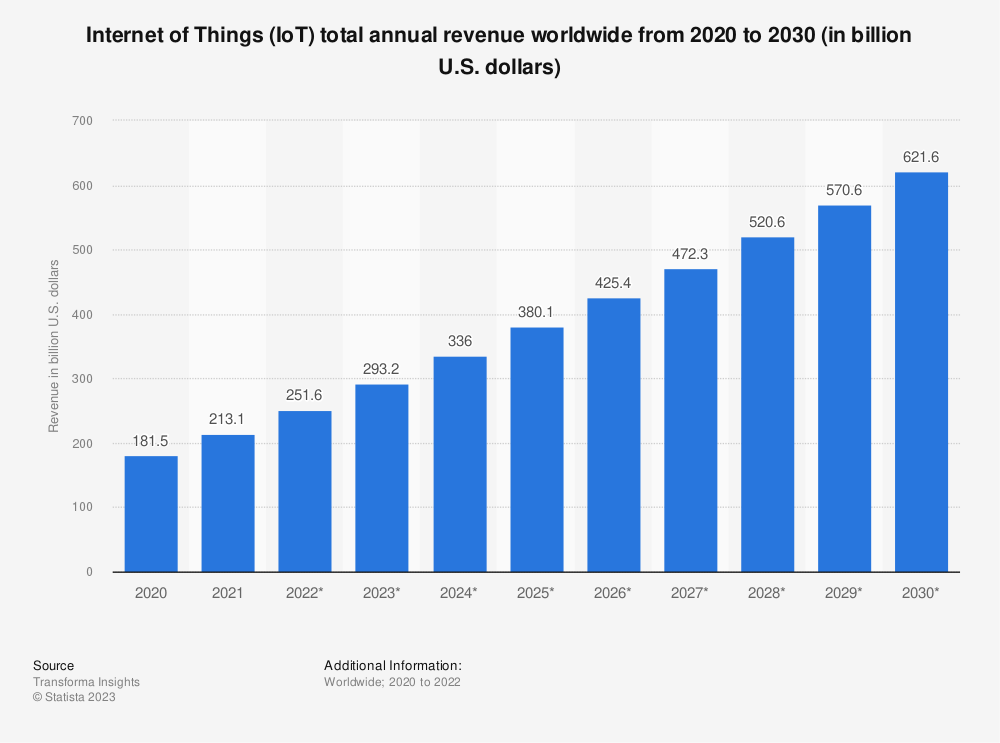
IoT is a network of connected devices embedded with sensors, software and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data. The capabilities of the IoT that drive business efficiencies are at the root of the enormous growth of the Internet of things. In fact, Statista forecasts that revenue in the IoT market will reach $621.6B by 2030 — a figure that will have tripled from 2020.
IoT devices range from everyday objects, such as a Vonage business phone or a home automation device, to connected vehicles, robotics, industrial monitoring and automation equipment and critical infrastructure that supplies energy and water to our cities. The underlying theme is that these devices can communicate with one another over wireless networks to provide an array of benefits such as true automation in Industry 4.0 applications, remote infrastructure management, and edge intelligence.
Edge computing is reshaping business’ operations across several sectors. While it requires careful consideration and implementation, there are numerous ways your business can leverage intelligence at the edge in the digital age.
Advantages of Edge Computing and IoT in Business
So, what are the benefits of IoT’s edge computing model and how could this empower your business to enhance and automate its operations?

Here are the overarching benefits of IoT edge computing that you should know about:
- Reduced latency: By processing data closer to edge devices, you’ll minimize the latency associated with sending data to a remote server for processing. This is crucial for real-time applications that require near-instantaneous responses to function correctly, which includes many IT devices.
- Bandwidth optimization: Edge computing reduces the need for transmitting large volumes of raw data to the cloud, as it only sends relevant or aggregated data. This helps optimize bandwidth usage and reduces network congestion, which in turn, can reduce your operational costs.
- Enhanced reliability of tech: With edge computing, critical applications can continue operating even without an Internet connection. Local processing and decision-making capabilities allow the system to remain functional, ensuring business continuity.
- Improved data privacy and security: Edge computing IoT devices reduce the exposure of sensitive data by processing it locally instead of sending it to the cloud. Such a model is attractive to industries where data protection is critical, such as healthcare, finance, utilities and infrastructure, where cyberattacks can have disastrous consequences.
- Access to real-time insights: By analyzing data at the edge, your business can extract immediate insights and take timely actions. This enables faster response times, proactive maintenance and more efficient operations.
In short, edge computing in IoT devices enables businesses to take computational power into their own hands and enhance operations for greater efficiency in the digital age. And today, network-wide management tools can provide a "single pane of glass" for gaining insights and instant notifications from across the network. For instance, with Digi Remote Manager®, you can track and manage all of your IoT devices in a single, intelligent network management interface.
10 Ways IoT and Edge Computing Can Transform Business Operations
To illustrate the advantages of IoT in business mentioned above, let’s explore ten important use cases showing how edge computing IoT technology is emerging as a powerful driver in digital transformation.
1. Smart Grids
IoT enables intelligent grid systems by connecting various energy assets, such as power plants, substations and meters, through a network of sensors and communication devices. These IoT devices collect real-time data on energy generation, consumption patterns and grid conditions.
For instance, smart meters equipped with IoT technology can measure energy usage at specific intervals and transmit the data wirelessly. This data allows utility companies to optimize energy distribution, balance loads and detect faults, resulting in more efficient energy management and reduced costs.
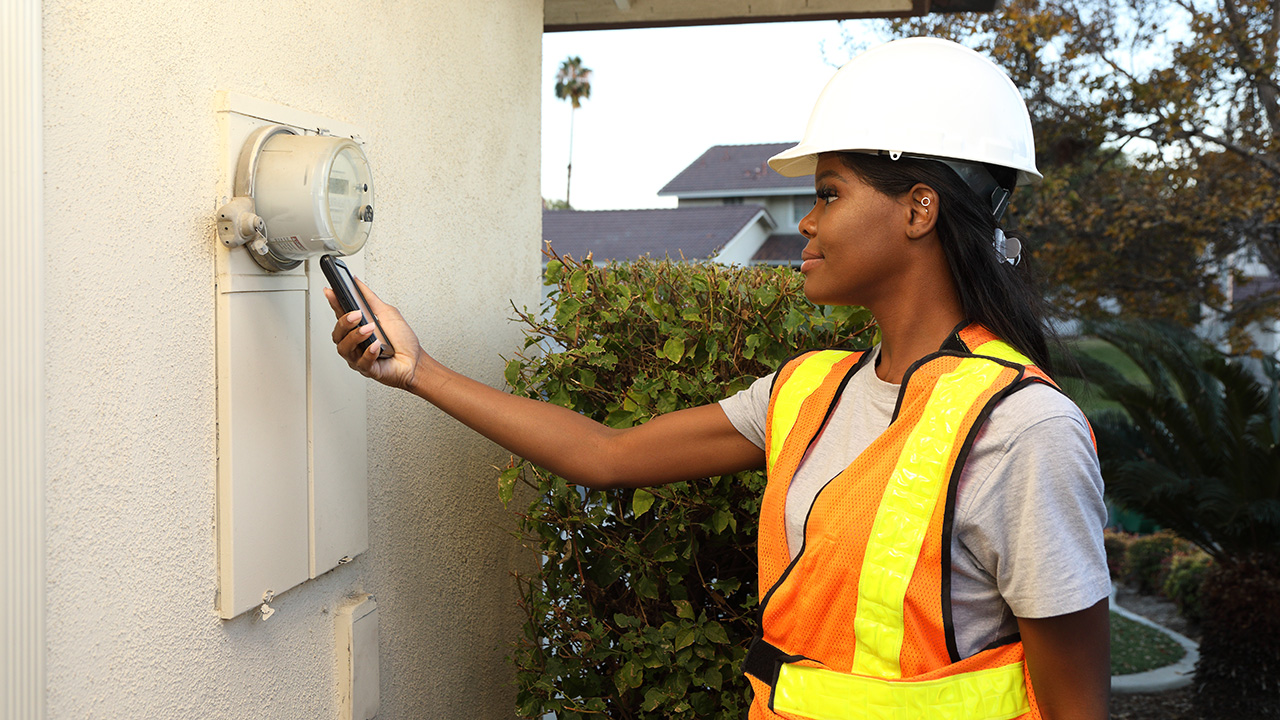

IoT devices in practice: Smart meters with built-in communication modules.
2. Environmental Monitoring
IoT devices with in-built sensors and data loggers are crucial in environmental monitoring. These devices can collect data on anything from air quality, water quality and soil conditions to biodiversity indicators.
The device can collect and analyze this data, only alerting external systems when it passes threshold levels. For instance, IoT-enabled air quality sensors can measure pollutant levels in real time, enabling authorities to identify pollution hotspots and take immediate corrective action.
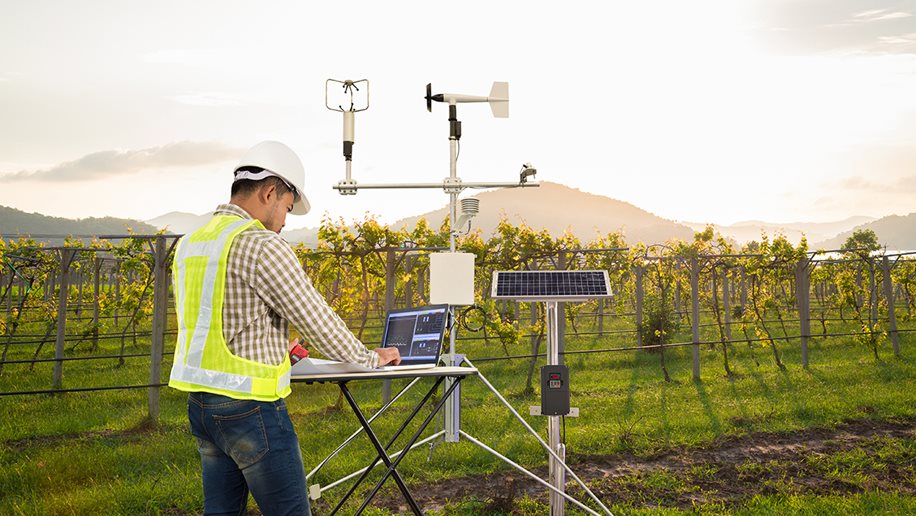

IoT devices in practice: Environmental sensors installed in a vineyard.
3. Connected Buildings and Building Security
One of the latest trends in the construction industry is a shift toward connected buildings.
Here, occupancy sensors can detect the presence of occupants, allowing for optimized energy usage by automatically adjusting lighting and HVAC systems. Smart thermostats use IoT technology to learn user preferences and adjust temperature settings accordingly.
Finally, IoT-enabled surveillance cameras provide real-time video feeds and alerts for enhanced security and remote monitoring.
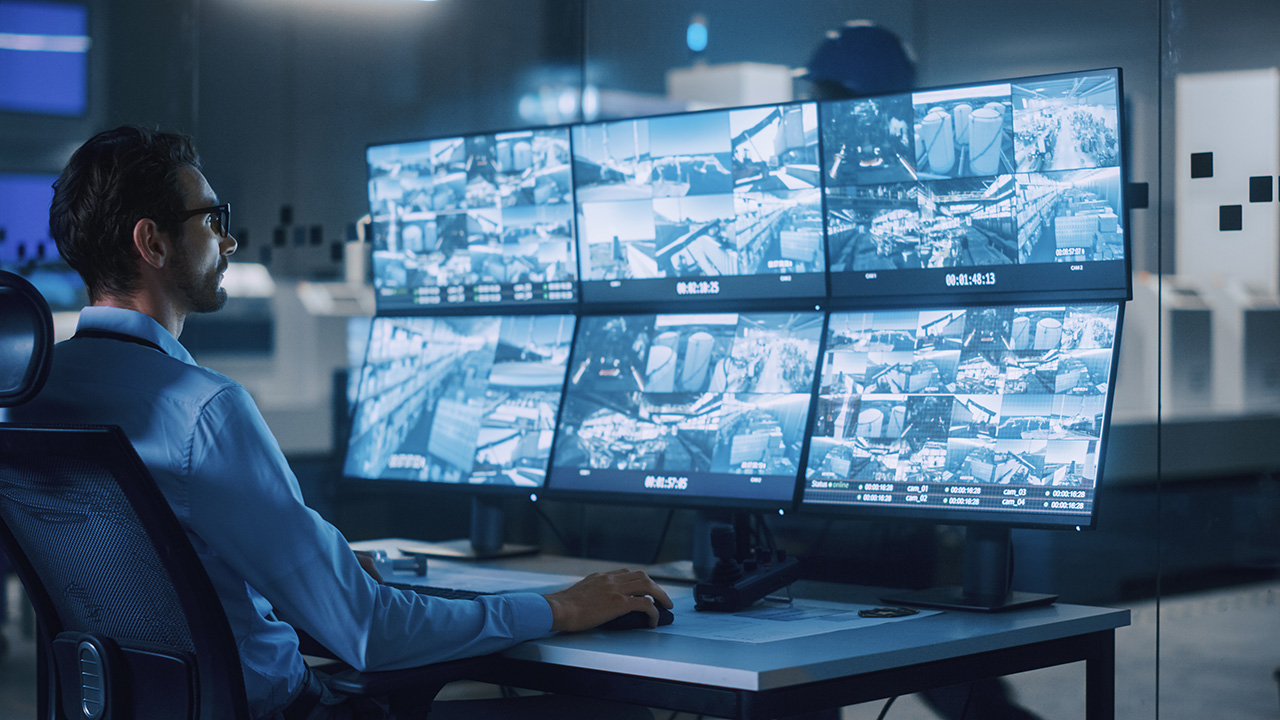

IoT devices in practice: Security monitoring in a manufacturing facility via distributed security cameras.
4. Supply Chain Management
IoT devices can be deployed throughout the entire supply chain to provide real-time visibility and tracking.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags attached to products or packaging enable accurate identification and tracking at various stages of the supply chain. GPS trackers monitor the location and movement of goods, allowing businesses to optimize logistics and provide customers with real-time shipment updates.
Meanwhile, temperature sensors ensure the integrity of perishable goods by monitoring temperature conditions during storage and transportation.
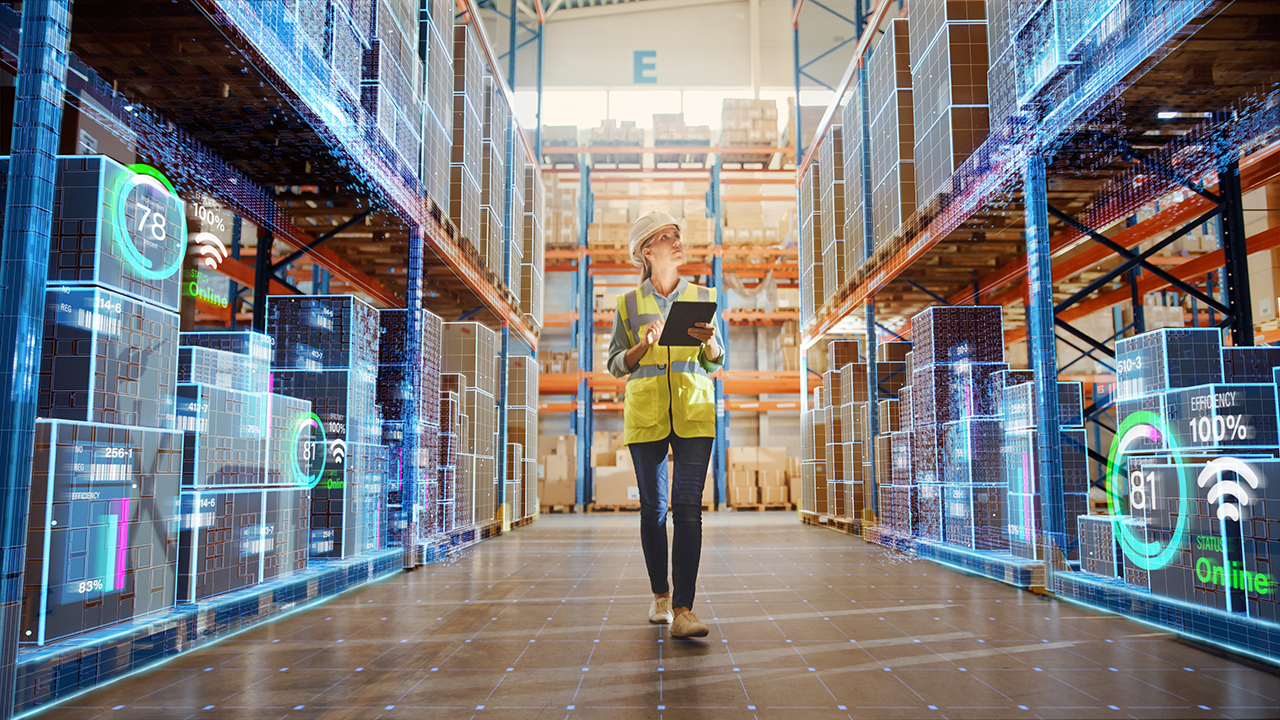

IoT devices in practice: RFID tags attached to individual products or pallets.
5. Self-Driving Cars
Technology is changing the way we interact with others and conduct daily activities. One exciting use case is self-driving cars.
IoT plays a crucial role in enabling driverless cars by connecting various vehicle components and systems. Devices such as cameras and LiDAR scanners collect data on the vehicle's surroundings, including road conditions, obstacles and traffic patterns.
This data is processed in real time by onboard computers to make informed decisions on navigation, speed and driving behavior. Self-driving cars can optimize routes, improve fuel efficiency and enhance road safety through advanced IoT-enabled technologies.
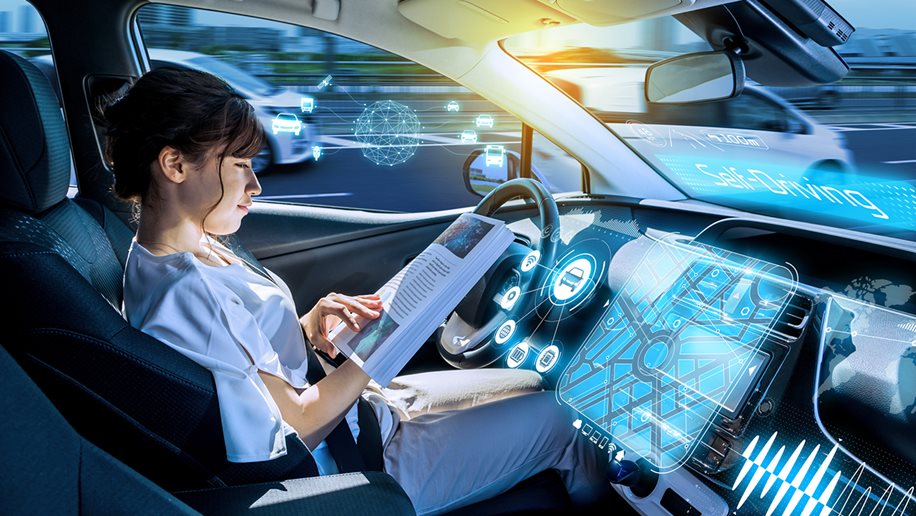

IoT devices in practice: Autonomous vehicle utilizing LiDAR scanners, sensors and connected vehicle technology.
6. Customer Service
IoT technologies are transforming call center operations by providing advanced features and capabilities. For example, VoIP phone features integrated with IoT enable call centers to streamline communication processes, such as call routing, call recording and intelligent call analytics.
These features enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of customer interactions, enabling agents to provide a personalized service and improve customer satisfaction. In addition, IoT-powered call center technologies leverage real-time data and analytics to provide agents with valuable insights about customers, enabling them to deliver more targeted and proactive support.
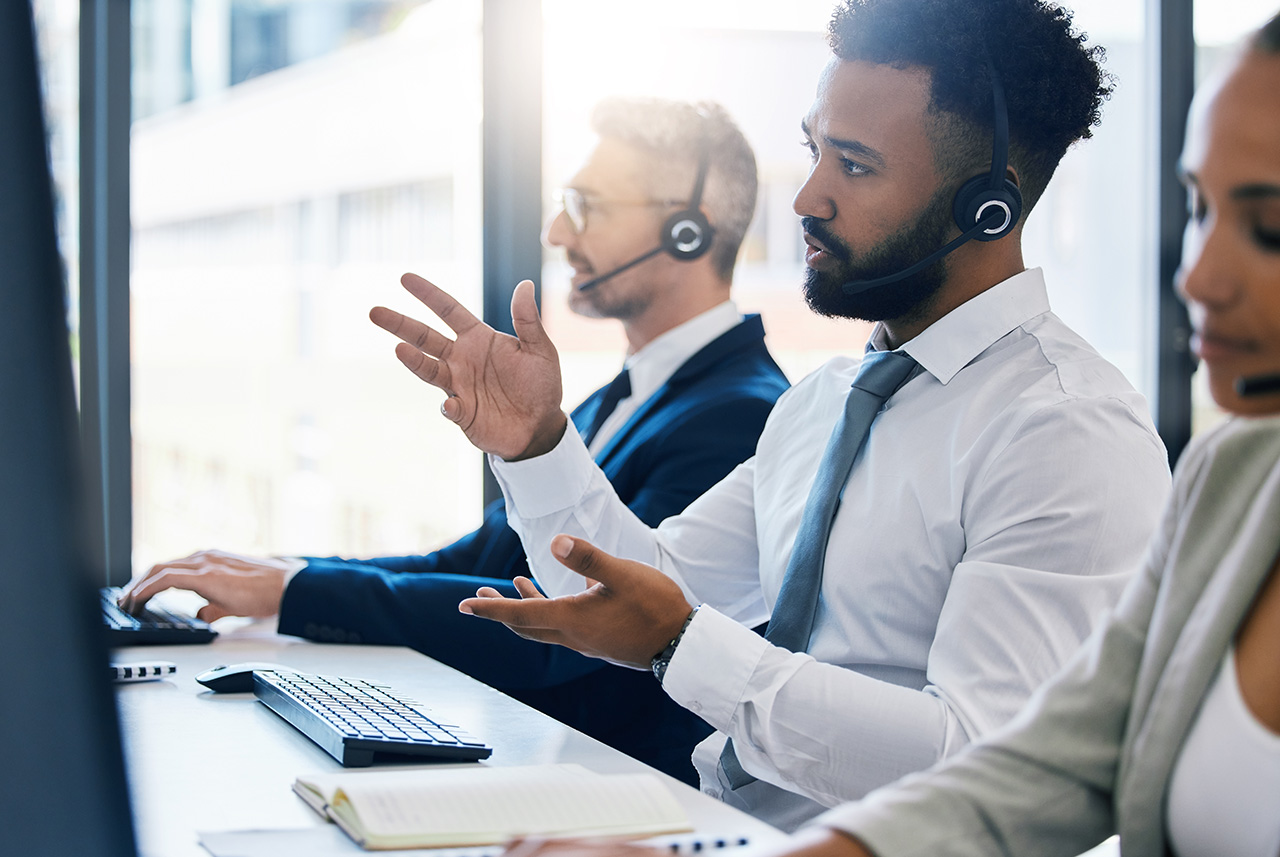

IoT devices in practice: VoIP phone systems with advanced call center technologies.
7. Healthcare
IoT has revolutionized healthcare by enabling remote patient monitoring and connected medical devices.
Wearable devices, such as biosensors and medical implants, collect real-time health data from patients and transmit it securely to healthcare providers. This allows for practitioners to continuously monitor vital signs, administer medication and manage diseases.
IoT also facilitates telehealth services, enabling virtual consultations and remote diagnosis. Connected medical devices, like smart insulin pumps or cardiac monitors, ensure accurate and timely healthcare interventions.
That means you could be seen by a doctor from the other side of the world.
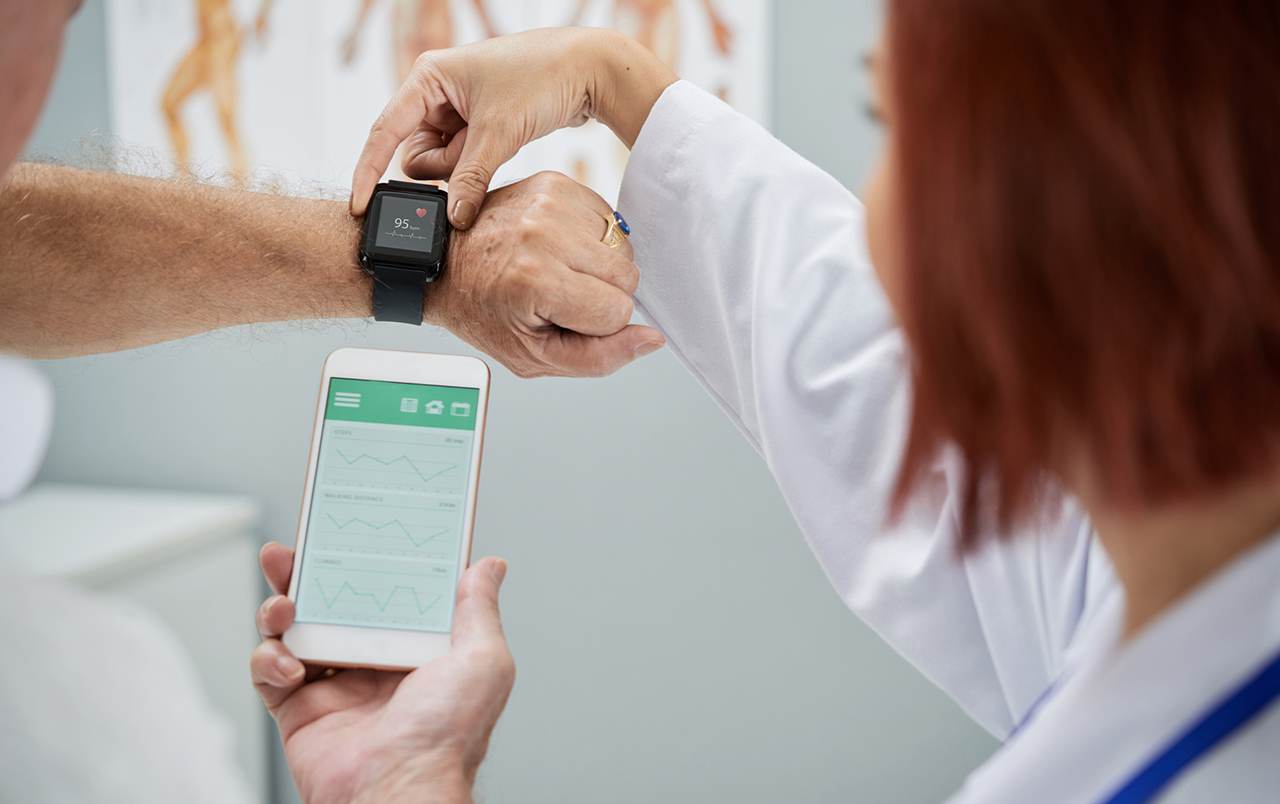

IoT devices in practice: Medical wearables that monitor steps, heart rate and other metrics.
8. Predictive Maintenance
IoT-enabled predictive maintenance strategies leverage data from devices to monitor technical equipment health in real time. These sensors collect data on various parameters, such as temperature, vibration and energy consumption.
By analyzing this data using machine learning algorithms, businesses can identify patterns and anomalies that indicate potential equipment failures. This proactive approach allows for timely maintenance interventions, reducing downtime and extending equipment lifespan.

IoT devices in practice: Condition monitoring in industrial machinery.
9. Agricultural Operations
IoT is transforming agriculture as we know it through precision farming techniques.
For instance, autonomous recording stations provide real-time data on soil conditions, weather conditions and patterns and crop health. Farmers can access this data remotely and make informed decisions on irrigation schedules, fertilization and pest control.
The availability of modern cellular routers makes reliable connectivity possible even in environments where traditional wired cabling doesn’t make sense, such as in agricultural settings.
In this way, IoT-enabled agricultural operations optimize resource usage, reduce environmental impact and return greater crop yields.
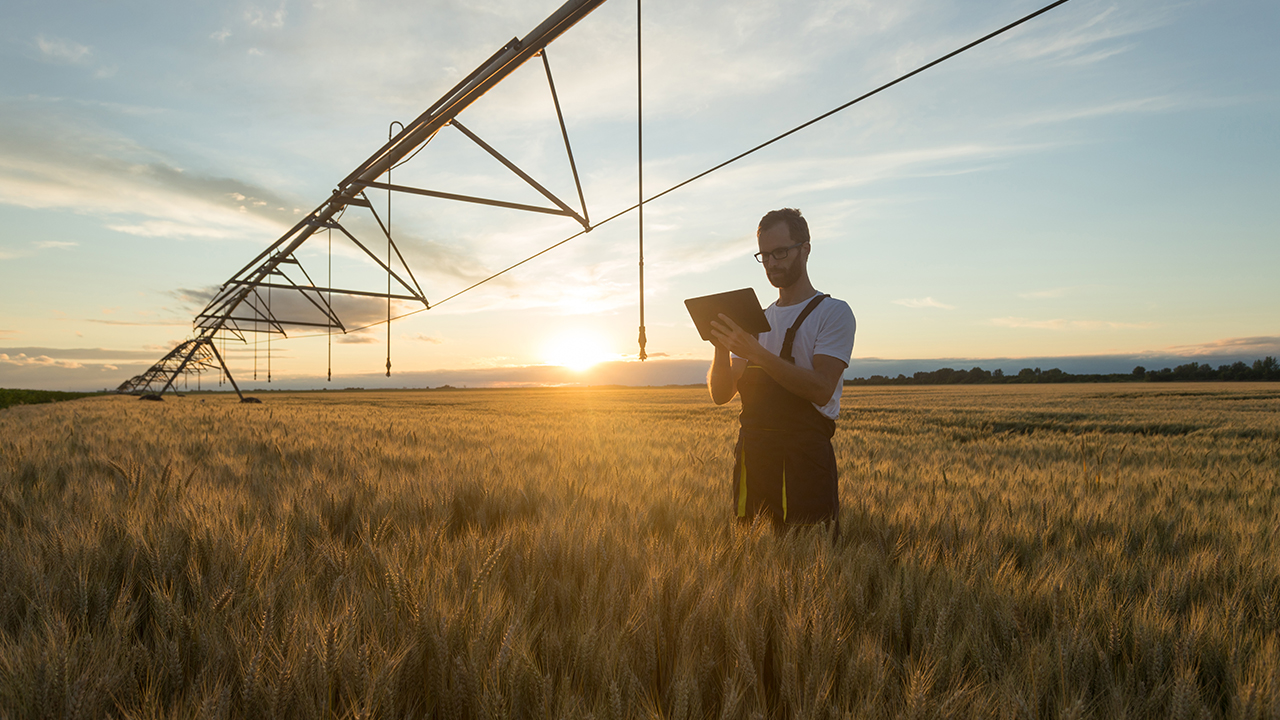

IoT devices in practice: Soil moisture and equipment monitoring devices in agriculture.
10. Retail Operations
IoT applications in the retail industry can enhance customer experience and optimize inventory management. IoT devices, such as smart shelves and beacons, provide real-time inventory tracking, enabling retailers to efficiently manage stock levels and reduce out-of-stock situations.
Companies can leverage Dynamic QR Codes for business to create interactive and engaging experiences for customers, allowing them to access product information, promotions, and special offers by scanning QR codes with their smartphones.
Moreover, IoT enables seamless checkout experiences with technologies like RFID-enabled self-checkout or mobile payment solutions. You may want to take note of this feature in your next website markup to promote accessibility.
In fact, you’ll find IoT devices using edge computing techniques in a wide range of applications at the core of retail operations. From self-serve kiosks to the top-tier connectivity needed to implement connectivity for secure financial transactions, IoT technology is at the heart of modern commerce.
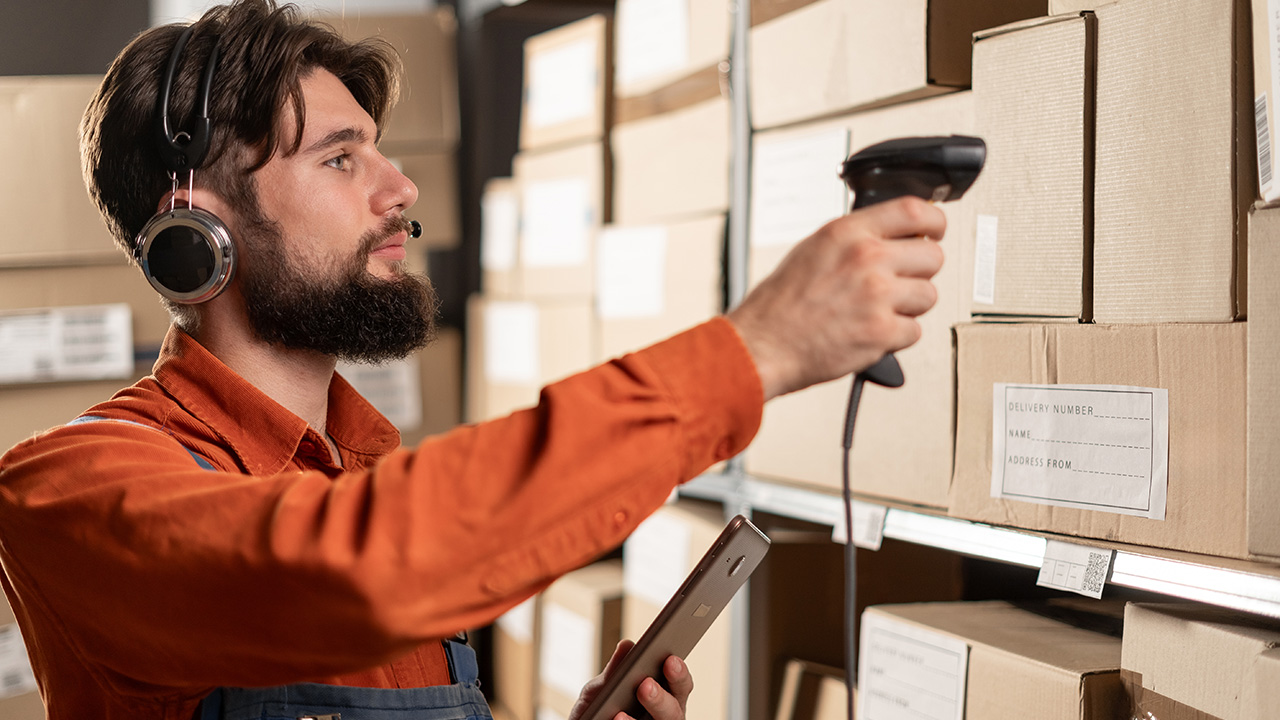

IoT devices in practice: RFID-enabled smart shelves that track inventory levels in real time
Conclusion
The Internet of Things is revolutionizing much of what we do online by facilitating a shift from cloud to edge computing.
What does this mean for businesses? In today’s digital landscape, it gives you more control of your digital footprint, unlocking new opportunities and bringing many benefits, such as affordability and security.
Regardless of your industry, you’re likely to see some form of disruption from IoT tech in the near future.
So, next time you ask a smart assistant to play your favorite music, check your daily steps with a wearable fitness tracker, or even track your pet with a smart collar, remember that you are experiencing just a taster of what this tech could one day become!
Next Steps
About the Author
 Ryan is an award-winning copywriter, with 20+ years of experience working alongside major US brands, emerging start-ups and leading tech enterprises. His copy and creative have helped companies in the B2B marketing, education and software sectors reach new customer bases and enjoy improved results. You can find him here on LinkedIn.
Ryan is an award-winning copywriter, with 20+ years of experience working alongside major US brands, emerging start-ups and leading tech enterprises. His copy and creative have helped companies in the B2B marketing, education and software sectors reach new customer bases and enjoy improved results. You can find him here on LinkedIn.