The growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) has produced a corresponding growth in the volume of data collected at the network edge. The need to manage that data volume, in turn, has driven rapid growth in edge computing use cases across almost every industry.
In a nutshell, edge computing is processing that takes place as close as possible to the process or thing being monitored by an IoT device. Edge computing can be performed by devices directly connected to sensors, by
routers or gateways that transmit data, or by small installations of servers that are deployed on-site in a closet or enclosure.
In the early days of the Internet of Things expansion, the relatively modest number of connected devices meant that organizations could afford to send all of their IoT data to the cloud or a corporate data center for processing, analysis and storage. But the recent proliferation of connected devices in virtually all industries and the steadily increasing volume of data they collect makes this approach impractical. Thus the need for edge computing.
We’ve discussed edge computing here in the Digi blog on several occasions. We’ve provided an
edge computing definition and outlined its business benefits in terms of
saving organizations bandwidth, time and money. In this article, we’ll look at edge computing examples and how they respond to the growing need for device and data optimization at the network edge. But first, let’s review some of the factors driving its growth.
Jump to:

There are several reasons why the edge computing market is increasing rapidly. In addition to the greater number of connected devices, there are three key drivers of growth for edge computing:
- Latency — For many time-sensitive applications, the process being monitored requires a response in near real time, with near-zero latency. In these situations a round trip of data to and from the cloud or a corporate data center is impractical.
- Bandwidth — Both the physical limits of available bandwidth and the cost of transmitting large quantities of data make edge computing an attractive alternative.
- Reliability — Network congestion can interrupt the flow of data, causing unacceptable interruptions in use cases such as point-of-sale systems.
On average, most monitoring data collected by IoT sensors tends to be standard “heartbeat” data, which simply indicates that systems are functioning normally. There’s no need to transmit that kind of data to the cloud or a distant corporate data center. By filtering out this unchanging heartbeat data right at the network edge, in close physical proximity to where the data is gathered, edge computing devices can greatly reduce the volume of data that needs to be transmitted, saving on bandwidth and dramatically reducing latency.
The number of edge computing use cases is growing steadily, along with the number of smart devices that can perform a variety of processing functions at the edge. The growth of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning capabilities are also expanding the range of edge computing use cases.

Examples of edge computing can be found in a wide variety of applications and industries. There is also a fair amount of overlap between different edge computing use cases. For example, edge computing functionality in autonomous vehicles is closely connected to edge computing functionality in traffic management applications.
Here are some of the most promising edge computing examples.
Autonomous Vehicles, Electric Vehicles and Charging Stations
 To function safely, autonomous vehicles need to collect and process data about their location, direction, speed, traffic conditions and more — all in real time. This involves sufficient onboard computing capacity to make every autonomous vehicle, in effect, its own network edge. Edge computing devices can gather data from vehicle sensors and cameras, process it and make decisions in milliseconds, with virtually no latency. This instantaneous decision making is a necessity in autonomous vehicles, for obvious safety reasons.
To function safely, autonomous vehicles need to collect and process data about their location, direction, speed, traffic conditions and more — all in real time. This involves sufficient onboard computing capacity to make every autonomous vehicle, in effect, its own network edge. Edge computing devices can gather data from vehicle sensors and cameras, process it and make decisions in milliseconds, with virtually no latency. This instantaneous decision making is a necessity in autonomous vehicles, for obvious safety reasons.
Edge computing features such as lane-departure warning and self-parking applications are already widely available. And as the ability of vehicles to interact with their environment becomes more widespread, so will the need for a fast and responsive network. Autonomous vehicles will operate in concert with other connected vehicles, traffic management systems, roadside units and pedestrians on busy thoroughfares and at intersections.
Electric vehicles need continuous monitoring and can use edge computing for management of data to support predictive maintenance. EV batteries must be monitored, as their longevity depends on the individual habits of drivers, the congestion of the areas they travel and how often they are charged. Edge computing supports data aggregation to report the actionable data for performance and maintenance.
In EV charging stations, edge computing can support real time monitoring and data aggregation of a range of usage and availability metrics to support optimization of charging stations and planning for placement of future stations.
Traffic Management Systems
 In traffic management applications, cameras and sensors can be used in conjunction with edge computing solutions to improve traffic flow. Today intelligent transportation systems generate enormous amounts of data and alerts, and this trend will accelerate as both 5G and connected vehicle technology, or "V2X" (vehicle-to-anything) communications mature.
In traffic management applications, cameras and sensors can be used in conjunction with edge computing solutions to improve traffic flow. Today intelligent transportation systems generate enormous amounts of data and alerts, and this trend will accelerate as both 5G and connected vehicle technology, or "V2X" (vehicle-to-anything) communications mature.
Highly sophisticated systems today, like New York City's traffic management system, can adjust the timing of traffic signals, manage the opening and closing of extra traffic lanes, ensure communications can continue in the case of a public emergency, and take other real-time actions to improve safety and convenience. As mentioned above, intelligent traffic management systems will play a key role the adoption of autonomous vehicles, where near-zero latency is critical.
Public Transit Systems
 In public transit applications, edge computing systems installed in buses, passenger rail systems and paratransit vehicles can aggregate and send only the data needed for to support in-vehicle processes and dispatcher insights.
In public transit applications, edge computing systems installed in buses, passenger rail systems and paratransit vehicles can aggregate and send only the data needed for to support in-vehicle processes and dispatcher insights.
For example, different types of data must be sent to passenger information systems, fleet monitoring and tracking systems, and intelligent surveillance of vehicles and stations for the safety of drivers and passengers. Information about arrival times or delays, or other time-sensitive information can be disseminated to passengers via digital signage or mobile applications.
Smart Cities, Clean Energy and Green Technology
The green tech movement is growing. Cities and smart grid systems can use edge computing devices to monitor public buildings and facilities for greater efficiency in lighting, heating, clean energy and more. For example:
- Intelligent lighting controls use edge computing devices to control individual lights or groups of lights to maximize efficiency while ensuring safety in public spaces.
- Solar fields use embedded edge computing devices to sense weather changes, adjust positioning, and report metrics such as battery usage.
- Wind farms use edge computing to connect to cell towers and route sensor data to substations using cellular routers and switches
Healthcare and Medical Applications
The healthcare and medical industries collect patient data from sensors, monitors, wearables and other equipment to provide healthcare professionals with accurate, timely insights on patient condition.
 Edge computing solutions can deliver that information to dashboards for a complete, at-a-glance view of important indicators.
Edge computing solutions can deliver that information to dashboards for a complete, at-a-glance view of important indicators.
Edge computing solutions equipped with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning can identify outlier data so that medical professionals can respond to health needs in real time with a minimum of false alarms.
Edge computing can also be used in robot-assisted surgery, where near-zero latency is essential. In addition, by processing data locally, edge computing devices can help address issues of data privacy and patient confidentiality.
Retail Applications
 Retail applications generate huge amounts of data from point-of-sale systems, merchandise stocking operations, security video and other business activities. Edge computing can help analyze this diverse data and identify issues that need immediate attention, as well as longer term sales trends and business opportunities, such as the most effective in-store promotions and best product configurations for specific store locations.
Retail applications generate huge amounts of data from point-of-sale systems, merchandise stocking operations, security video and other business activities. Edge computing can help analyze this diverse data and identify issues that need immediate attention, as well as longer term sales trends and business opportunities, such as the most effective in-store promotions and best product configurations for specific store locations.
Edge computing also offers the means to process customer information locally, without data leaving the geographical region where the customer lives, which is an issue of rising concern as it pertains to privacy regulations such as the European Union’s GDPR mandates.
Industrial Process Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
 The use cases in industrial IoT (IIoT) continue to expand with the increasing capabilities, security and sophistication of devices, networks and remote management capabilities.
The use cases in industrial IoT (IIoT) continue to expand with the increasing capabilities, security and sophistication of devices, networks and remote management capabilities.
Sensors and IoT devices in industrial applications such as water and wastewater management, oil and gas and processing plants can track a variety of metrics and monitor the performance of machinery. For example, edge computing architecture can support efficient communications across highly complex SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) systems, to manage the high volumes of data from sensors and PLCs (programmable logic controllers).
Digi Remote Manager® — Digi’s remote IoT device management platform — is a key component of many such operations. SCADA systems very often integrate with critical business intelligence applications via cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud, and Digi Remote Manager facilitates this integration, ensuring that all data is delivered to the correct application.
Additionally, edge computing functionality supports management of failure detection and predictive maintenance. Predicting when a machine or component will fail allows factory operators to perform maintenance or replace a part before a failure occurs, saving costs from lost productivity.
If sensors detect a malfunction or conditions that indicate imminent failure, edge computing devices can trigger an actuator to take immediate corrective action, for example, adjusting the flow rate of a fluid, or modifying the movements of an industrial robot. After taking action, the result can be reported to the cloud for notification or further actions. Edge computing, plus cloud, enables communication between machinery and IoT sensors to improve quality control.
In the oil and gas industry, real-time responses facilitated by edge computing can prevent small problems from becoming catastrophic failures. Oil and gas plants are often located in remote locations and edge computing enables analytical processing close to the facility, meaning there is less reliance on the quality of connectivity to a data center, yet linking edge compute with the cloud allows the remote team to monitor large numbers of sites.
Harness Edge Computing with Digi's Industry 4.0 Solutions
Learn more about Industry 4.0 and Edge Computing with our Industry 4.0 Ebook
Download PDF
Manufacturing
 Industrial IoT has added millions of connected devices in manufacturing plants to gather data on production line performance and the quality of finished products. The low latency of edge computing enables an immediate response to problems on the assembly line, helping to drive improvements in quality and efficiency while reducing the need for human supervision.
Industrial IoT has added millions of connected devices in manufacturing plants to gather data on production line performance and the quality of finished products. The low latency of edge computing enables an immediate response to problems on the assembly line, helping to drive improvements in quality and efficiency while reducing the need for human supervision.
Another edge computing use case in manufacturing is quality assurance. Fully autonomous assembly lines that use robots depend on edge computing solutions along with AI and machine learning to identify production errors and improve product quality.
Agriculture
 Farmers using precision agriculture technology can use edge computing to track growing conditions such as temperature, humidity, soil moisture levels, nutrient levels and other metrics to guide decision-making about watering, fertilizer application and other activities. Edge computing is useful not only across vast acres of farm fields, but also in greenhouses and hydroponic growing facilities where sensors enable operators to track inputs precisely.
Farmers using precision agriculture technology can use edge computing to track growing conditions such as temperature, humidity, soil moisture levels, nutrient levels and other metrics to guide decision-making about watering, fertilizer application and other activities. Edge computing is useful not only across vast acres of farm fields, but also in greenhouses and hydroponic growing facilities where sensors enable operators to track inputs precisely.
Aquaculture (fish farming) is another industry where on-site data processing is critical. Precise monitoring of complex environmental variables is essential in ensuring the health of fish, as well as proper feeding and automation that takes the guesswork out of these processes, which improves vitality and growth, while reducing costs. See the bioFeeder case study.
Security and Worker Safety
 Edge computing can utilize data from on-site cameras, employee safety devices and sensors to help businesses prevent unauthorized physical access to the site, and oversee workplace conditions to ensure employees are following established safety policies. This is especially important for workplaces that operate in hazardous or remote locations, such as at a construction site or on an oil platform at sea.
Edge computing can utilize data from on-site cameras, employee safety devices and sensors to help businesses prevent unauthorized physical access to the site, and oversee workplace conditions to ensure employees are following established safety policies. This is especially important for workplaces that operate in hazardous or remote locations, such as at a construction site or on an oil platform at sea.
Edge computing devices can be used in conjunction with video monitoring and biometric scanning to ensure that only authorized individuals enter restricted areas. Surveillance systems can benefit from the low latency and reliability of edge computing because it’s often necessary to respond to security threats within seconds. Edge computing also significantly reduces bandwidth costs in video surveillance, since the vast majority of surveillance footage requires no response. See a case study.
There are two broad categories of users who require edge computing technology:
- Network managers and systems integrators who need drop-in connectivity to link devices across their IoT networks and quickly establish edge computing functionality for optimal system performance and data management.
- Developers and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) who design and build products with embedded edge computing capabilities, and need programmable development modules, wireless radios and gateways to support rapid development and fast time-to-market.
Digi offers edge computing solutions across the full range of industries to meet the needs of network managers and systems integrators as well as OEMs.
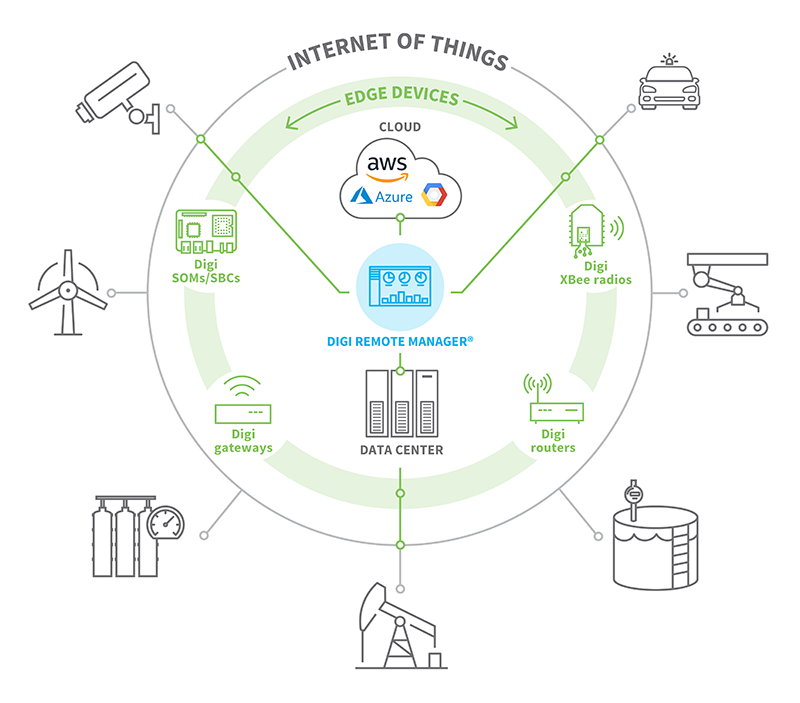
Digi Edge Computing Solutions for Network Managers and Systems Integrators
Digi offers industrial routers, enterprise routers, transportation routers, and IoT gateways capable of supporting many edge computing use cases. Digi routers can also filter and compress the data to minimize bandwidth requirements.
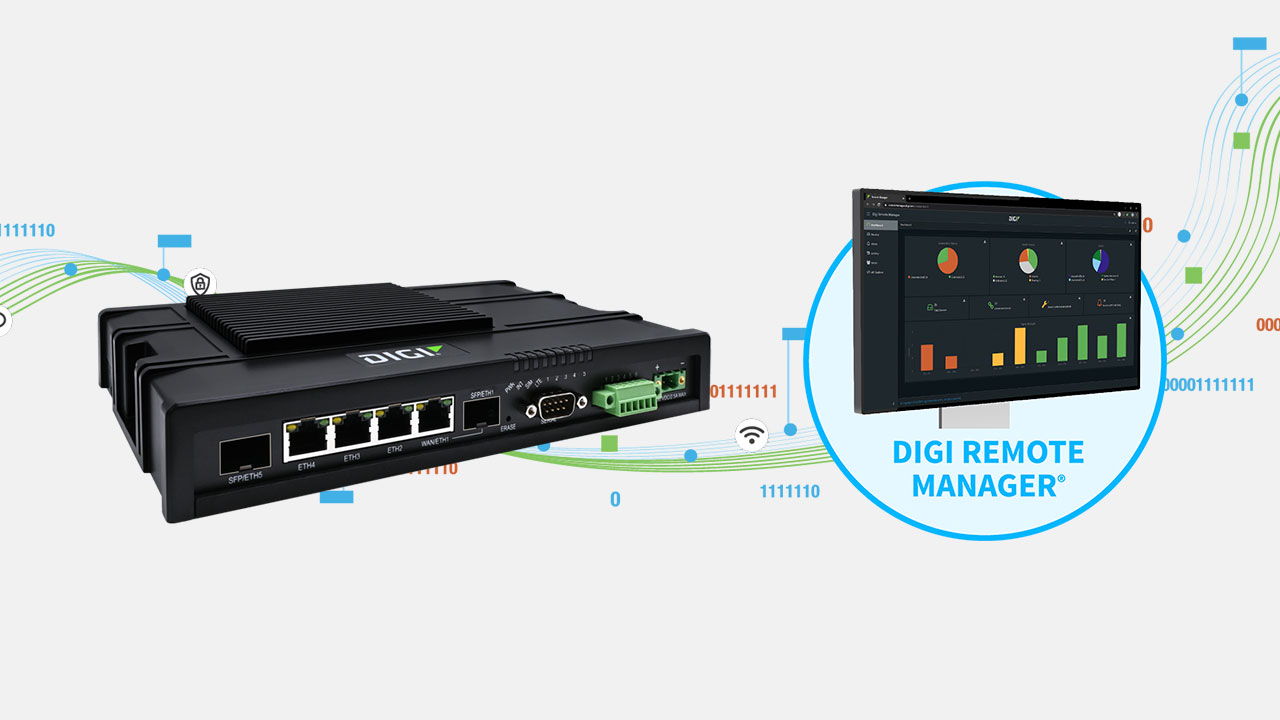 Digi IX40 is a 5G edge computing industrial IoT cellular router solution, purpose-built for Industry 4.0 use cases in industrial infrastructure and manufacturing automation — as well as precision monitoring and control, utilities and traffic management — with industrial-grade components capable of withstanding the challenging environmental conditions found in many industrial settings.
Digi IX40 is a 5G edge computing industrial IoT cellular router solution, purpose-built for Industry 4.0 use cases in industrial infrastructure and manufacturing automation — as well as precision monitoring and control, utilities and traffic management — with industrial-grade components capable of withstanding the challenging environmental conditions found in many industrial settings.
The Digi TX64 5G cellular router offers fast uplink speeds, making it ideal for demanding applications in public transit, transportation and mobile environments. Digi TX64 5G provides true enterprise class routing, security, and firewall — with integrated VPN and reliable 4G failover for areas with limited 5G coverage.
The enterprise-grade Digi EX50 5G cellular router provides reliable primary or backup connectivity in a wide range of indoor edge computing use cases, with an extended operating temperature range for deployment in smart factories, warehouses, construction sites or infrastructure sheds..
Digi Connect® Sensor XRT-M connects sensors deployed across any industrial environment to gather and transmit sensor readings and route critical data for insights and automation, such as operating a switch to shut a valve in a pipeline if a predefined threshold is reached. This trigger functionality makes Digi Connect Sensor a popular choice for edge environments.
 An indispensable tool for deploying and optimizing a network with edge computing is Digi Remote Manager®, the centralized management and control platform that lets users edit device configurations, update firmware, schedule and automate tasks all from their desktop, tablet or smartphone.
An indispensable tool for deploying and optimizing a network with edge computing is Digi Remote Manager®, the centralized management and control platform that lets users edit device configurations, update firmware, schedule and automate tasks all from their desktop, tablet or smartphone.
Digi Remote Manager supports remote management of your entire distributed IoT device network, whether your devices are mobile routers on municipal transit systems, or industrial devices on construction sites or in SCADA systems. With Digi Remote Manager, you can configure any number of devices at one time, keep tabs on your entire network, get alerts, automate security monitoring, and establish your edge computing functionality with ease.
Best of all Digi Remote Manager is now included with all Digi cellular routers based on the DAL OS operating system with one Digi 360 SKU!
 Digi system-on-modules (SOMs), such as the Digi ConnectCore® 8X, provide multiple processing units capable of performing AI and machine vision tasks at the edge of the network.
Digi system-on-modules (SOMs), such as the Digi ConnectCore® 8X, provide multiple processing units capable of performing AI and machine vision tasks at the edge of the network.
Machine vision solutions, for example, can perform image-based analysis for applications including automatic inspection, process control and robot guidance in industry.
Digi XBee® embedded devices can be programmed to perform various functions at the edge. These compact, embedded modems can take readings on a regular basis and initiate action when certain thresholds are reached. MicroPython programmability also enables developers to control the functionality of edge computing devices.
Digi EX15 IoT gateways are all-in-one solutions. These devices perform gateway functions, including aggregating data, converting it from analog to digital format, and encrypting it before transmitting it over the network, and also act as cellular routers, delivering secure, persistent connectivity anywhere.
Embedded Security for Edge Devices
Security, of course, is a critical consideration on the edge as it is everywhere. The integrated features and scalability of the Digi TrustFence® security framework give all Digi embedded solutions a powerful toolset for building security into edge computing-deployments. Additionally, OEMs working with Digi ConnectCore system-on-modules have access to two important value-added services:
- Digi ConnectCore Security Services are services and tools that enable you to maintain the security of your devices throughout the entire product lifecycle.
- Digi ConnectCore Cloud Services enable OEMs to create connected devices with remote-dashboard, -service and -application capabilities using Digi ConnectCore system-on-modules (SOMs).
Design, Development and Deployment Services for Edge Computing
For those who need to augment their capabilities with additional engineering or deployment resources, Digi has supporting services.
- Digi Wireless Design Services provides design consultation, product development, integration of board support packages, certification assistance, and other go-to-market support.
- Digi Professional Services can support organizations in the implementation of virtually any edge computing use case, with everything from Python coding and BASH scripting to device configuration and on-site deployment services.
The edge computing examples we've shared demonstrate the breadth of this growing trend, and the many vertical industries it supports. Our edge computing solutions are helping organizations, industrial outfits and smart cities get better performance and efficiency from their IoT deployments. And Digi is ready to help you with any aspect of your edge compute planning, from defining a strategy, to programming edge intelligence, to building out your solution.
Learn More
See our Edge Computing Technology page, and the collection of blog posts in our series on edge computing:
What is edge computing, and why is it so important now?
Edge computing has risen in importance because IoT device volume and data sizes are growing, making it impractical to rely solely on cloud / central-data-center processing. Because edge computing means processing data as close as possible to where it’s generated — at the sensor, gateway, router, or on-site server instead of sending everything back to a distant cloud it resolves some of the challenges of traditional cloud computing.
Key drivers of edge computing adoption include:
- Reducing latency: Some applications require near-instant responses that cloud round-trips cannot reliably meet
- Improving bandwidth and cost: Transmitting all raw sensor data to the cloud can overload networks or incur high cost
- Increasing reliability: Local processing ensures operations can continue even when connectivity to the cloud is degraded or lost
What are some real-world use cases of edge computing in different industries?
The main examples of edge computing across industries include predictive maintenance in manufacturing, real-time fleet tracking in transportation and logistics, remote patient monitoring in healthcare, computer vision–based loss prevention in retail, grid monitoring in energy and utilities, traffic management in smart cities, and network optimization in telecommunications. In each case, data is processed close to where it is generated to enable faster decisions and reduce reliance on centralized cloud infrastructure.
Here are some examples of edge computing use cases, by vertical, at a glance:
- Automotive/transportation: Connected vehicles and EV charging stations use edge compute to process sensor data in real time (for example autonomous vehicle decisions) and to monitor charging station usage locally
- Traffic/smart city infrastructure: Edge devices at intersections or along roads perform data capture and initial processing for adaptive signal control and traffic management
- Manufacturing/industrial IoT: Factories use edge compute to monitor machinery, detect anomalies, optimize production lines and reduce downtime
- Healthcare: Medical devices, wearables and patient-monitoring systems process data locally to reduce latency, protect privacy, and enable rapid response
- Retail/commercial spaces: In-store or local edge systems handle analytics such as inventory tracking, customer behavior, or personalized offers without sending every data point to the cloud
How does edge computing reduce latency?
Edge computing reduces latency by moving computation closer to where data is generated, such as sensors, machines, cameras, or IoT devices. By avoiding long-distance data transmission to centralized cloud servers, edge computing minimizes network delays and enables near-instant responses for time-critical applications.
How does edge computing help reduce latency in industrial operations?
Edge computing helps reduce latency in industrial operations by processing data locally on devices or gateways instead of sending it to distant cloud data centers. This eliminates network round-trip delays, allowing machines, sensors, and control systems to respond in milliseconds, which is critical for automation, safety systems, and time-sensitive industrial processes.
Which industries benefit most from edge computing?
Industries that benefit most from edge computing include manufacturing, transportation and logistics, healthcare, retail, energy and utilities, telecommunications, and smart cities. These industries rely on real-time data, low latency, high reliability, and secure local processing to support mission-critical operations and distributed environments.
Why is edge computing important for real-time insights?
Edge computing is important for real-time insights because it enables immediate data analysis at the source, without waiting for cloud transmission and processing. This allows organizations to detect anomalies, trigger alerts, and take action instantly, making edge computing essential for use cases like quality control, patient monitoring, autonomous systems, and public safety.
What is the difference between edge computing and cloud computing?
The primary difference between edge computing and cloud computing is where data is processed. Edge computing processes data locally at or near the source, while cloud computing processes data in centralized data centers. Edge computing is optimized for low latency, real-time decision making, and local autonomy, whereas cloud computing is better suited for large-scale data storage, advanced analytics, and centralized management.
How do organizations decide whether to use edge computing vs cloud computing?
When choosing between edge computing and cloud computing, the best answer isn't always one or the other. Often both exist in a hybrid architecture. Considerations include:
- Latency and real-time needs: If decisions must be made in milliseconds (e.g., vehicle control, machine safety), local edge processing is essential
- Connectivity/network reliability: In environments with unreliable or high-latency connectivity, edge reduces dependence on continual cloud links
- Data volume and bandwidth cost: If the sensors generate high-volume data (video, vibration, etc.), processing/filtering locally (edge) can significantly reduce what must be sent upstream
- Security and compliance: Edge processing can keep sensitive data on-site, reducing exposure and meeting regulatory or privacy constraints
- Scalability and architecture complexity: Many deployments start small at edge, then incorporate cloud analytics and long-term storage when appropriate
What are the key challenges when deploying edge computing solutions?
Some of the common challenges in deploying edge computing solutions include:
- Device and infrastructure management: Ensuring firmware, security patches, hardware health and lifecycle across distributed edge nodes
- Edge analytics and data strategy: Capturing data is one thing; turning it into actionable insight requires analytics, sometimes AI/ML, and good integration
- Legacy systems/integration: Many organizations must connect older machines or sensors into new edge architectures
- Security and governance: Edge devices often sit in less controlled environments; they must include strong security, monitoring, and fail-safes
- Designing for scale and resilience: As edge deployments grow across many sites, architecture needs to support updates, manage failures, and maintain consistency
Is edge computing secure?
Edge computing can be highly secure when implemented correctly, using device authentication, encrypted communications, secure boot, and centralized device management. By keeping sensitive data local and reducing unnecessary data transmission, edge computing can also lower exposure to cyber threats while supporting regulatory and data sovereignty requirements.
What practical first steps should organizations take to implement edge computing effectively?
A structured approach can improve success:
- Identify a use case with measurable business value: For example, consider ways to reduce downtime, improve response time, or reduce data transport cost
- Map the data flow: What sensors/data points exist, what needs processing locally vs what can go to cloud
- Select edge-capable hardware and connectivity: This includes rugged routers/gateways, processing units, and reliable links for the specific environment
- Define analytics and filtering logic: Decide what data gets processed locally, what is sent upstream, and how alerts/actions are triggered
- Ensure management and security: Deploy remote management tools, monitoring, remote updates, and robust security controls
- Pilot and scale: Test the solution in a defined environment, measure outcomes, extract learning and then expand
Next Steps
This blog post was originally published in September 2021, and was updated in December 2025 with new Digi solutions and related resources.