You may be wondering, "What are the benefits of 5G technology?" and "What is 5G good for?" When we think about what’s important about 5G, and all the 5G benefits, the list is long. The features of 5G technology unlock new innovations across many different industries. Applications for 5G include faster and more efficient communication in factories and between people. 5G supports increased device density, enabling a massive number of connected devices in a given area, which is essential for the increasing number of connected devices in smart cities and industrial applications.
5G is a huge enabler of edge computing, which has applications in Industry 4.0, healthcare and telemedicine, as well as transportation and public safety — powering faster image processing and data transfer and improving the speed of emergency response. Additionally, there will be some "futuristic" benefits of 5G, including new ways of communicating. These use cases will include things like remote, real-time collaboration, and communicating with experts or physicians through augmented reality (AR) or via a 3D hologram.
In this article, we’ll investigate some of the benefits of 5G, as well as 5G features and capabilities and the advantages of 5G over 4G.
Get Our White Paper
Plan your journey to 5G and beyond
Download PDF
What Is So Special About 5G?
What is the advantage of 5G and what does 5G do? Today’s world is highly distributed thanks to cloud, edge devices and remote operations in industry and agriculture. These technologies allow everyone and everything to connect seamlessly, whatever their location. That’s why 5G benefits future industries, cities, jobs and the economy. As the fifth generation of cellular technology, 5G provides new frequencies and core network capabilities compared to 4G.
Because 5G empowers new use cases, advanced technologies and massive innovation, now is the time for organizations to harness next generation 5G solutions. In fact, according to Accenture research, companies that invest in 5G will grow revenue 2.5 times faster in the next three years.
Advantages of 5G at a glance:
- Higher speed and lower latency makes it possible to control devices remotely in near-real time, fueling new machine-to-machine communications use cases. In fact, Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC) is a key feature of 5G, enabling high-reliability and low-latency communication for a range of mission-critical applications.
- Higher capacity means 5G can deliver up to 100 times more capacity than 4G, which opens many new use cases across cities, factories and private networks requiring higher levels of reliability and throughput.
- Increased bandwidth allows businesses to more easily process and make sense of large amounts of data so they can make better decisions about products, customers and operational efficiency.
- Network slicing allows operators to create multiple virtual networks on a single physical infrastructure. Each slice can be optimized for specific use cases, providing tailored network capabilities for diverse applications.
- 5G enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) capabilities offer faster and more reliable Internet access for mobile devices, making it suitable for high-bandwidth applications such as streaming 4K video.
- Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC) is a capability of 5G that supports the connectivity needs of a massive number of devices simultaneously, making it a game changer for IoT applications with large-scale sensor deployments.
Why Is 5G Better Than 4G?
Why is 5G important and how does it improve upon 4G? 5G has many exciting new use cases, but that doesn’t mean 4G is going away. In fact, 4G is currently the most prevalent network. That means that the two can coexist to provide multiple network technology options. Yet, when thinking about the future, the many 5G advantages organizations experience mean that it is rapidly becoming the dominant network. That’s because 5G’s speed not only improves cell phone performance but also opens wireless technology opportunities for connected cars, hospitals, factories and other data-intensive applications.
A Few Key Advantages of 5G over 4G
5G supports many more connected devices within an area than 4G can support. That opens the door for IoT devices that will power the data-intensive requirements of applications in smart cities, manufacturing automation and infrastructure management. 5G benefits applications such as factory automation, video surveillance and connected vehicles due to its lower latency, high speeds and support for numerous connected devices compared with 4G networks.
5G takes a massive leap from forward in speed and throughput from 4G and 3G, as shown in our illustration.

Still wondering what’s different? Read more about the differences between LTE vs 5G.
6 Key Features and Benefits of 5G
What are the key benefits of 5G? 5G is already creating value in several key industries that depend on its low latency, increased bandwidth and higher speeds. For example, a Swedish mine reduced its drilling and blasting costs by 1 percent by creating 5G-enabled automation systems. A European Ford factory is using 5G to power a human gesture recognition and virtual reality application to improve production line efficiency. In healthcare settings, hospitals can use IoT sensors to track insulin pumps, ventilators, and EKG machines. This makes it easier to find equipment for servicing.
How will 5G benefit us? Let’s break down the benefits of 5G:
Wondering how 5G architecture is designed to deliver better performance for connected devices?
Speed
How fast are 5G speeds? The short answer is that 5G speed capabilities depend on many factors such as location, how many people connect to the network, what 5G network you’re using, and what 5G device you have. In the U.S., nationwide networks mostly depend on low-band 5G, although some are accelerating deployment of mid-band 5G. Mid-band spectrum 5G can carry plenty of data while traveling significant distances and provides speed improvements over the low-band. High-band mmWave spectrum provides very fast download speeds, but because the radio waves can’t penetrate obstacles or travel far, places such as sports stadiums benefit the most.
- 4G speed — Up to 100 Mbps
- 5G speed — Up to 20 Gbps
Low Latency
5G benefits reduced latency, especially for data intensive and mission critical applications. The term latency refers to the time it takes to send data and it is arguably more important than speed. With 5G technology, latency could be as low as 1 millisecond. That is 250 times faster than a human can react to visual stimuli. This ultra-low latency enables things such as autonomous vehicles, remote surgeries and sophisticated robotics to respond to commands nearly instantly. In fact, in the case of autonomous vehicles, latency enables a car traveling at 60 mph to react to an obstruction on the road and start braking before the car rolls just a bit more than an inch. This is an incredible improvement over a human’s braking reaction, which allows the car to roll over thirty yards before braking.
- 4G latency — 200 milliseconds
- 5G latency — 1 millisecond
Bandwidth
5G bandwidth comprises three major frequency bands that each provide their own benefits. The speed and range of 5G radio signals depend on the spectrum they represent. The three bands include the low-band, the mid-band and the high-band. Low-band 5G includes frequencies between 600 MHz and 1 GHz. Mid-band 5G ranges from 1 GHz to 6 GHz and includes the C-Band which ranges from 3.7 to 3.98 GHz. The high-band frequencies reside in the millimeter wave spectrum and range from 24 to 39 GHz. Although only effective over short distances and where there are no obstacles, high-band 5G can produce speeds of up to 10 Gbps under optimal conditions.
- 4G bandwidth — 4G LTE bands include spectrum at 600 MHz, 700 MHz, 1.7/2.1 GHz, 2.3 GHz, and 2.5 GHz and support mobile broadband.
- 5G bandwidth —
- Low-band — This frequency range is next to where 4G and 3G networks operate. Carriers often use existing spectrum and infrastructure to quickly deploy 5G.
- Mid-band — Mid-band 5G can cover large areas and provide speeds from 300 Mbps to 1 Gbps. This band blends speed, range, penetration, and capacity that rivals traditional broadband Internet.
- High-band — 5G high-band mmWaves travel short distances and can’t penetrate buildings or other obstructions, so 5G antennas and equipment must relay these signals inside buildings. But this band is useful in densely populated areas and large, crowded venues.
Edge Slicing
5G edge slicing enables mobile operators to slice their network into multiple Virtual Private Networks to better serve industrial and enterprise customers that have different requirements. The benefit of 5G edge slicing is that a slice can be flexibly deployed. For example, organizations can dedicate a slice to one base station, confined to a campus area, in a city or even a larger area. These Virtual Private Network slices isolate the Internet and critical enterprise traffic to keep business data secure. Edge slicing works great for applications requiring low latency and high bandwidth when device and application performance matters.
- 4G edge slicing — 4G network slicing exists in the limited form of isolating a service in an infrastructure.
- 5G edge slicing — 5G Radio Access Network (RAN) slicing enables new innovative applications such as Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X).
Coverage
In the U.S., 62 percent of Americans can receive high-speed 5G coverage at home. According to VIAVI, 47 of the world’s 70 largest economies by GDP now have active 5G networks. Although the U.S. leads the world in coverage, it isn’t keeping pace with demand. According to the Boston Consulting Group, by 2027 annual 5G data traffic will balloon to 7 to 9 times the level of annual data traffic before 5G. Mobile traffic will expand almost sixfold by 2033. As innovative uses for 5G networks continue, cities will need to add extra mid-band 5G services. To meet this enormous demand, the US needs to add up to 250 percent more mid-band spectrum for mobile use.
A recent mobility report provides these data points:
- 4G coverage — By the end of 2021, 4G coverage surpassed 85 percent of the population globally and may top 95 percent by 2028.
- 5G coverage — 30 percent of the global population is currently covered by 5G networks and may reach 85 percent by 2028.
More Connected Devices
Designed from the start to support massive IoT, 5G networks help industries realize a fully connected world. Not only can 5G networks support 1 million devices for 0.386 square miles, but they also support low power consumption. This means connected devices can operate for months or years without issue. This provides a huge benefit over current IoT services such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and Zigbee that must make performance trade-offs.
Although 5G importance cannot be underestimated, not all devices need 5G-level speed, latency and capacity. For these devices, LTE-M or NB-IoT might work best. LTE-M uses the same spectrum and base stations as 4G/LTE but is more limited. With speeds up to 1 Mbps with a latency of 50 to 100 milliseconds, it works great for real-time communications. But many machines can perform fine with even lower performance requirements. That’s where NB-IoT can help. NB-IoT uses simpler chips that use less power and speeds up to 62.5 kbps. With a latency of 1.5 to 10 seconds, NB-IoT works best for intermittent data transfers. As a result, NB-IoT sensors can go up to 10 years without battery replacement.
- 4G connected devices — LTE-M and NB-IoT provide low to moderate speeds and latency for devices that don’t need large volumes and lots of real-time communication.
- 5G connected devices — 5G networks can support up to 1 million devices in 0.386 square miles while also supporting low power consumption. This makes 5G transformational for many industries.
The autonomous car is here. Read more about how 5G is bringing IoT connectivity to vehicles.
More Benefits of 5G mmWave
Early 5G mmWave implementations failed to live up to their hype as limited range and high costs kept the technology from wider usage. However, recent innovations promise lower costs and better range. For example, Qualcomm recently announced its compact macro 60 dBm EIRP design, promising up to 240 percent increase in range compared to its other small cell RAN platforms. Both the U.S. and Japan plan to densify their networks at existing light poles. With its extremely high bandwidth and low latency, it is perfect for large data transmission networks. It is also more reliable than previous wireless technologies while minimizing power consumption.
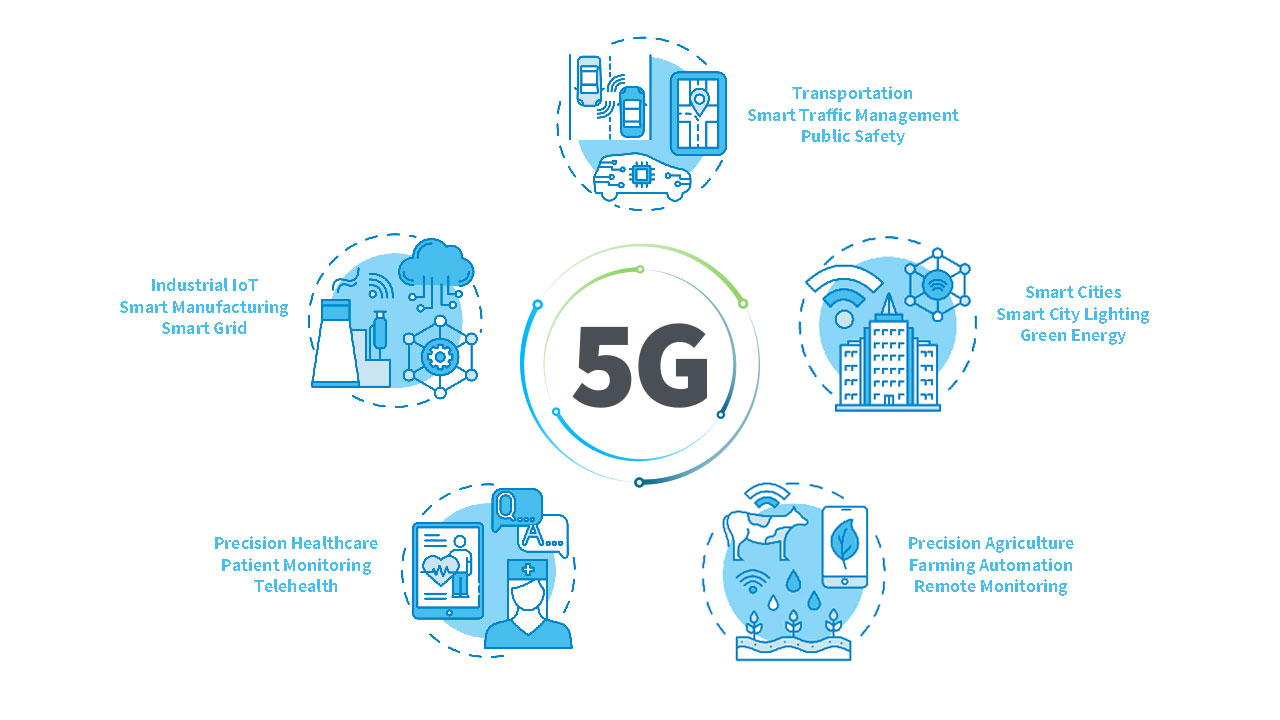
Who Does 5G Benefit?
Many use cases already exist showing how industries benefit from 5G networks. Of course, the industries poised to benefit the most include those that take advantage of large numbers of IoT devices communicating in real time. Because of 5G’s ability for edge slicing, it helps organizations simultaneously deliver services tailored to specific requirements. The market sectors that stand to benefit significantly include:
- Transportation — By enabling both vehicle-to-vehicle and vehicle-to-infrastructure connections, 5G will change transportation across many use cases, including enabling vehicle-to-everything communications and autonomous vehicles, as well as adaptive traffic lights, advanced public transit and faster emergency response.
- Smart cities — With its massive capacity, 5G is enabling a range of smart city applications from smart city street lighting to emergency management, smart buildings, waste management, digital signage and green energy.
- Agriculture — With 5G technology, IoT sensors on plants, in the soil, in silos and irrigation systems, as well as in drones and autonomous tractors can gather valuable data to optimize fertilizer, water, and pesticide applications and have a massive impact on advancing precision agriculture systems.
- Healthcare — As 5G becomes more widespread, healthcare is seeing a wide range of emerging applications such as remote patient monitoring, with things like surgical robots, remote telehealth and ambulance drones on the horizon.
- Manufacturing — 5G is a key enabler of large-scale machine-to-machine communications designed to reduce human error and increase production efficiency in manufacturing automation use cases. 5G speeds combined with edge computing are mission critical in the realization of Industry 4.0.
Explore more transformational applications and use cases for 5G.
Benefits of 5G For Businesses
What’s the benefit of 5G for business operations? If your enterprise involves downloading large media files, you know it can take 10 minutes on a 4G network. With 5G, the same file can download in 10 seconds. As digital tools become standard communications for everyone everywhere, 5G will provide improved business connectivity for clients and employees, regardless of location. Finally, network slicing enables businesses to own their private 5G network so they can control and assign resources to each application.
As we’ve already noted, by 2028 85 percent of the world’s population will have access to 5G. That means there’s a lot of value to capture from 5G over the next few years. It also means that you should no longer ask the question, “What are the benefits of 5G?” Now that you know about all the incredible 5G capabilities, it’s time to select a trusted solution provider who can help you through a transition to a 5G network. That's Digi.
Digi successfully enables 5G for businesses across industries and the enterprise. Our more than 35-year track record of quality, reliability, security and scalability of connectivity solutions means we’ve been helping organizations in diverse industries way before 5G existed. Now our innovative end-to-end solutions help businesses gain all the advantages that 5G has to offer.
Reach out today, and let’s talk about your project. We can show you how 5G can advance your initiatives, add value, and capture untapped opportunity before your competitors.
Next Steps