Today, the integration of IoT in manufacturing is transforming the industry and powering a massive digital transformation. From manufacturing automation using robotics and “cobotics” — human/robot collaboration — to predicting equipment failure on the factory floor and tracking assets in a warehouse, the industrial IoT is at the center of the future of manufacturing. In this article, we cover the varying IoT use cases in manufacturing and discuss future trends.
Get Our eBook
Learn about Industry 4.0 technology
Download PDF
IoT in Manufacturing
Today, every industry is turning to the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize and automate processes, take advantage of the power of edge processing, and gain actionable insights from across the network. Manufacturing is no exception. IoT in manufacturing is an increasing trend where companies can take advantage of faster networks, smarter devices and improvements in edge technology. Combined, these technologies pave the way for the capabilities of Industry 4.0. Continue reading to learn about the applications and benefits of IoT in manufacturing and smart factories.
The Impact of IoT in the Manufacturing Industry
Industrial robots have become commonplace on the factory floor thanks to their accuracy, precision, endurance and speed. Now, manufacturers can extend the impact of industrial robots by connecting them to IoT devices. Connected manufacturing IoT sensors enable machines to communicate with each other, share data, and coordinate their activities autonomously. By sharing data between machines, IoT devices improve robotic efficiency and productivity while also improving safety and reducing unscheduled maintenance.
The following factors are some of the key impacts of IoT in manufacturing:
- Efficiency and productivity: According to a report by McKinsey, IoT applications in manufacturing have the potential to create an economic impact of $1.2 to $3.7 trillion per year by 2025.
- Predictive maintenance: Research by Deloitte indicates that predictive maintenance enabled by IoT technologies can reduce equipment breakdowns by 70% and decrease maintenance costs by 25%.
- Energy and sustainability: The use of IoT in manufacturing can reduce energy usage. For example, Armal, a manufacturer of portable toilets, found that real-time IoT monitoring of the production line helped reduce the energy costs of machinery by almost 40%.
- Supply chain optimization: Today, 78% of supply chain leaders are seeking technology solutions to increase operational efficiency, improve production and delivery speeds, and automate repetitive tasks.

Benefits of IoT in Manufacturing
There are many measurable benefits of IoT for manufacturing. Automated manufacturing systems are engineered to orchestrate complex workflows with minimal human intervention. These systems leverage cutting-edge technologies such as robotics, artificial intelligence (AI), and smart edge devices to optimize every facet of the production cycle. By seamlessly integrating disparate components and processes, automated manufacturing systems dramatically improve efficiency and agility, empowering organizations to meet evolving market demands.
The following are some of the key benefits of IoT in manufacturing.
Improved Operational Efficiency
By implementing IoT solutions, manufacturers can automate more processes, detect anomalies and reduce errors, and therefore increase operational efficiency. IoT enables industrial robots to operate autonomously using sensors, cameras, wireless devices and edge computing, conducting tasks such as assembly, defect detection, sorting, stacking and routing. Intelligent automation gathers data on machine performance, inventory levels, and other metrics that then allow manufacturers to optimize processes and make data-driven decisions.
Prevention of Unplanned Downtime
Machine downtimes can significantly impact manufacturing companies' productivity. An analyst report noted that 82 percent of companies have experienced unplanned downtime. These unplanned downtime events can cost a manufacturer up to $260,000 an hour, and according to Industry EMEA, these issues cost manufacturers about $50 billion annually. Internet of Things industrial applications rely on advanced sensors that can monitor equipment operating parameters such as temperature, vibration, electrical metrics, and specified indicators of equipment failure to predict malfunctions before they happen.
Quality Improvement and Defect Reduction
Digital transformation and smart manufacturing processes can have a huge impact on quality improvement. Using cameras, sensors, AI and machine learning, robotic systems can monitor product quality faster and more accurately than the human eye, detect defects and respond rapidly. According to a McKinsey report, digitization and automation have resulted in a more than 65 percent reduction in overall deviations in manufacturing. By reacting quickly, manufacturers can avoid recalls due to defective products, which improves customer satisfaction.
Improved Safety
Automation enhances workplace safety by reducing the risk of accidents and injuries associated with manual labor and hazardous tasks. Automated systems adhere to strict safety standards and regulations, mitigating the potential for human error and ensuring compliance with industry guidelines and protocols. And today manufacturing companies are increasingly investing in wearable technology wearable technology solutions, such as IoT-enabled smart glasses and vests, to support better posture for heavy lifting, and alerts to hazardous behaviors.
Reduced Costs
Automation reduces the need for human intervention in repetitive or labor-intensive tasks, which not only minimizes labor costs but also frees up human workers to focus on higher-value activities such as problem-solving, innovation, and process optimization.
Additionally, with the maintenance of industrial equipment contributing to nearly 70 percent of overall cost, operational efficiency and predictive maintenance are key. Industrial IoT technology offers significant benefits, such as improving remote troubleshooting and reducing the number of service calls when no maintenance is required. And finally, the use connected devices and sophisticated management platforms allows operators to remotely manage operations including remote out-of-band management.
Scalability
Automated systems are inherently scalable and adaptable to changing production requirements and market dynamics, vs. the traditional method of scaling up or scaling down staffing. Whether ramping up production volumes or diversifying product offerings, automation allows manufacturers to respond quickly and effectively to evolving business needs, maintaining competitiveness and agility.
IoT Use Cases in Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry often contends with supply chain shocks, talent shortages, the effects of inflation and geopolitical instability. The net result is that manufacturers must continually seek ways to reduce costs and leverage technology to optimize output to manage complexity and dynamic conditions. That is where smart manufacturing can help, and why the top IoT use cases in manufacturing include automation, predictive maintenance, quality control and supply chain optimization. The following use cases illustrate some key IoT in manufacturing examples:
- Factory floors and fields
- Supply chain management
- Remote operations
Smart Factory IoT for Shop Floors and Fields
 From automation to predictive maintenance, it all starts with sensors, cameras, robotics and smart devices like embedded system-on-modules and high-speed 5G cellular routers. In smart factory automation, these technologies, paired with AI and machine learning, drive product assembly, packaging and supply chain processes.
From automation to predictive maintenance, it all starts with sensors, cameras, robotics and smart devices like embedded system-on-modules and high-speed 5G cellular routers. In smart factory automation, these technologies, paired with AI and machine learning, drive product assembly, packaging and supply chain processes.
IoT sensors for manufacturing, along with smart devices, capture shop floor machine data such as temperature, voltage, vibrations, humidity and more for predictive maintenance. This data is processed and analyzed at the edge and key reporting data is then communicated through wireless networks to the cloud. When an anomaly is detected, the edge systems can pull the defective item, halt machinery or take other actions. These include predicting failure and sending an alert or service ticket to an operator who can schedule maintenance.
Another key advancement in smart factories is the use of digital twins. These are models that support factory design, automation planning, workflow and more — enabling manufacturers to visualize complex machinery and operations before putting them into practice in real life. See our blog describing digital twin examples.
Here are a few examples of smart factory use cases and case studies.
- Reducing labor costs in industrial automation — The Honeywell corporation builds next-generation technology for the aerospace industry. The company uses automation in production and warehousing to reduce human labor costs and improve margins. From conveyor systems and controls that transport materials through production, to pick-and-pack systems, loaders, palletizing machinery and robotics for distribution processes, Honeywell offers a broad range of solutions for Industry 4.0.
- Decreasing maintenance costs in the paper and pulp industry — Paper and pulp production equipment company, Artesis, implemented a predictive maintenance method using IoT sensors to collect data on their equipment and predict failures before they occurred. The company decreased maintenance costs by 20 percent and boosted its production efficiency by 10 percent.
- Keeping production running in the snack food manufacturing industry — Frito-Lay is one of the most notable snack chip brands,producing popular snacks including Lays, Ruffles, Cheetos and Doritos. Its real-time equipment health monitoring program predicts failures and plans maintenance before breakdowns occur.
View on Demand - Industrial IoT at the Edge: Remote Access to Critical Infrastructure
Manufacturing IoT for Supply Chain Optimization
 From consumer packaged goods to fertilizer, pet food and equipment, all manufacturing relies on the supply chain. The movement of goods through the supply chain is a complex and challenging process as manufacturers contend with a wide range of transportation and inventory challenges.
From consumer packaged goods to fertilizer, pet food and equipment, all manufacturing relies on the supply chain. The movement of goods through the supply chain is a complex and challenging process as manufacturers contend with a wide range of transportation and inventory challenges.
According to a Deloitte and Manufacturers Alliance survey, 56 percent of survey participants cited parts shortages as a key operational challenge. Thanks to IoT, supply chain managers within manufacturing can tackle some of these challenges. In fact, 76 percent of the Deloitte survey respondents plan to rely on digital supply chain tools to enhance their supply chain visibility.
Here are some of the ways IoT in the smart factory and smart manufacturing helps optimize the supply chain and improves visibility, tracking, and efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance of assets — To reduce the impact of transportation delays, supply chain managers can rely on IoT sensors and onboard communication devices to monitor trucks, ships and airplanes for maintenance issues before they can cause breakdowns.
- Fleet management — IoT enables transportation logistics managers to identify bottlenecks in the fleet, an important aspect of the overall manufacturing process.
- Inventory management — Manufacturers can use IoT sensors to optimize their inventory levels, so they always have the components they need for production.
Autonomous Mobile Robots
Seegrid, an autonomous mobile robot manufacturer, incorporates sophisticated connected cameras and LiDAR sensors to safely complete dangerous, repetitive tasks in a warehouse environment.
Real-time Monitoring of Inventory Levels
Today, advanced inventory management systems use automation and robotics to improve inventory tracking across warehouses, distribution centers and even retail outlets. With real-time access to inventory, managers can make better decisions to optimize inventory levels and ensure sufficient stock.
Monitoring the Condition of Goods in Transit
To ensure quality and meet stringent compliance requirements, manufacturers and shipping companies can use IoT sensors and communications devices to monitor goods in transit and report temperatures and other conditions.
IIoT for Remote Operations
 Industrial IoT provides insights across an organization’s device network — whether that means a manufacturing facility, an expansive industrial complex, or a network of mobile assets like autonomous vehicles and drones.
Industrial IoT provides insights across an organization’s device network — whether that means a manufacturing facility, an expansive industrial complex, or a network of mobile assets like autonomous vehicles and drones.
With IoT management platforms providing the ability to monitor operations in real-time, remote teams have eyes and ears on manufacturing and industrial processes, and can monitor asset location, fulfillment, job completion, operational uptime and many other factors.
This capability also enables instant alerts on specified conditions, simplified analysis and reporting, leading to a range of benefits:
- Rapid insights — IIoT in manufacturing provides operators with visibility across the network
- Faster response times — Data from the network edge enables rapid response to indicators from any point in the manufacturing process
- Remote monitoring and control — Remote-controlled devices enable operators to implement automated interventions, such as adjusting flow and volume, gaining knowledge for troubleshooting, and remotely rebooting systems
Asset Tracking
With the help of real-time location technologies such as GPS, RFID and other wireless technologies, manufacturers can rapidly pinpoint the location of assets such as fleet vehicles, equipment and materials.
Warehouse Management
One of the most powerful applications of IIoT sensor technology is the ability to track the condition of materials and components regardless of their location in the supply chain. With automated alerts, operators receive notice immediately when there is an inventory disruption so they can act before the issue impacts production.
Energy Monitoring
Optimizing energy is a key industrial IoT use case. By adding IIoT connectivity to machinery, HVAC systems, and other equipment that uses large amounts of energy, manufacturers can optimize energy consumption to not only create cost savings but also meet decarbonization goals.
IoT Challenges in Manufacturing

Clearly, IoT provides tremendous value to manufacturing. The right IoT solution provider can help address these challenges to ensure your deployment is scalable, secure and integrated with existing infrastructure. Here are a few key challenges that manufacturers should consider when implementing IoT systems:
- Security — Security remains one of the biggest risks to industrial IoT systems. Hackers who break into an industrial IoT environment might steal or modify critical process information, potentially compromising product quality. For highly regulated industries such as defense, healthcare and critical infrastructure, these issues are paramount. If IoT devices are not properly updated, attackers pose risks from business disruption to enormous impacts on revenue and reputation.
- Interoperability — IoT platforms and protocols are subject to a range of standards, which means manufacturers, systems integrators and organizations must manage interoperability issues when incorporating IoT devices into existing IT systems.
- Data privacy — By connecting IoT sensors to the Internet, manufacturers become immediately exposed to cyber threats that create potential data privacy risks.
One answer to some of these challenges is a private network. Today, private networks are growing in popularity as organizations seek to lock down security within their own network and improve quality of service.
IoT Solutions for Manufacturing
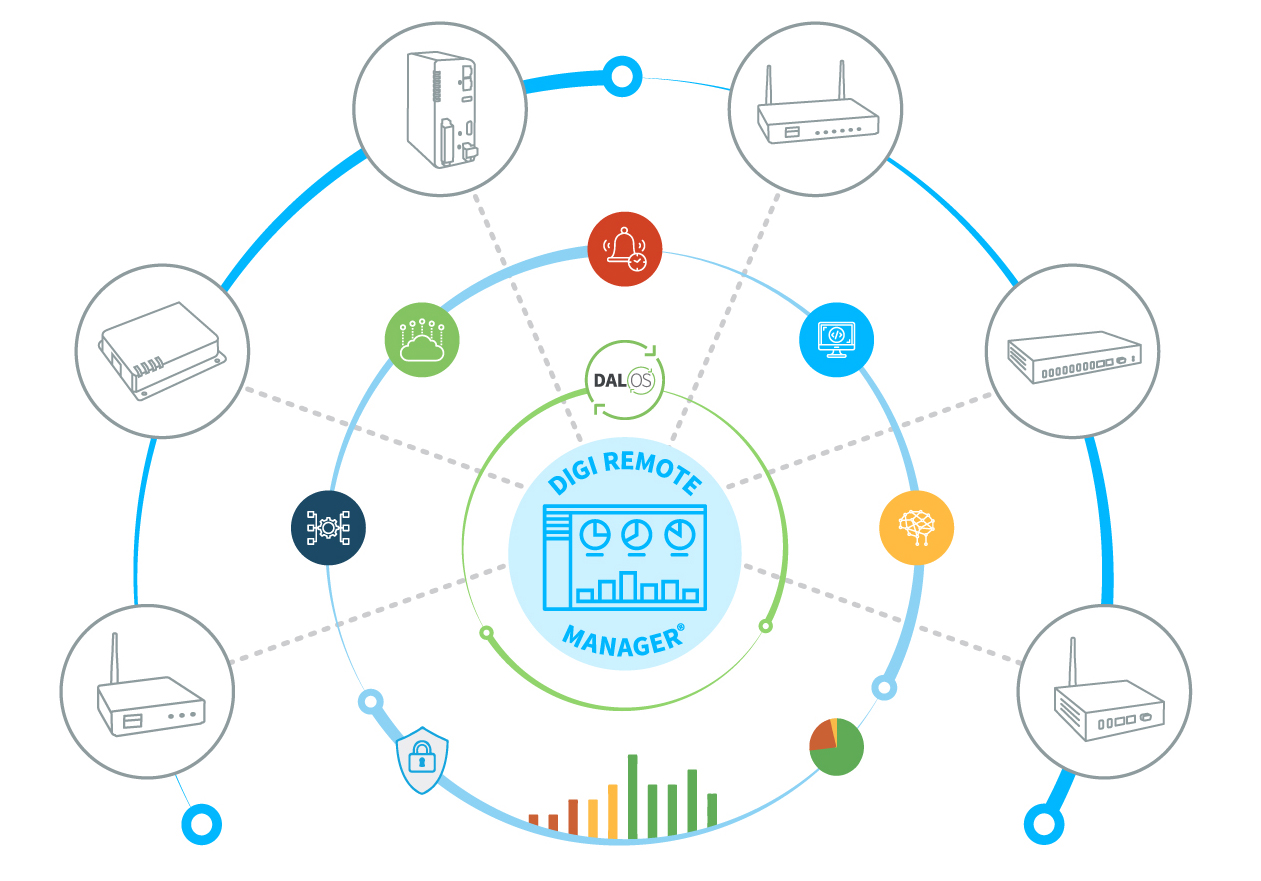
IoT solutions for the manufacturing industry form the backbone of modern manufacturing operations, enabling everything from process automation to predictive maintenance. Digi comprehensive wireless connectivity solutions seamlessly integrate with a centralized, cloud-based software system so manufacturers can instantly get information from factory floor operations. Whether it is for monitoring equipment or sending firmware updates, Digi IoT manufacturing solutions help organizations dramatically reduce maintenance costs while also increasing productivity.
Digi High-Performance Cellular Routers
Digi has been a provider of connectivity solutions since 1985, supporting the mission critical needs of organizations in the most demanding applications, from industrial operations to medical applications and emergency response, and we continue to add to our portfolio of high-performance cellular routers for enterprise, industrial and transportation use cases.
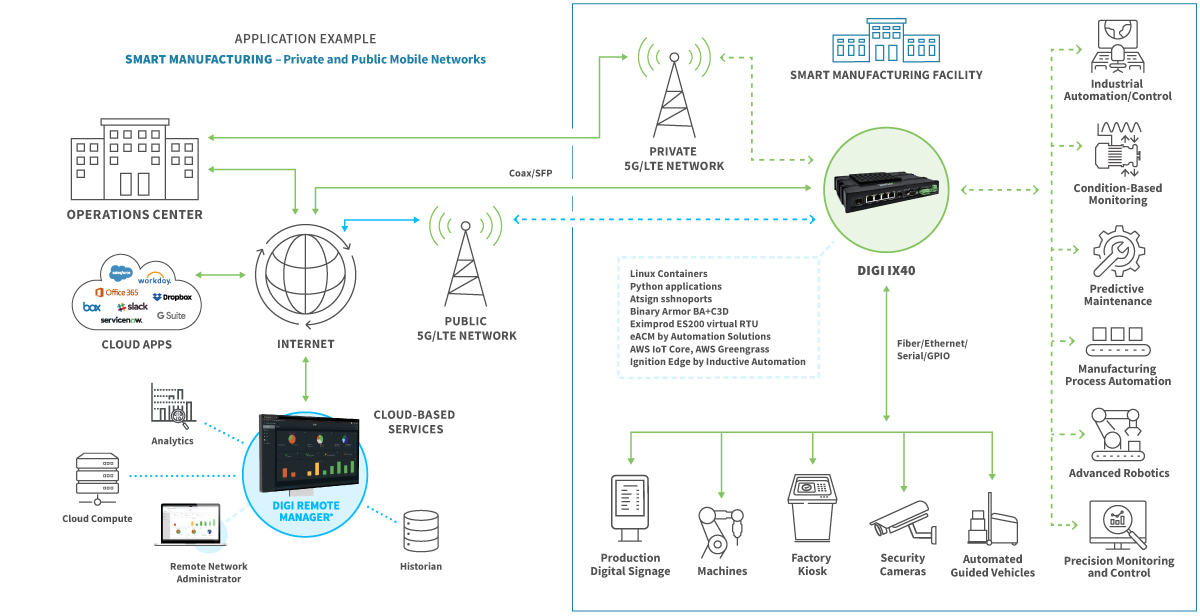
One of our latest additions to these IoT solutions for manufacturing and industrial use cases is Digi IX40, a 5G edge computing solution that is purpose built for Industry 4.0 use cases. This solution offers global 5G and LTE support, and certification on major carrier networks around the world. Additionally, they support Digi Containers to enable powerful, cost-efficient applications at the edge.
Digi Embedded Systems for Developers
OEMs designing solutions for IoT in the manufacturing market require a range of embedded solutions. Digi offers two complete developer ecosystems:
- The Digi XBee® ecosystem of wireless communications modules, tools and services: These low-cost communication modules provide wireless RF or cellular connectivity when low power is essential. Digi XBee modules are pre-certified, easy to deploy, and can be quickly configured with local tools like Digi XCTU® and Digi XBee Studio, or for network wide deployment with Digi Remote Manager.
- The Digi ConnectCore® ecosystem of system-on-modules, tools and services. The extensive Digi ConnectCore offering includes SOMs, SBCs, code libraries, security and remote management services, and more. The powerful Digi ConnectCore SOMs incorporate the latest technology for edge computing, rapid development and time-to-market, along with a full suite of tools and resources for scalability of design and ease of maintenance.
Digi IX15 IoT Gateway and Cellular Router
Some industrial manufacturing processes provide unique challenges to IoT communications due to harsh environmental conditions. Digi IX15 is an industrial-grade IoT gateway with Class 1 Division 2 deployment certification and a rugged enclosure specifically designed for harsh environments. It seamlessly integrates with the Digi XBee ecosystem and the Digi Remote Manager to drive efficiencies whether you deploy dozens or thousands of devices.
Digi Connect Sensor+ with Digi Remote Manager
The Digi Connect Sensor+ with Digi Remote Manager is perfect for remote monitoring in harsh environments without easy access to power. Easy installation, reliability and low data usage make Digi Connect Sensor+ a great solution for remote monitoring in areas where IoT was previously cost-prohibitive.
Join the Future of IoT in Manufacturing with Digi
From improving process control and manufacturing automation to robotics, IoT in manufacturing creates efficiencies and productivity improvements all along the manufacturing value chain. However, implementing IoT in the manufacturing industry requires specialized expertise. That is why it is important to partner with experts.
Digi has been providing wireless communication services since 1985 and has since grown to offer applications across the entire IoT landscape. As manufacturers prepare for a more digitally integrated and connected future that promises incredible efficiency and productivity improvements, they need secure, reliable and scalable solutions. That is where Digi can help. Our complete network infrastructure, connectivity and remote management solutions help manufacturers achieve the efficiencies and productivity they envision as they embrace the future of IoT in manufacturing.
FAQs for IoT in Smart Manufacturing

How Is IoT Used in Manufacturing?
In the manufacturing IoT environment, the term IoT refers to the network of sensors and devices throughout a manufacturing operation. Think machinery, warehouse robots, vehicles and inventory all sending and receiving data through embedded devices, routers and wireless networks. With everything connected over high-speed 5G networks, we see a whole new world of smart industry IoT emerging.
What Problems Do IoT and Smart Sensors Solve for Factories?
When manufacturers transition to using IoT analytics, they open the doors to numerous advantages such as the ability to spot trends, act immediately to reduce outages and gain insights into optimizing operations. As a result, IoT in factories, through sensors and data analytics, adds value across the board.
How Can IoT Devices Minimize Downtime in a Manufacturing Plant?
Predictive techniques help detect potential failures allowing operators to eliminate unplanned downtime by scheduling maintenance before equipment breakdowns occur. That way, equipment is less likely to fail during production, minimizing downtime.
How Can the IoT Improve Physical Safety in Manufacturing?
The Internet of Things in manufacturing uses sensors to detect unsafe operating conditions and trigger alerts to workers before an accident occurs. From panic buttons and smart alarms to smart lights and IoT wearables, there are many ways IoT devices help keep people safe from potential hazards on the factory floor.
How Can the IoT Improve Predictive Maintenance in Manufacturing?
With IoT and manufacturing, predictive maintenance boosts immediate value by improving equipment efficiency and minimizing maintenance costs. Thanks to IoT, data collection enables more advanced use cases for predictive maintenance.
How Is IoT Disrupting Aerospace Manufacturing?
With IoT in the manufacturing industry, monitoring and control tools on the aerospace manufacturing assembly line can improve quality and productivity by up to 30 percent. IoT and accompanying advanced algorithms can even help optimize energy used in aircraft production, reducing energy consumption by up to 20 percent.
How Can Manufacturers Optimize PCBs for Better IoT Design?
Every IoT device has a printed circuit board (PCB). To optimize a PCB for better IoT design, manufacturers should carefully consider sensor placement to maintain signal integrity. Everything from materials used to the type of application should be considered in designing and manufacturing electrical and mechanical engineering aspects of IoT devices.
Next Steps